|
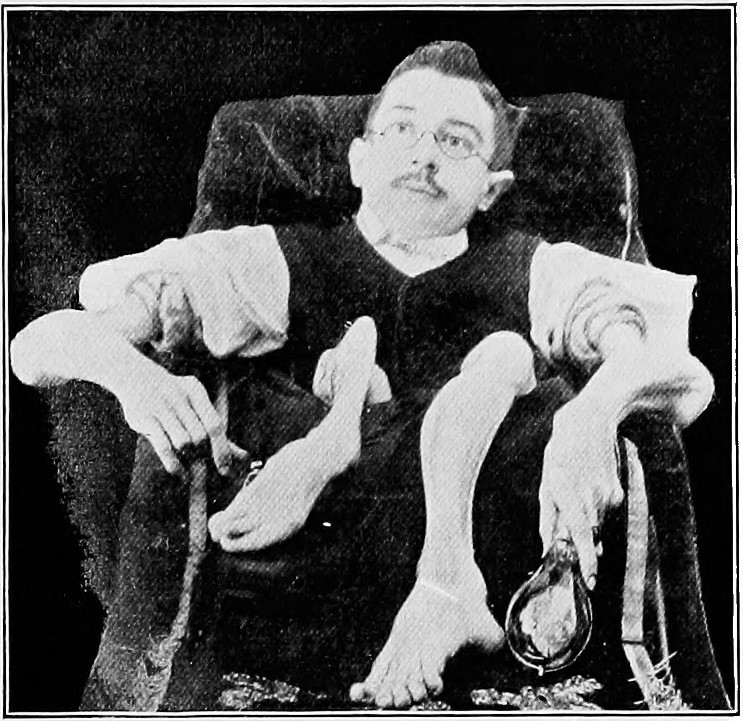
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other human organs, organs. Over 30 different disorders are classified as muscular dystrophies. Of those, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) accounts for approximately 50% of cases and affects males beginning around the age of four. Other relatively common muscular dystrophies include Becker muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and myotonic dystrophy, whereas limb–girdle muscular dystrophy and congenital muscular dystrophy are themselves groups of several – usually extremely rare – genetic disorders. Muscular dystrophies are caused by mutations in genes, usually those involved in making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystrophin
Dystrophin is a rod-shaped cytoplasmic protein, and a vital part of a protein complex that connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane. This complex is variously known as the costamere or the dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC). Many muscle proteins, such as α-dystrobrevin, syncoilin, synemin, sarcoglycan, dystroglycan, and sarcospan, colocalize with dystrophin at the costamere. It has a molecular weight of 427 kDa. Dystrophin is coded for by the ''DMD'' gene – the largest known human gene, covering 2.4 megabases (0.08% of the human genome) at Locus (genetics), locus X chromosome, Xp21. The primary transcript in muscle measures about 2,100 kilobases and takes 16 hours to transcribe; the Mature messenger RNA, mature mRNA measures 14.0 kilobases. The 79-exon muscle transcript codes for a protein of 3685 amino acid residues. Spontaneous or inherited mutations in the dystrophin gene can cause different form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
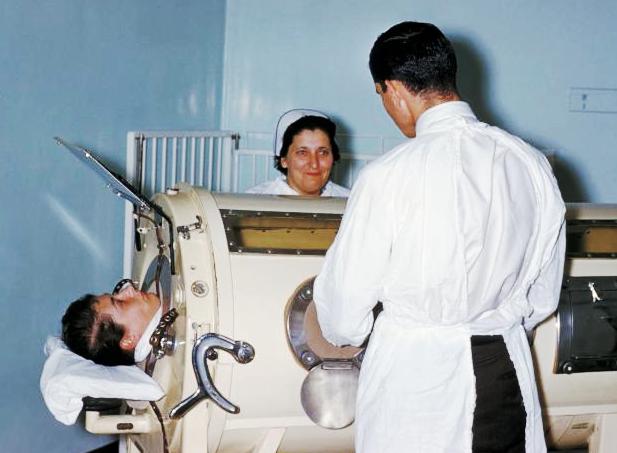
Assisted Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the medical term for using a ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types of mechanical ventila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisense Therapy
Antisense therapy is a form of treatment that uses antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) to target messenger RNA (mRNA). ASOs are capable of altering mRNA expression through a variety of mechanisms, including ribonuclease H mediated decay of the pre-mRNA, direct steric blockage, and exon content modulation through Splicing (genetics), splicing site binding on pre-mRNA. Several ASOs have been approved in the United States, the European Union, and elsewhere. Nomenclature The common stem for antisense oligonucleotides drugs is -rsen. The substem -virsen designates antiviral antisense oligonucleotides. Antisense Oligonucleotide Development Developments in ASO modification are separated into three generations. Generation one is called backbone-modified and focuses on the phosphodiester group of the nucleotide. This impacts inter-nucleotide binding. These modifications led to better distribution, reduced urinary excretion, and prolonged residence time of the ASOs in the cell. Some exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delandistrogene Moxeparvovec
Delandistrogene moxeparvovec, sold under the brand name Elevidys, is a recombinant gene therapy used for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It is designed to deliver into the body a gene that leads to production of Elevidys micro-dystrophin that contains selected domains of the dystrophin protein present in normal muscle cells. It is an adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapy that is given by intravenous infusion (slow injection into a vein). The most commonly reported side effects include vomiting, nausea, acute liver injury, pyrexia (fever), and thrombocytopenia (abnormally low platelet count in the blood). One patient may have died from acute liver failure. Delandistrogene moxeparvovec was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2023. It was developed by Sarepta Therapeutics, together with Roche, and is manufactured by Catalent. Medical uses Delandistrogene moxeparvovec is indicated In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980, by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990. Between 1989 and December 2018, over 2,900 clinical trials were conducted, with more than half of them in Phases of clinical research, phase I. In 2003, Gendicine became the first gene therapy to receive regulatory approval. Since that time, further gene therapy drugs were approved, such as alipogene tiparvovec (2012), Strimvelis (2016), tisagenlecleucel (2017), voretigene neparvovec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or through biochemical analysis to measure specific protein output. In a medical setting, genetic testing can be used to diagnose or rule out suspected genetic disorders, predict risks for specific conditions, or gain information that can be used to customize medical treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. Genetic testing can also be used to determine biological relatives, such as a child's biological parentage (genetic mother and father) through DNA paternity testing, or be used to broadly predict an individual's ancestry. Genetic testing of plants and animals can be used for similar reasons as in humans (e.g. to assess relatedness/ancestry or predict/diagnose genetic disorders), to gain information used for selective breed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse. Extraction A venipuncture is useful as it is a minimally invasive way to obtain cells and extracellular fluid ( plasma) from the body for analysis. Blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium that provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues and carries waste products back to the excretory systems f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Embryogenesis
Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Human embryonic development covers the first eight weeks of development, which have 23 stages, called Carnegie stages. At the beginning of the ninth week, the embryo is termed a fetus (spelled "foetus" in British English). In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features and a more complete set of developing organs. Human embryology is the study of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Novo Mutation
A de novo mutation (DNM) is any mutation or alteration in the genome of an individual organism (human, animal, plant, microbe, etc.) that was not inherited from its parents. This type of mutation spontaneously occurs during the process of DNA replication during cell division. De novo mutations, by definition, are present in the affected individual but absent from both biological parents' genomes. A de novo mutation can arise in a sperm or egg cell and become a germline mutation, or after fertilization as a post-zygotic mutation that cannot be inherited by offspring. These mutations can occur in any cell of the offspring, but those in the germ line (eggs or sperm) can be passed on to the next generation. In most cases, such a mutation has little or no effect on the affected organism due to the redundancy and robustness of the genetic code. However, in rare cases, it can have notable and serious effects on overall health, physical appearance, and other traits. Disorders that most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of the organism's genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |