|
Message-oriented Middleware
Message-oriented middleware (MOM) is software or hardware infrastructure supporting sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. MOM allows application modules to be distributed over heterogeneous platforms and reduces the complexity of developing applications that span multiple operating systems and network protocols. The middleware creates a distributed communications layer that insulates the application developer from the details of the various operating systems and network interfaces. APIs that extend across diverse platforms and networks are typically provided by MOM. This middleware layer allows software components (applications, Enterprise JavaBeans, servlets, and other components) that have been developed independently and that run on different networked platforms to interact with one another. Applications distributed on different network nodes use the application interface to communicate. In addition, by providing an administrative interface, this new, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed System
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming'' is the process of writing such programs. There are many different types of implementations for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Message Queue
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter- thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the passing of control or of content. Group communication systems provide similar kinds of functionality. The message queue paradigm is a sibling of the publisher/subscriber pattern, and is typically one part of a larger message-oriented middleware system. Most messaging systems support both the publisher/subscriber and message queue models in their API, e.g. Java Message Service (JMS). Remit and ownership Message queues implement an asynchronous communication pattern between two or more processes/threads whereby the sending and receiving party do not need to interact with the message queue at the same time. Messages placed onto the queue are stored until the recipient retrieves them. Message queues have implicit or explicit limits on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Performance
In computing, computer performance is the amount of useful work accomplished by a computer system. Outside of specific contexts, computer performance is estimated in terms of accuracy, efficiency and speed of executing computer program instructions. When it comes to high computer performance, one or more of the following factors might be involved: * Short response time for a given piece of work. * High throughput (rate of processing work). * Low utilization of computing resource(s). ** Fast (or highly compact) data compression and decompression. * High availability of the computing system or application. * High bandwidth. * Short data transmission time. Technical and non-technical definitions The performance of any computer system can be evaluated in measurable, technical terms, using one or more of the metrics listed above. This way the performance can be * Compared relative to other systems or the same system before/after changes * In absolute terms, e.g. for fulfilling a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
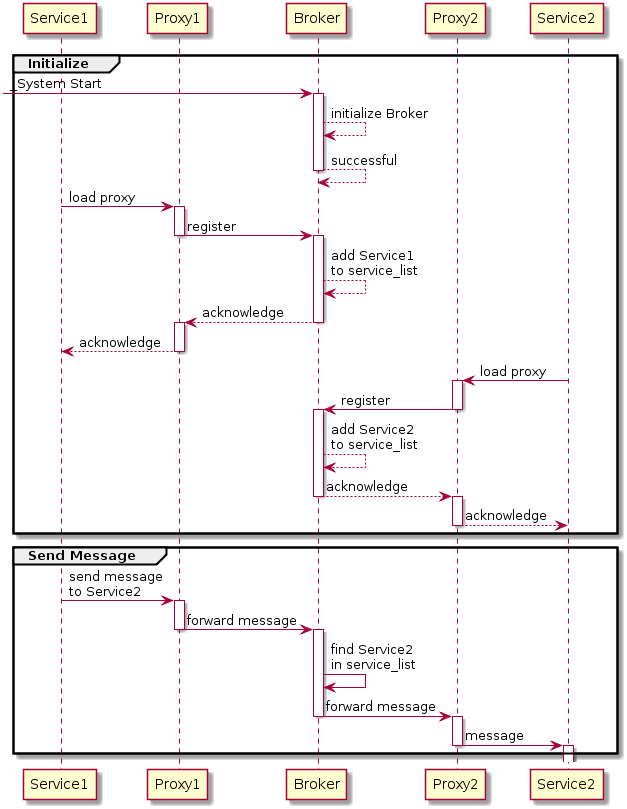
Message Broker
A message broker (also known as an integration broker or interface engine) is an intermediary computer program module that translates a message from the formal messaging protocol of the sender to the formal messaging protocol of the receiver. Message brokers are elements in telecommunication or computer networks where software applications communicate by exchanging formally-defined messages. Message brokers are a building block of message-oriented middleware (MOM) but are typically not a replacement for traditional middleware like MOM and remote procedure call (RPC). Overview A message broker is an architectural pattern for message validation, transformation, and routing. It mediates communication among applications, minimizing the mutual awareness that applications should have of each other in order to be able to exchange messages, effectively implementing decoupling. Purpose The primary purpose of a broker is to take incoming messages from applications and perform some action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Architecture
Software architecture is the fundamental structure of a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements and relations. The ''architecture'' of a software system is a metaphor, analogous to the architecture of a building. It functions as a blueprint for the system and the developing project, which project management can later use to extrapolate the tasks necessary to be executed by the teams and people involved. Software architecture is about making fundamental structural choices that are costly to change once implemented. Software architecture choices include specific structural options from possibilities in the design of the software. For example, the systems that controlled the Space Shuttle launch vehicle had the requirement of being very fast and very reliable. Therefore, an appropriate real-time computing language would need to be chosen. Additiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag-and-drop
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, it can be used to invoke many kinds of actions, or create various types of associations between two abstract objects. As a feature, drag-and-drop support is not found in all software, though it is sometimes a fast and easy-to-learn technique. However, it is not always clear to users that an item can be dragged and dropped, or what is the command performed by the drag and drop, which can decrease usability. Actions The basic sequence involved in drag and drop is: * Move the pointer to the object * Press, and hold down, the button on the mouse or other pointing device, to "grab" the object * "Drag" the object to the desired location by moving the pointer to this one * "Drop" the object by releasing the button Dragging requires more physical effort than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, instead of text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of CLIs ( command-line interfaces), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-display resolution types of interfaces, such as video games (where HUD (''head-up display'') is preferred), or not including flat screens like volumetric displays bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Developer
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development involves writing and maintaining the source code, but in a broader sense, it includes all processes from the conception of the desired software through to the final manifestation of the software, typically in a planned and structured process. Software development also includes research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities that result in software products. Methodologies One system development methodology is not necessarily suitable for use by all projects. Each of the available methodologies are best suited to specific kinds of projects, based on various technical, organizational, project, and team considerations. Software development activities Identification of need The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Transformation
In computing, data transformation is the process of converting data from one format or structure into another format or structure. It is a fundamental aspect of most data integrationCIO.com. Agile Comes to Data Integration. Retrieved from: https://www.cio.com/article/2378615/data-management/agile-comes-to-data-integration.html and data management tasks such as data wrangling, data warehousing, data integration and application integration. Data transformation can be simple or complex based on the required changes to the data between the source (initial) data and the target (final) data. Data transformation is typically performed via a mixture of manual and automated steps.DataXFormer. Morcos, Abedjan, Ilyas, Ouzzani, Papotti, Stonebraker. An interactive data transformation tool. Retrieved from: http://livinglab.mit.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/DataXFormer-An-Interactive-Data-Transformation-Tool.pdf Tools and technologies used for data transformation can vary widely based on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused with physical layer point-to-multipoint communication. Group communication may either be application layer multicast or network-assisted multicast, where the latter makes it possible for the source to efficiently send to the group in a single transmission. Copies are automatically created in other network elements, such as routers, switches and cellular network base stations, but only to network segments that currently contain members of the group. Network assisted multicast may be implemented at the data link layer using one-to-many addressing and switching such as Ethernet multicast addressing, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), point-to-multipoint virtual circuits (P2MP) or InfiniBand multicast. Network-assisted multicast may also be imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting (networking)
In computer networking, telecommunication and information theory, broadcasting is a method of transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Broadcasting can be performed as a high-level operation in a program, for example, broadcasting in Message Passing Interface, or it may be a low-level networking operation, for example broadcasting on Ethernet. All-to-all communication is a computer communication method in which each sender transmits messages to all receivers within a group. In networking this can be accomplished using broadcast or multicast. This is in contrast with the point-to-point method in which each sender communicates with one receiver. Addressing methods There are four principal addressing methods in the Internet Protocol: Overview In computer networking, broadcasting refers to transmitting a packet that will be received by every device on the network. In practice, the scope of the broadcast is limited to a broadcast domain. Broadcasting is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |