|
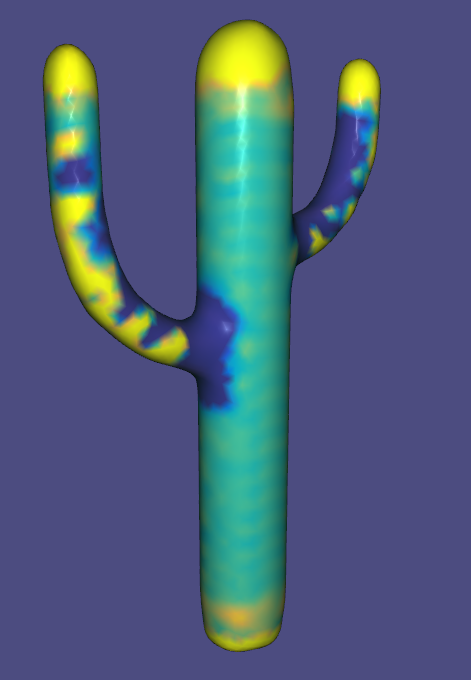
MeshLab
MeshLab is a 3D mesh processing software system that is oriented to the management and processing of unstructured large meshes and provides a set of tools for editing, cleaning, healing, inspecting, rendering, and converting these kinds of meshes. MeshLab is free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2 or later, and is used as both a complete package and a library powering other software. It is well known in the more technical fields of 3D development and data handling. Overview MeshLab is developed by the ISTI - CNR research center; initially MeshLab was created as a course assignment at the University of Pisa in late 2005. It is a general-purpose system aimed at the processing of the typical not-so-small unstructured 3D models that arise in the 3D scanning pipeline. The automatic mesh cleaning filters includes removal of duplicated, unreferenced vertices, non-manifold edges, vertices, and null faces. Remeshing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Scanning
3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect data on its shape and possibly its appearance (e.g. color). The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models. A 3D scanner can be based on many different technologies, each with its own limitations, advantages and costs. Many limitations in the kind of objects that can be digitised are still present. For example, optical technology may encounter many difficulties with dark, shiny, reflective or transparent objects. For example, industrial computed tomography scanning, structured-light 3D scanners, LiDAR and Time Of Flight 3D Scanners can be used to construct digital 3D models, without destructive testing. Collected 3D data is useful for a wide variety of applications. These devices are used extensively by the entertainment industry in the production of movies and video games, including virtual reality. Other common applications of this technology include augmented reality, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISTI
The "Alessandro Faedo" Istituto di Scienza e Tecnologie dell'Informazione (''Institute of Information Science and Technologies'') is an institute of the Italian National Research Council (CNR). The institute is located in the CNR research area in the Ghezzano Province of Pisa about 5 km from San Giuliano Terme. The institute was founded in 2002 as a merge of two previous CNR institutes: Istituto CNUCE and Istituto di Elaborazione dell’Informazione (IEI). The institute is named in honor of Alessandro Faedo, former President of CNR and former rector of the University of Pisa, for his important contributions to the development of Computer Science in Italy. The mission of the institute is ''producing scientific excellence and playing an active role in technology transfer'' in the field of Computer Science. In 2022 the research staff of the institute counts more than 120 researchers and a total staff (including PhD students and fellows) of around 230. Since 1 April 2019 the ISTI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Detail (computer Graphics)
In computer graphics, level of detail (LOD) refers to the complexity of a 3D model representation. LOD can be decreased as the model moves away from the viewer or according to other metrics such as object importance, viewpoint-relative speed or position. LOD techniques increase the efficiency of rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline stages, usually vertex transformations. The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast. Although most of the time LOD is applied to geometry detail only, the basic concept can be generalized. Recently, LOD techniques also included shader management to keep control of pixel complexity. A form of level of detail management has been applied to texture maps for years, under the name of mipmapping, also providing higher rendering quality. It is commonplace to say that "an object has been ''LOD-ed''" when the object is simplified by the underlying ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynth
Photosynth is a discontinued app and service from Microsoft Live Labs and the University of Washington that analyzes digital photographs and generates a three-dimensional model of the photos and a point cloud of a photographed object. Pattern recognition components compare portions of images to create points, which are then compared to convert the image into a model. Users are able to view and generate their own models using a software tool available for download at the Photosynth website. History Photosynth is based on Photo Tourism, a research project by University of Washington graduate student Noah Snavely. Shortly after Microsoft's acquisition of Seadragon in early 2006, that team began work on Photosynth, under the direction of Seadragon founder Blaise Agüera y Arcas. Microsoft released a free tech preview version on November 9, 2006. Users could view models generated by Microsoft or the BBC, but not create their own models at that time. Microsoft teamed up with NASA o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COLLADA
COLLADA (for ''COLLA''borative ''D''esign ''A''ctivity) is an interchange file format for interactive 3D applications. It is managed by the nonprofit technology consortium, the Khronos Group, and has been adopted by ISO as a publicly available specification, ISO/PAS 17506. COLLADA defines an open standard XML schema for exchanging digital assets among various graphics software applications that might otherwise store their assets in incompatible file formats. COLLADA documents that describe digital assets are XML files, usually identified with a .dae (digital asset exchange) filename extension. History Originally created at Sony Computer Entertainment by Rémi Arnaud and Mark C. Barnes, it has since become the property of the Khronos Group, a member-funded industry consortium, which now shares the copyright with Sony. The COLLADA schema and specification are freely available from the Khronos Group. The COLLADA DOM uses thSCEA Shared Source License 1.0 Several graphics companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VRML
VRML (Virtual Reality Modeling Language, pronounced ''vermal'' or by its initials, originally—before 1995—known as the Virtual Reality Markup Language) is a standard file format for representing 3-dimensional (3D) interactive vector graphics, designed particularly with the World Wide Web in mind. It has been superseded by X3D. WRL file format VRML is a text file format where, e.g., vertices and edges for a 3D polygon can be specified along with the surface color, UV-mapped textures, shininess, transparency, and so on. URLs can be associated with graphical components so that a web browser might fetch a webpage or a new VRML file from the Internet when the user clicks on the specific graphical component. Animations, sounds, lighting, and other aspects of the virtual world can interact with the user or may be triggered by external events such as timers. A special Script Node allows the addition of program code (e.g., written in Java or ECMAScript) to a VRML file. VRML ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry Processing
Geometry processing, or mesh processing, is an area of research that uses concepts from applied mathematics, computer science and engineering to design efficient algorithms for the acquisition, reconstruction, analysis, manipulation, simulation and transmission of complex 3D models. As the name implies, many of the concepts, data structures, and algorithms are directly analogous to signal processing and image processing. For example, where image smoothing might convolve an intensity signal with a blur kernel formed using the Laplace operator, geometric smoothing might be achieved by convolving a surface geometry with a blur kernel formed using the Laplace-Beltrami operator. Applications of geometry processing algorithms already cover a wide range of areas from multimedia, entertainment and classical computer-aided design, to biomedical computing, reverse engineering, and scientific computing. Geometry processing is a common research topic at SIGGRAPH, the premier comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iterative Closest Point
Iterative closest point (ICP) is an algorithm employed to minimize the difference between two clouds of points. ICP is often used to reconstruct 2D or 3D surfaces from different scans, to localize robots and achieve optimal path planning (especially when wheel odometry is unreliable due to slippery terrain), to co-register bone models, etc. Overview The Iterative Closest Point algorithm keeps one point cloud, the reference or target, fixed, while transforming the other, the source, to best match the reference. The transformation (combination of translation and rotation) is iteratively estimated in order to minimize an error metric, typically the sum of squared differences between the coordinates of the matched pairs. ICP is one of the widely used algorithms in aligning three dimensional models given an initial guess of the rigid transformation required. The ICP algorithm was first introduced by Chen and Medioni, and Besl and McKay. The Iterative Closest Point algorithm contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLY (file Format)
PLY is a computer file format known as the Polygon File Format or the Stanford Triangle Format. It was principally designed to store three-dimensional data from 3D scanners. The data storage format supports a relatively simple description of a single object as a list of nominally flat polygons. A variety of properties can be stored, including color and transparency, surface normals, texture coordinates and data confidence values. The format permits one to have different properties for the front and back of a polygon. There are two versions of the file format, one in ASCII, the other in binary. The file format A Ply file starts with the "header" attribute, which specifies the elements of a mesh and their types, followed by the list of elements itself. The elements are usually vertices and faces, but may include other entities such as edges, samples of range maps, and triangle strips. The header of both ASCII and binary files is ASCII text. Only the numerical data that follows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS X
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers it is the Usage share of operating systems#Desktop and laptop computers, second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of ChromeOS. macOS succeeded the classic Mac OS, a Mac operating system with nine releases from 1984 to 1999. During this time, Apple cofounder Steve Jobs had left Apple and started another company, NeXT Computer, NeXT, developing the NeXTSTEP platform that would later be acquired by Apple to form the basis of macOS. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released in March 2001, with its first update, 10.1, arriving later that year. All releases from Mac OS X Leopard, Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and after are UNIX 03 certified, with an exception for OS X Lion, OS X 10. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android (operating System)
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |