|
Mass-independent Fractionation
Mass-independent isotope fractionation or Non-mass-dependent fractionation (NMD), refers to any chemical or physical process that acts to separate isotopes, where the amount of separation does not scale in proportion with the difference in the masses of the isotopes. Most isotopic fractionations (including typical kinetic fractionations and equilibrium fractionations) are caused by the effects of the mass of an isotope on atomic or molecular velocities, diffusivities or bond strengths. Mass-independent fractionation processes are less common, occurring mainly in photochemical and spin-forbidden reactions. Observation of mass-independently fractionated materials can therefore be used to trace these types of reactions in nature and in laboratory experiments. Mass-independent fractionation in nature The most notable examples of mass-independent fractionation in nature are found in the isotopes of oxygen and sulfur. The first example was discovered by Robert N. Clayton, Toshiko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Fractionation
Isotope fractionation describes fractionation processes that affect the relative abundance of isotopes, phenomena which are taken advantage of in isotope geochemistry and other fields. Normally, the focus is on stable isotopes of the same element. Isotopic fractionation can be measured by isotope analysis, using isotope-ratio mass spectrometry or cavity ring-down spectroscopy to measure ratios of isotopes, an important tool to understand geochemical and biological systems. For example, biochemical processes cause changes in ratios of stable carbon isotopes incorporated into biomass. Definition Stable isotopes partitioning between two substances ''A'' and ''B'' can be expressed by the use of the isotopic fractionation factor (alpha): where ''R'' is the ratio of the heavy to light isotope (e.g., 2H/1H or 18O/16O). Values for alpha tend to be very close to 1. McGlynn, Shawn E.; "Biological Isotope Fractionation and Earth History: From Enzymes to Cells to Ecosystems" pp 59-79 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets— Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excited State
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation (with the notable exception of systems that exhibit negative temperature). The lifetime of a system in an excited state is usually short: spontaneous or induced emission of a quantum of energy (such as a photon or a phonon) usually occurs shortly after the system is promoted to the excited state, returning the system to a state with lower energy (a less excited state or the ground state). This return to a lower energy level is often loosely described as decay and is the inverse of excitation. Long-lived excited states are often calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Isotope Effect
In physical organic chemistry, a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is the change in the reaction rate of a chemical reaction when one of the atoms in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes. Formally, it is the ratio of rate constants for the reactions involving the light (''kL'') and the heavy (''kH'') isotopically substituted reactants (isotopologues): :\text=\frac This change in reaction rate is a quantum mechanical effect that primarily results from heavier isotopologues having lower vibrational frequencies compared to their lighter counterparts. In most cases, this implies a greater energetic input needed for heavier isotopologues to reach the transition state (or, in rare cases, the dissociation limit), and consequently, a slower reaction rate. The study of kinetic isotope effects can help the elucidation of the reaction mechanism of certain chemical reactions and is occasionally exploited in drug development to improve unfavorable pharmacokinetics by protectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph Marcus
Rudolph Arthur Marcus (born July 21, 1923) is a Canadian-born chemist who received the 1992 Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his contributions to the theory of electron transfer reactions in chemical systems". Marcus theory, named after him, provides a thermodynamic and kinetic framework for describing one electron outer-sphere electron transfer. He is a professor at Caltech, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore and a member of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science. Education and early life Marcus was born in Montreal, Quebec, the son of Esther (born Cohen) and Myer Marcus. His father was born in New York and his mother was born in England. His family background is from Ukmergė.Marcus, Rudolph A. Interview by Shirley K. Cohen. Pasadena, California, December 1, 7, and 14, 1993. Oral History Project, California Institute of Technology Archives. Retrieved 2020 from the World Wide Web: http://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechOH:OH_Marcus_R He is Jewish and grew up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air high in the sky and the cool layers of air in the low sky, close to the planetary surface of the Earth. The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer. The temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, near the Earth's surface, where temperature decreases with altitude. Between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at midlatitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of near the mesosphere. Stratospheric temperatures also vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Thiemens
Mark Howard Thiemens (born January 6, 1950 in St. Louis, Missouri) is a Distinguished Professor and the Chancellors Associates Chair in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California San Diego. He is best known for the discovery of a new physical chemical phenomena termed the mass independent isotope effect. His studies have crossed a broad range of topics including basic physical and quantum chemistry, solar system origin, tracking the origin and evolution of life on early earth; stratospheric chemistry, climate change and greenhouse gas identification, Mars atmospheric chemistry, past and future and isotope geochemistry. His work combines photochemical isotope studies, both laboratory and synchrotron based, field work in the South Pole, Greenland Summit and the Tibetan Himalayas for climate and geological sampling across China for early earth rock records. His non-isotope work has included discovery of an unknown source of the greenhouse gas nitrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to ( dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodissociation
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule. Photodissociation is not limited to visible light. Any photon with sufficient energy can affect the chemical bonds of a chemical compound. Since a photon's energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength, electromagnetic radiations with the energy of visible light or higher, such as ultraviolet light, x-rays, and gamma rays can induce such reactions. Photolysis in photosynthesis Photolysis is part of the light-dependent reaction or light phase or photochemical phase or Hill reaction of photosynthesis. The general reaction of photosynthetic photolysis can be given in terms of photons as: :\ce + 2 \text \longrightarrow \ce The chemical nature of "A" depends on the type of organism. Purple sulfur bacteria oxidize hydrogen sulfide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis (spacecraft)
''Genesis'' was a NASA sample-return probe that collected a sample of solar wind particles and returned them to Earth for analysis. It was the first NASA sample-return mission to return material since the Apollo program, and the first to return material from beyond the orbit of the Moon. ''Genesis'' was launched on August 8, 2001, and the sample return capsule crash-landed in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevented the deployment of its drogue parachute. The crash contaminated many of the sample collectors. Although most were damaged, some of the collectors were successfully recovered. The ''Genesis'' science team demonstrated that some of the contamination could be removed or avoided, and that the solar wind particles could be analyzed using a variety of approaches, achieving all of the mission's major science objectives. Objectives The mission's primary science objectives were: * To obtain precise solar isotopic abundances of ions in the solar wind, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
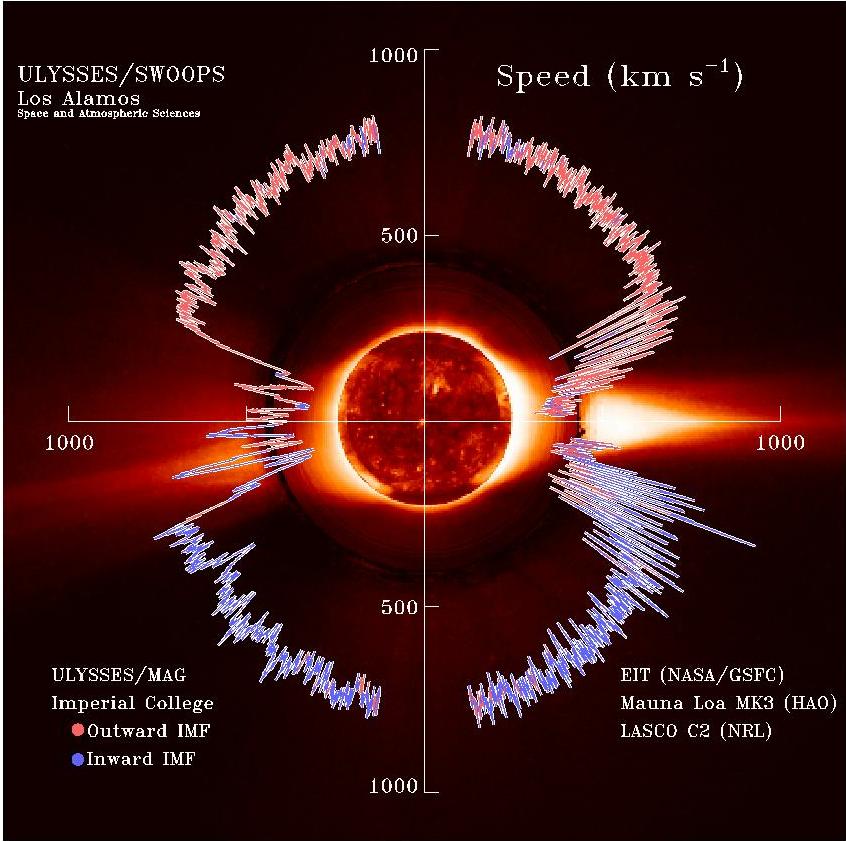
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(2).png)