|
Macduff, Aberdeenshire
Macduff () is a town in the Banff and Buchan area of Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is situated on Banff Bay and faces the town of Banff across the estuary of the River Deveron. Macduff is a former burgh and was the last place in the United Kingdom where deep-water wooden fishing boats were built. History The settlement of Doune (from the Scottish Gaelic , "hill fort") was purchased in 1733 by William Duff, who became the first Earl Fife. In 1760, James Duff, the second earl, built a harbour there and in 1783 succeeded in raising Doune to the status of a burgh of barony, renaming it " Macduff" after his supposed ancestor. The 2nd Earl Fife appointed his factor, William Rose, as the first Provost of Macduff in 1783. The town celebrated its bicentenary in 1983, and the signs erected in that year still stand on the main approaches to the town (most visibly, a large sign next to the Banff Bridge on the Macduff side). Banff and Macduff are separated by the valley of the River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire (; ) is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland#council areas of Scotland, council areas of Scotland. It takes its name from the Shires of Scotland, historic county of Aberdeenshire (historic), Aberdeenshire, which had substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area includes all of the areas of the historic counties of Aberdeenshire and Kincardineshire except the area making up Aberdeen City Council area, as well as part of Banffshire. The historic county boundaries are still officially used for a few purposes, namely land registration and Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy. Aberdeenshire Council is headquartered at Woodhill House in Aberdeen, making it the only Scottish council whose headquarters are located outside its jurisdiction. Aberdeen itself forms a different council area (Aberdeen City). Aberdeenshire borders onto Angus, Scotland, Angus and Perth and Kinross to the south, Highland (council area), Highland and Moray to the west a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macduff (Macbeth)
Lord Macduff, the Thane of Fife, is a character and the heroic main antagonist in William Shakespeare's ''Macbeth'' (c.1603–1607) that is loosely based on history. Macduff, a legendary hero, plays a pivotal role in the play: he suspects Macbeth of regicide and eventually kills Macbeth in the final act. He can be seen as the avenging hero who helps save Scotland from Macbeth's tyranny in the play. The character is first known from '' Chronica Gentis Scotorum'' (late 14th century) and '' Orygynale Cronykil of Scotland'' (early 15th century). Shakespeare drew mostly from ''Holinshed's Chronicles'' (1587). Although characterised sporadically throughout the play, Macduff serves as a foil to Macbeth and a figure of morality. Origin The overall plot that would serve as the basis for ''Macbeth'' is first seen in the writings of two chroniclers of Scottish history, John of Fordun, whose prose '' Chronica Gentis Scotorum'' was begun about 1363, and Andrew of Wyntoun's Scots verse ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
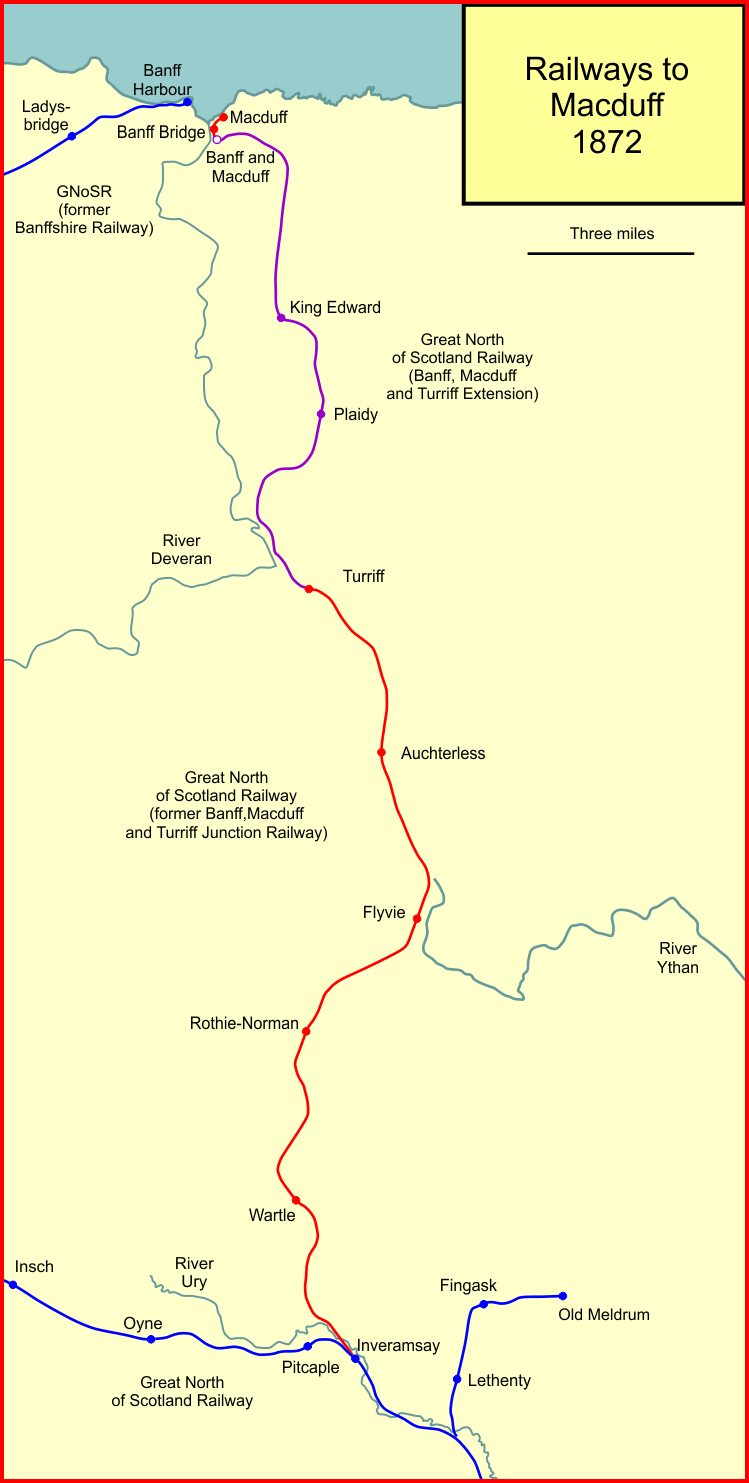
Banff, Macduff And Turriff Junction Railway
The Banff, Macduff and Turriff Junction Railway was a railway company that connected the Aberdeenshire town of Turriff with the main line of the Great North of Scotland Railway (GNoSR) at Inveramsay. It had earlier been intended to reach Macduff, but shortage of finance forced curtailment. It opened its line in 1857. A separate company, the Banff, Macduff and Turriff Extension Railway, was formed to build an extension to Macduff. There was a road bridge connecting Macduff with Banff, crossing the River Deveron, and it was intended that both towns would be served by the railway’s terminus. The Extension Railway opened in 1860, but its terminus was some distance short of Macduff and of the bridge to Banff. Both railways were absorbed by the Great North of Scotland Railway in 1866, and the line was extended by the to a new station in 1872, with an intermediate station at the river bridge. The companies and the branch line were never commercially successful. In 1951 the line w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
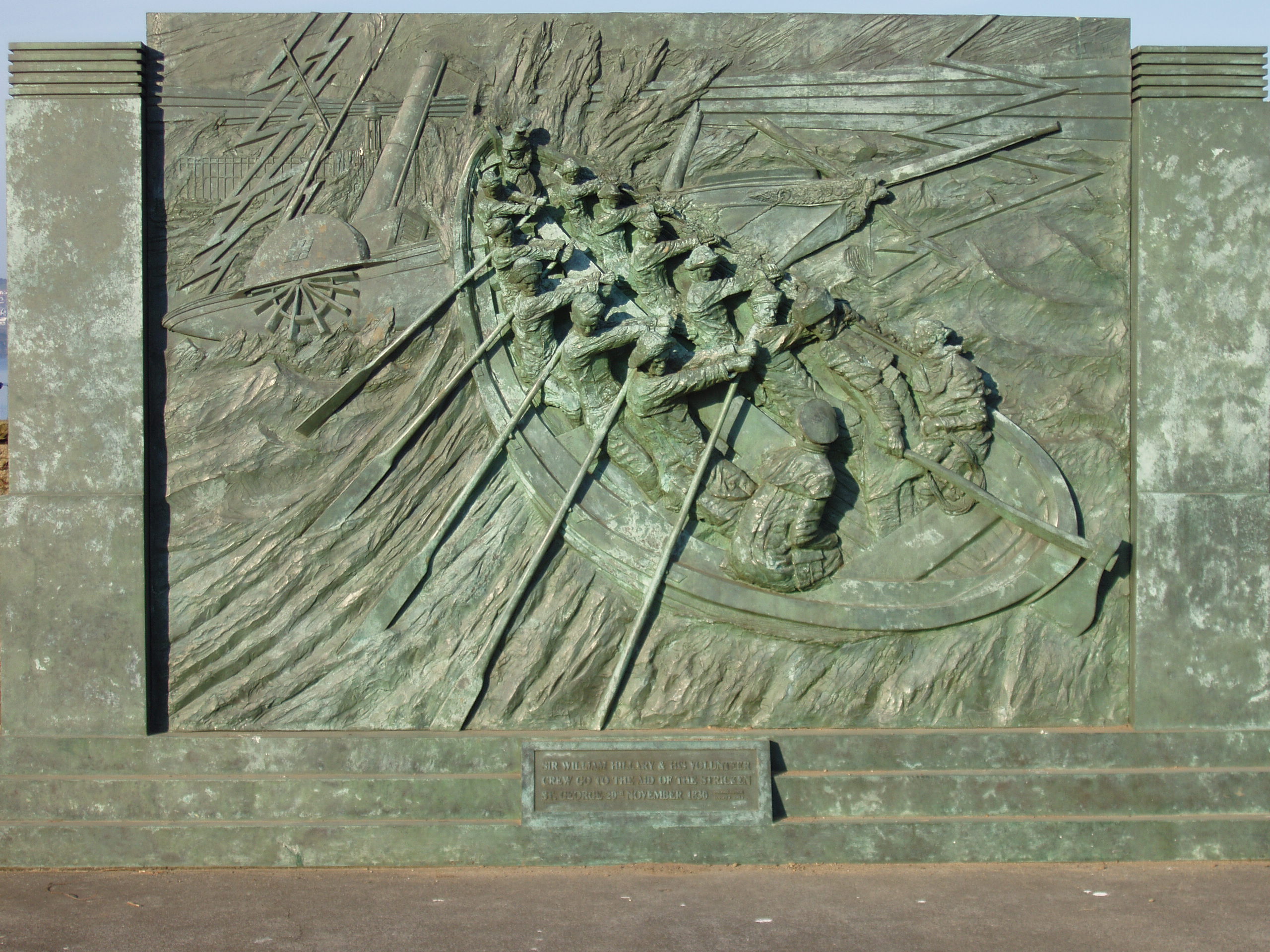
Royal National Lifeboat Institution
The Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) is the largest of the lifeboat (rescue), lifeboat services operating around the coasts of the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, as well as on some inland waterways. Founded in 1824 as the National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck, it soon afterwards became the Royal National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck because of the patronage of King George IV. Royal patronage has continued up to the present day with Charles III, King Charles III. The organisation changed its name to the Royal National Lifeboat Institution on 5 October 1854 and was granted a royal charter in 1860. The RNLI is a charity based in Poole, Dorset. It is principally funded by Will (law), legacies (65%) and donations (30%). Most of its lifeboat crews are unpaid volunteers. They operate more than 400 lifeboats from 238 stations. Paid lifeguards provide services at near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNLI
The Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) is the largest of the lifeboat services operating around the coasts of the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, as well as on some inland waterways. Founded in 1824 as the National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck, it soon afterwards became the Royal National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck because of the patronage of King George IV. Royal patronage has continued up to the present day with King Charles III. The organisation changed its name to the Royal National Lifeboat Institution on 5 October 1854 and was granted a royal charter in 1860. The RNLI is a charity based in Poole, Dorset. It is principally funded by legacies (65%) and donations (30%). Most of its lifeboat crews are unpaid volunteers. They operate more than 400 lifeboats from 238 stations. Paid lifeguards provide services at nearly 250 beaches. The RNLI also provides free safety advice to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Historic Environment Division of the Department for Communities in Northern Ireland. The classification schemes differ between England and Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland (see sections below). The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000, although the statutory term in Ireland is "Record of Protected Structures, protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macduff Town Hall
Macduff Town Hall is a municipal building in Shore Street, Macduff, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The structure, which was the meeting place of Macduff Burgh Council, is a Category B listed building. History The first municipal building in Macduff was an early 19th century townhouse in Shore Street. Following significant population growth, largely associated with the fishing industry, the town became a police burgh in 1853. In the 1880s, the police commissioners decided to demolish the old townhouse and erect a new building in its place. The new building was designed by John Bridgeford Pirie and Arthur Clyne in the Scottish baronial style, built in ashlar stone and completed in 1885. The design involved a symmetrical main frontage with three bays facing onto Shore Street; the central bay, which slightly projected forward, featured a doorway with a fanlight on the ground floor, a sash window on the first floor and a Diocletian window with a blind oculus above at attic level. The cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Hall (geograph 3923022)
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city or town council and at least some other arms of the local government. It also often functions as the office of the mayor (or other executive), if the relevant municipality has such an officer. In large cities, the local government is often administratively expansive, and the city hall may bear more resemblance to a municipal capitol building. By convention, until the middle of the 19th century, a single large open chamber (or "hall") formed an integral part of the building housing the council and such other organs of government as supported it. The hall may be used for council meetings and other significant events. This large chamber, the "town hall" (and its later variant "city hall") became synonymous with the whole building, and, synecd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennan
Pennan () is a small village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, consisting of a small harbour and a single row of homes, including a hotel. It is on the north-facing coast and is about one hour's drive from Aberdeen. It was formerly known as St Magnus Haven or Auchmedden. Etymology The name ''Pennan'' was recorded in 1587 as ''Pennand''. It is possibly derived from the Brittonic element ''*pen'' meaning "head, end, promontory" ( Welsh ''pen''). Area history Pennan seems to have come into existence as a fishing village in the 18th century. The people of Pennan were dependent on the sea. Most families had small boats for their own personal use. Where the men would catch the fish, it was usually down to the women and children to try to sell it to clients in the country. Until the 1930s, the population of the village seems to have come under three main surnames - Watt, Gatt and West. In the last 50 years, most of the native families have moved out and most of the houses have been bough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardenstown
Gardenstown is a small coastal village, by road east of Banff, Scotland, Banff in Aberdeenshire, northeastern Scotland. It lies in the civil parish of Gamrie, formerly part of Banffshire. The village's main economic base is fishing. Gardenstown is served by Gardenstown New Church. The hamlet of Dubford is to the south, and a footpath along the shore to the east leads to the village of Crovie. History There is evidence of Neolithic or Bronze Age peoples having settled in the vicinity of Gardenstown; notably at Longman Hill and Cairn Lee. Nearby are the remains of the Church of St John the Evangelist which was built in 1513, and celebrates the defeat of the Danes at this site in 1004 in the Battle of the Bloody Pits. Gardenstown and its harbour were founded in 1720 by Alexander Garden. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarlair Swimming Pool
Tarlair Swimming Pool is a lido at the base of a sea cliff just outside Macduff in Aberdeenshire in Scotland. This outdoor swimming complex was built in an Art Deco style with a main building backing onto the cliffs and changing rooms to its left hand side. It is considered by Historic Environment Scotland to be the best example of only three surviving outdoor seaside pools in Scotland, the others being at Stonehaven and Gourock. The design of the pool was a clever use of pumped sea water to fill the pools, and flooding of the main pool at high tide to flush out the old water. The main pool had a diving board at the deep end and a child's chute at the shallow end, though both are now missing. The second-largest pool was a boating pool with the two remaining pools being paddling pools. The complex is now in the process of being repaired with the help of Friends of Tarlair. Channel 4 television made "Tarlair Outdoor Pool" the subject of the third episode of a series of six docum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macduff Marine Aquarium
Macduff Marine Aquarium is an aquarium in Macduff, Scotland, opened in 1997. In 2017, the aquarium closed to allow the main tank to be drained and repaired. In 2023, Aberdeenshire Council Aberdeenshire Council is the local authority for Aberdeenshire, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. The council has been under no overall control since its creation in 1996. It is based at Woodhill House, which is outside its own territory ... announced that its bid for funding from the Levelling Up Fund had been successful. The aquarium was due to be expanded with a second storey added containing a cafe. References External links * {{coord, 57.6720, -2.4917, type:landmark_region:GB, display=title Macduff, Aberdeenshire Aquaria in the United Kingdom 1997 establishments in Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |