|
Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), but little is known about them. The continental masses of the Mesoproterozoic were more or less the same ones that exist today, although their arrangement on the Earth's surface was different. Major events and characteristics The major events of this era are the breakup of the Columbia supercontinent, the formation of the Rodinia supercontinent, and the evolution of sexual reproduction. This era is marked by the further development of continental plates and plate tectonics. The supercontinent of Columbia broke up between 1500 and 1350 million years ago, and the fragments reassembled into the supercontinent of Rodinia around 1100 to 900 million years ago, on the time boundary between the Mesoproterozoic and the subsequent Neoproterozoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Era (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picuris Orogeny
The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and interpreted either as the suturing of the Granite-Rhyolite crustal province to the southern margin of the proto-North American continent Laurentia or as the final suturing of the Mazatzal crustal province onto Laurentia. According to the former hypothesis, this was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism. Description Age and isotope data show that southern North America is composed of a series of northeast-trending provinces representing island arc terranes accreted onto the 1800 Mya core of Laur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenville Orogeny
The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, from Labrador to Mexico, as well as to Scotland. Grenville orogenic crust of mid-late Mesoproterozoic age (c. 1250–980 Ma) is found worldwide, but generally only events which occurred on the southern and eastern margins of Laurentia are recognized under the "Grenville" name. These orogenic events are also known as the Kibaran orogeny in Africa and the Dalslandian orogeny in Western Europe. Timescale The problem of timing the Grenville orogeny is an area of some contention today. The timescale outlined by Toby Rivers in 2008 is derived from the well-preserved Grenville Province and represents one of the most detailed records of the orogeny. This classification considers the classical Grenville designation to cover two separate oro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia (supercontinent)
Columbia, also known as Nuna or Hudsonland, was one of Earth's ancient supercontinents. It was first proposed by John J.W. Rogers and M. Santosh in 2002 and is thought to have existed approximately , in the Paleoproterozoic Era. The assembly of the supercontinent was likely completed during global-scale collisional events from 2100 to 1800 million years ago. Columbia consisted of proto-cratons that made up the cores of the continents of Laurentia, Baltica, Ukrainian Shield, Amazonian Shield, Australia, and possibly Siberia, North China, and Kalaharia as well. The evidence of Columbia's existence is provided by geological and paleomagnetic data.; Size and location Columbia is estimated to have been approximately from north to south at its broadest part. The eastern coast of India was attached to western North America, with southern Australia against western Canada. In this era most of South America was rotated such that the western edge of modern-day Brazil lined up with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
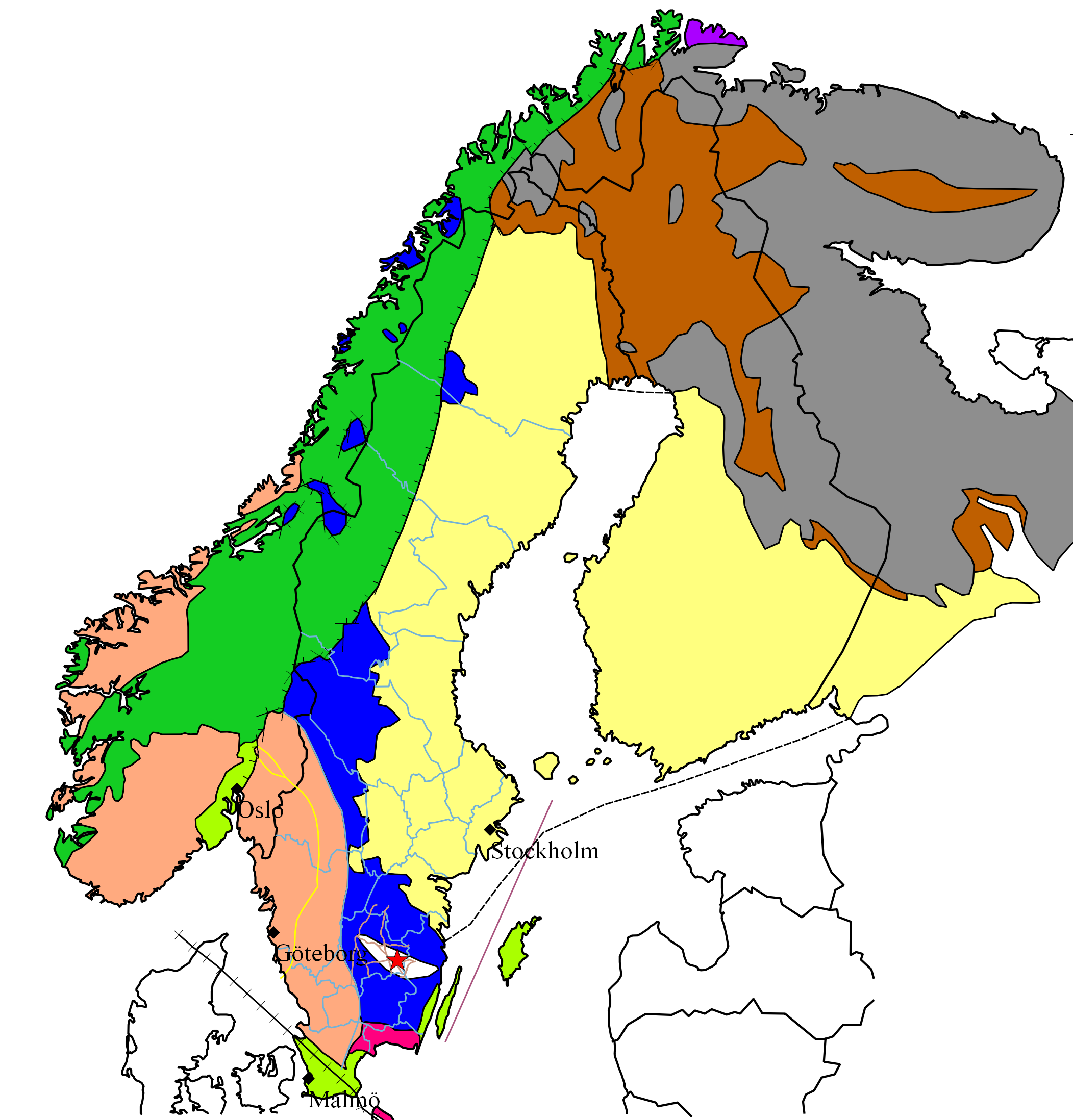
Sveconorwegian Orogeny
The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites. Tectonic segments The Sveconorwegian orogen orogenic belt is composed of five segments largely made up of gneiss that were disrupted by both extension and compression in the timespan between 1140 and 980 million years ago. From west to east the segments are the terranes of Telemarkia, Bamble, Kongsberg and Idefjorden plus the Eastern Segment. The segments are separated from each other by large-scale shear zones. *Bamble Terrane: The Bamble Terrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectasian
The Ectasian Period (from grc, ἔκτασις, éktasis, meaning "extension") is the second geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya ago to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. Geologically the name refers to the continued expansion of platform covers during this period. This period is interesting for the first evidence of sexual reproduction. The 1.2 billion years old Hunting Formation on Somerset Island, Canada, dates from the end of the Ectasian. It contains the microfossils of the multicellular filaments of ''Bangiomorpha pubescens'' (type of red algae), the first taxonomically resolved eukaryote. This was the first organism that exhibited sexual reproduction, which is an essential feature for complex multicellularity. Complex multicellularity is different from "simple" multicellularity, such as colonies of organisms living together. True multicellular organisms contain cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calymmian
The Calymmian Period (from grc, κάλυμμα, kálymma, meaning "cover") is the first geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The period is characterised by expansion of existing platform covers, or by new platforms on recently cratonized basements. The supercontinent In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leav ... Columbia started to break during the Calymmian some 1500 Mya. See also * * References * * Mesoproterozoic Geological periods Proterozoic geochronology {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenian
The Stenian Period (, from grc, στενός, stenós, meaning "narrow") is the final geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The name derives from narrow polymetamorphic belts formed over this period. Preceded by the Ectasian Period and followed by the Neoproterozoic Era. The supercontinent Rodinia assembled during the Stenian. It would last into the Tonian Period. This period includes the formation of the Keweenawan Rift at about 1100 Mya. Fossils of the oldest known sexually reproducing organism, ''Bangiomorpha pubescens ''Bangiomorpha pubescens'' is a red alga. It is the first known sexually reproducing organism. A multicellular fossil of ''Bangiomorpha pubescens'' was recovered from the Hunting Formation in Somerset Island, Canada Canada is a countr ...'', first appeared in the Stenian. See also * * Notes Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's geological history. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized. Paleontological evidence suggests that the Earth's rotational rate ~1.8 billion years ago equated to 20-hour days, implying a total of ~450 days per year. Atmosphere Before the enormous increase in atmospheric oxygen, almost all existing lifeforms were anaerobic organisms whose metabolism was based on a form of cellular respiration that did not require oxygen. Free oxygen in large amounts is toxic to most anaerobic organisms. Consequently, most died when the atmospheric free oxygen levels soared in an extinction event called the Great Oxidation Event, which brought atmospheric oxygen levels to up to 10% of their current level. The only creatures that sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent. Rodinia formed at c. 1.23 Ga by accretion and collision of fragments produced by breakup of an older supercontinent, Columbia, assembled by global-scale 2.0–1.8 Ga collisional events.; Rodinia broke up in the Neoproterozoic with its continental fragments reassembled to form Pannotia 633–573 million years ago. In contrast with Pannotia, little is known yet about the exact configuration and geodynamic history of Rodinia. Paleomagnetic evidence provides some clues to the paleolatitude of individual pieces of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. To separate supercontinents from other groupings, a limit has been proposed in which a continent must include at least about 75% of the continental crust then in existence in order to qualify as a supercontinent. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). According to modern definitions, a supercontinent does not exist today; the closest in existence to a supercontinent is the current Afro-Eurasian landmass, which covers approx. 57% of Earth's total land area. The last time the continental landmasses were near to one another was 336 to 175 million years ago as the supercontinent, Pangaea. The positions of continents h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibaran Orogeny
The Kibaran orogeny is a term that has been used for a series of orogenic events, in what is now Africa, that began in the Mesoproterozoic, around 1400 Ma and continued until around 1000 Ma when the supercontinent Rodinia was assembled. The term "Kibaran" has often been used for any orogenic rocks formed during this very extended period. Recently, it has been proposed that the term should be used in a much narrower sense for an event around 1375 Ma and a region in the southeast of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). These orogenic events are also known as the Grenville orogeny in North America and the Dalslandian orogeny in Western Europe. Broad sense Regions that contain relics of Kibaran age include the Kibara Mountains of the eastern DRC and Namaqua-Natal belt in southern Africa. Rocks of this age have been found in the Hoggar Mountains, in northwest and southwest Nigeria and in Cameroon to the north of the Congo Craton. The orogeny in northwest Nigeria was a majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |