|
Musical Tone
Traditionally in Western classical music, Western music, a musical tone is a steady periodic function, periodic sound. A musical tone is characterized by its duration (music), duration, pitch (music), pitch, amplitude, intensity (or loudness), and timbre (or quality). The Musical note, notes used in music can be more complex than musical tones, as they may include aperiodic aspects, such as attack transient (acoustics), transients, vibrato, and envelope modulation. A ''simple tone'', or ''pure tone'', has a Sine wave, sinusoidal waveform. A ''complex tone'' is a combination of two or more pure tones that have a periodic pattern of repetition, unless specified otherwise. The Fourier theorem states that any periodic waveform can be approximated as closely as desired as the sum of a series of sine waves with frequencies in a harmonic series (mathematics), harmonic series and at specific phase (waves), phase relationships to each other. The common denominator frequency, which is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspects Of Music Illustration
Aspect or Aspects may refer to: Companies * Aspect Capital, a London-based investment manager * Aspect Co., a Japanese video game company * Aspect Software, an American call center technology and customer experience company Literature * ''Aspect'' (magazine), a biannual DVD magazine showcasing new media art * ''Aspects'' (novel), a fantasy novel by John M. Ford Music * Aspects (band), a hip hop group from Bristol, England, UK * ''Aspects'' (Benny Carter album), a 1959 album * ''Aspects'' (The Eleventh House album), a 1976 album by Larry Coryell and The Eleventh House ** "Aspects" , the title track of the album Other uses * Alain Aspect (born 1947), French physicist and Nobel laureate * Aspect (computer programming), a feature linked to many parts of a program but not necessarily the primary function of the program * Aspect (geography), the compass direction that a slope faces * Aspect (religion), a particular manifestation of a deity * Astrological aspect, an angle the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Theorem
A Fourier series () is an expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. For example, Fourier series were first used by Joseph Fourier to find solutions to the heat equation. This application is possible because the derivatives of trigonometric functions fall into simple patterns. Fourier series cannot be used to approximate arbitrary functions, because most functions have infinitely many terms in their Fourier series, and the series do not always converge. Well-behaved functions, for example smooth functions, have Fourier series that converge to the original function. The coefficients of the Fourier series are determined by integrals of the function multiplied by trigonometric functions, described in . The study of the conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
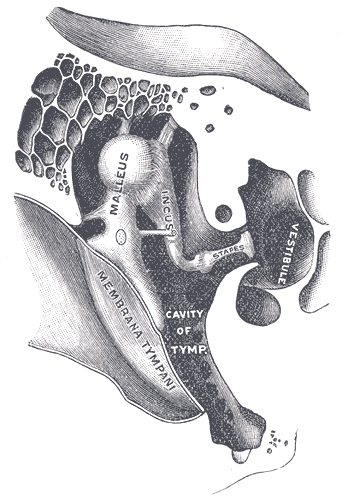
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics, acoustical engineering, telecommunications, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, not to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band. In discrete time, white noise is a discrete signal whose samples are regarded as a sequence of serially uncorrelated random variables with zero mean and finite variance; a single realization of white noise is a random shock. In some contexts, it is also required that the samples be independent and have identical probability distribution (in other words independent and identically distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitch (music), pitches and / or chord (music), chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived ''relations'', ''stabilities'', ''attractions'', and ''directionality''. In this hierarchy, the single pitch or the root (music), root of a triad (music), triad with the greatest ''stability'' in a melody or in its harmony is called the tonic (music), ''tonic''. In this context "stability" approximately means that a pitch occurs frequently in a melody – and usually is the final note – or that the pitch often appears in the harmony, even when it is not the pitch used in the melody. The ''root'' of the tonic triad forms the name given to the key (music), key, so in the key of C major, C major the note C can be both the tonic of the scale (music), scale and the root of the tonic triad. However, the tonic can be a different Musical tone, tone in the same scale, and then the work is said to be in one of the mode (music), ''modes'' of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Tone
A signal tone or signalling tone is a steady or pulsating Periodic function, periodic signal typically in the frequency range of sound for indicating a condition, communication protocol state, or serve as an audible warning. It may be composed of multiple frequency components, or could be a pure tone. In telephone systems, signaling tones are used as call progress tones for in-band indications to subscribers or operators. Certain telephone switching systems used tones, in-band or out-of-band, for signaling (telecommunications), signaling on trunks. Typical well-known call progress tones are dial tone, ringing tone, busy tone, and the reorder tone. A loud stutter tone is used to alert subscribers of a handset left off-hook, effectively disabling the circuit for receiving calls. Telephone service subscribers may subscribe to services, such as call forwarding, which may indicate function by a stutter dial tone. See also * Musical tone * Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Test Tone
A reference tone is a pure tone corresponding to a known frequency, and produced at a stable sound pressure level (volume), usually by specialized equipment. In media The most common reference tone in audio engineering is a at −20 dB. It is meant to be used by audio engineers in order to adjust the playback equipment so that the accompanying media is at a comfortable volume for the audience. In video production, this tone is usually accompanied by a test card so the video programming may be calibrated as well. It is sometimes played in sequence between a 100 Hz and 10 kHz tone to ensure an accurate response from the equipment at varying audio frequencies. This is also the "bleep" tone commonly used to censor obscene or sensitive audio content. In music Many electronic tuners used by musicians emit a tone of 440Hz, corresponding to a pitch of A above Middle C (A4). More sophisticated tuners offer a choice of other reference pitches to account for differences in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Of Musical Scales
Music theory analyzes the pitch, timing, and structure of music. It uses mathematics to study elements of music such as tempo, chord progression, form, and meter. The attempt to structure and communicate new ways of composing and hearing music has led to musical applications of set theory, abstract algebra and number theory. While music theory has no axiomatic foundation in modern mathematics, the basis of musical sound can be described mathematically (using acoustics) and exhibits "a remarkable array of number properties". History Though ancient Chinese, Indians, Egyptians and Mesopotamians are known to have studied the mathematical principles of sound, the Pythagoreans (in particular Philolaus and Archytas) of ancient Greece were the first researchers known to have investigated the expression of musical scales in terms of numerical ratios, particularly the ratios of small integers. Their central doctrine was that "all nature consists of harmony arising out of numbers". From t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristoxenus
Aristoxenus of Tarentum (; born 375, fl. 335 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek Peripatetic school, Peripatetic philosopher, and a pupil of Aristotle. Most of his writings, which dealt with philosophy, ethics and music, have been lost, but one musical treatise, ''Elements of Harmony'' (Greek: ; Latin: ''Elementa harmonica''), survives incomplete, as well as some fragments concerning rhythm and Metre (music), meter. The ''Elements'' is the chief source of our knowledge of Music of ancient Greece, ancient Greek music. Life Aristoxenus was born at Taranto, Tarentum (in modern-day Apulia, southern Italy) in Magna Graecia, and was the son of a learned musician named Spintharus (otherwise Mnesias). He learned music from his father, and having then been instructed by Lamprus of Erythrae and Xenophilus (philosopher), Xenophilus the Pythagorean, he finally became a pupil of Aristotle, whom he appears to have rivaled in the variety of his studies. According to the ''Suda'', he heaped insults ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |