|
Maharashtri Prakrit
Maharashtri or Maharashtri Prakrit ('), is a Prakrit language of ancient as well as medieval India and the ancestor of Marathi and Konkani. Maharashtri Prakrit was commonly spoken until 875 CEV.Rajwade, ''Maharashtrache prachin rajyakarte''The Linguist List Dr.Kolarkar, ''Marathyancha Itihaas'' and was the official language of the . Works like ''Karpūramañjarī'' and (150 BCE) were written in it. |
Brahmi
Brahmi (; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi [''sc. lipi''], which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T[errien] de Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paishachi
Paishachi or Paisaci () is a largely unattested literary language of the middle kingdoms of India mentioned in Prakrit and Sanskrit grammars of antiquity. It is generally grouped with the Prakrits, with which it shares some linguistic similarities, but is still not considered a spoken Prakrit by the grammarians because it was purely a literary language, and because of its archaicism. Identity The etymology of the name suggests that it is spoken by piśācas, "ghouls". In works of Sanskrit poetics such as Daṇḍin's ''Kavyadarsha'', it is also known by the name of , an epithet which can be interpreted either as a "dead language" (i.e. with no surviving speakers), or as "a language spoken by the dead" (i.e. ghouls or ghosts), the former interpretation being more realistic and the latter being the more fanciful. Evidence which lends support to the former interpretation is that literature in Paiśācī is fragmentary and extremely rare but may have been once common. The Siddha-H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaudavaho
''Gaudavaho'' ("Slaying of the Gauda king") is an 8th-century Prakrit-language epic poem by Vakpati-raja. It narrates the exploits of the poet's patron, king Yashovarman, who ruled in northern India. The poem deifies the king as an incarnation of the god Vishnu, and credits him with several military achievements, including slaying of the Gauda king. A little over 1200 verses of the text are known from several manuscripts. According to some scholars such as Georg Bühler, the surviving text is only a prelude to the larger poem that Vakpati intended to write, but possibly never finished. Authorship Gaudavaho was composed by Vakpati-raja (Prakrit: "Bappai-rāa"), a court poet of king Yashovarman. He wrote in the first half of the 8th century. He states that he was known as ''Kavi-raja'' (Prakrit: "Kairāa", "king of poets"), an epithet possibly awarded to him by his patron Yashovarman. Kalhana's ''Rajatarangini'' suggests that both Vakpati and Bhavabhuti were court poets of Lalita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravarasena II
Pravarasena II () was a ruler of the Nandivardhana-Pravarapura branch of the Vakataka dynasty. He was the son of Rudrasena II and Prabhavatigupta, the daughter of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta II. He succeeded his brother Damodarasena as Maharaja. Pravarasena's reign seems to have been mostly peaceful and prosperous, and is noted for an efflorescence of religious patronage. Chronology That all of Pravarasena's extant records are dated in terms of regnal years (rather than any calendar era), the precise era of Pravarasena's reign remains disputed. The only record that provides a firm chronological basis for Vakataka dynastic history is the Hisse-Borala stone inscription of Devasena, a ruler of the Vatsagulma branch, which contains a precise calendar date of year 380 of the Saka era (corresponding to 457/58 CE). Due to the absence of any earlier records that can be precisely dated, different historians have proposed differing dates for Pravarasena's reign, though it is widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hāla
(r. 20–24 CE) was a Satavahana king who ruled in present-day Deccan region.Mahajan V.D. (1960, reprint 2007) ''Ancient India'', S.Chand, New Delhi, ,pp.394-95 The Matsya Purana mentions him as the 17th ruler of the Satavahana dynasty. The Maharashtri Prakrit poem by ''Kouhala'', ''Lilavai'' (c. 800 CE) describes his romance with a princess of Simhaladvipa (identified with present-day Sri Lanka). Vijayananda, the commander-in-chief of Hala's army led a successful campaign in Ceylon. On his way back, he stayed at ''Sapta Godavari Bhimam''. Here, he learned of Lilavai, the beautiful daughter of the king of Ceylon. He narrated her story to . King secured Lilavai and married her. is famous for compiling an anthology of Maharashtri Prakrit poems known as the Gaha Sattasai (Sanskrit Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada Language
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western India
Western India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of its western part. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra along with the Union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, while the Ministry of Culture and some historians also include the state of Rajasthan. The Geological Survey of India includes Maharashtra but excludes Rajasthan whereas Ministry of Minority Affairs includes Karnataka but excludes Rajasthan. Madhya Pradesh is also often included and Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and southern Punjab are sometimes included. Western India may also refer to the western half of India, i.e. all the states west of Delhi and Chennai, thus also including Punjab, Kerala and surrounding states. The region is highly industrialised, with a large urban population. Roughly, western India is bounded by the Thar Desert in the north, the Vindhya Range in the east and no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
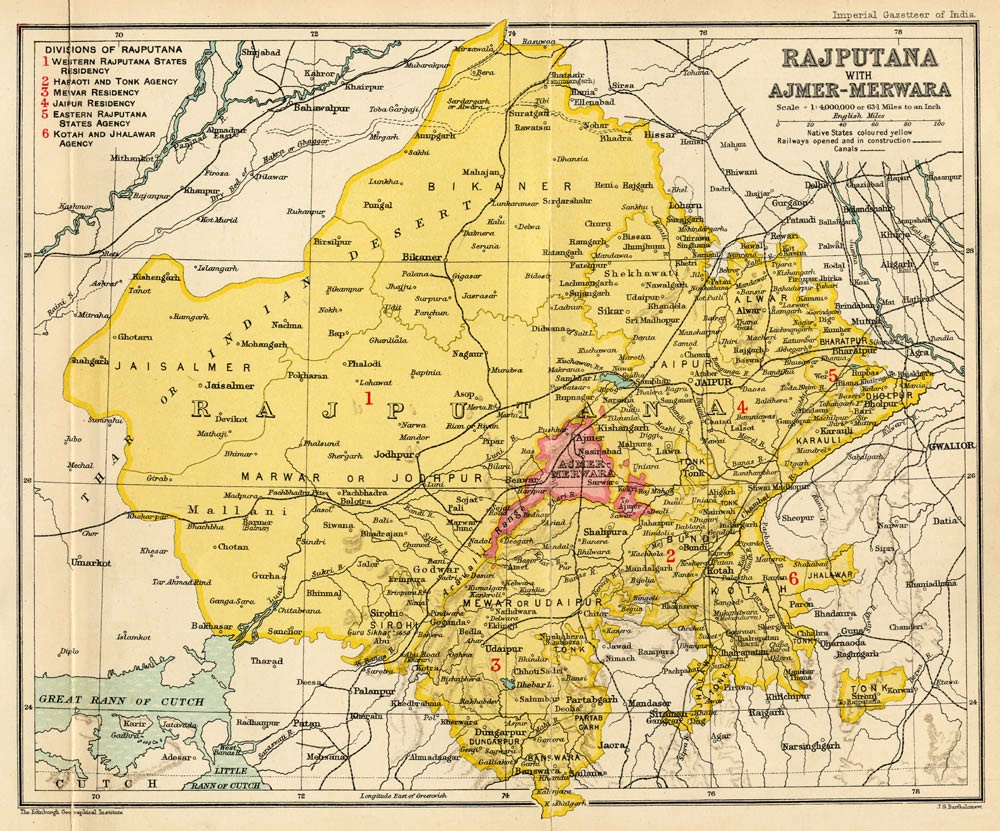
Rajputana
Rājputana, meaning "Land of the Rajputs", was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sindh in modern-day southern Pakistan. The main settlements to the west of the Aravalli Hills came to be known as ''Rajputana'', early in the Medieval Period. The name was later adopted by British government as the Rajputana Agency for its dependencies in the region of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān. The Rajputana Agency included 18 princely states, two chiefships and the British district of Ajmer-Merwara. This British official term remained until its replacement by "Rajasthan" in the constitution of 1949. Name George Thomas (''Military Memories'') was the first in 1800, to term this region the ''Rajputana Agency''. The historian John Keay in his book, ''India: A History'', stated that the ''Rajputana'' name was coined by the British, but that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also synonymous with the former state of Madhya Bharat which was later merged with Madhya Pradesh. At present the historical Malwa region includes districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. Sometimes the definition of Malwa is extended to include the Nimar region south of the Vindhyas. The Malwa region had been a separate political unit from the time of the ancient Malava Kingdom. It has been ruled by several kingdoms and dynasties, including the Avanti Kingdom, The Mauryans, the Malavas, the Guptas, the Paramaras, the Delhi Sultanate, the Malwa sultans, the Mughals and the Marathas. Malwa continued to be an administrative division until 1947, when the Malwa Agency of British India was merged into Madhya Bharat (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |