|
Moritz Wagner (naturalist)
Moritz Wagner (Bayreuth, 3 October 1813 – Munich, 31 May 1887) was a German explorer, collector, geographer and natural historian. Wagner devoted three years (1836–1839) to the exploration of Algiers: it was here that he made important observations in natural history, which he later supplemented and developed: that geographical isolation could play a key role in speciation. From 1852 to 1855, together with Carl Scherzer, Wagner travelled through North and Central America and the Caribbean. In May 1843, Wagner toured the Lake Sevan region of Armenia with Armenian writer Khachatur Abovian. He committed suicide in Munich, aged 73. His brother Rudolf was a physiologist and anatomist. Wagner's significance in evolutionary biology Wagner's early career was as a geographer, and he published a number of geographical books about North Africa, the Middle East, and Tropical America. He was also a keen naturalist and collector, and it is for this work he is best known among biologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Wagner - Geograph Und Naturforscher
Moritz may refer to: *Moritz (name), a given name and surname *Moritz, Germany, a village and a former municipality *Moritz (beer), a Spanish beer brand See also * St. Moritz (other) *Moriz Moriz is a masculine given name which may refer to: * Moriz Haupt (1808–1874), German philologist * Moriz Heider (1816–1866), Austrian dentist * Moriz Henneberger (1878–1959), Swiss chess master * Moriz von Kuffner (1854–1939), Jewish-A ..., a given name and surname * Moric, a given name and surname {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Concept
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes in zoological nomenclature). For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Rensch
Bernhard Rensch (21 January 1900 – 4 April 1990) was a German evolutionary biologist and ornithologist who did field work in Indonesia and India. Starting his scientific career with pro- Lamarckian views, he shifted to selectionism and became one of the architects of the modern synthesis in evolutionary biology, which he popularised in Germany. Besides his work on how environmental factors influenced the evolution of geographically isolated populations and on evolution above the species level, which contributed to the modern synthesis, he also worked extensively in the area of animal behavior (ethology) and on philosophical aspects of biological science. His education and scientific work were interrupted by service in the German military during both World War I and World War II. Biography Rensch was born in Thale and as a young boy, he took an interest in observing the natural world and discovered a talent for drawing and painting. He served in the German army from 1917 to 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Starr Jordan
David Starr Jordan (January 19, 1851 – September 19, 1931) was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford University, he served as president of Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana University from 1885 to 1891. Jordan was also a strong supporter of eugenics, and his published views expressed a fear of "race-degeneration", asserting that cattle and human beings are "governed by the same laws of selection". He was an antimilitarist since he believed that war killed off the best members of the gene pool, and he initially opposed American involvement in World War I. Early life and education Jordan was born in Gainesville (town), New York, Gainesville, New York, and grew up on a farm in upstate New York. His parents made an unorthodox decision to educate him at a local girls' high school. His middle name, Starr, does not appear in early census records, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Origin Of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'')The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''. In the 1872 sixth edition, "On" was omitted, so the full title is ''The origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life.'' This edition is usually known as ''The Origin of Species.'' The 6th is Darwin's final edition; there were minor modifications in the text of certain subsequent issues. See Freeman, R. B. In Van Wyhe, John, ed. ''Darwin Online: On the Origin of Species'', 2002. is a work of scientific literature by Charles Darwin that is considered to be the foundation of evolutionary biology. It was published on 24 November 1859. Darwin's book introduced the scientific theory that p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerry Coyne
Jerry Allen Coyne (born December 30, 1949) is an American biologist and skeptic known for his work on speciation and his commentary on intelligent design. A professor emeritus at the University of Chicago in the Department of Ecology and Evolution, he has published numerous papers on the theory of evolution. His concentration is speciation and ecological and evolutionary genetics, particularly as they involve the fruit fly, '' Drosophila''. In 2023 he became a fellow with the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry. He is the author of the text ''Speciation'' and the bestselling non-fiction book '' Why Evolution Is True''. Coyne maintains a website and writes for his blog, also called ''Why Evolution Is True''. He is a hard determinist. Coyne gained attention outside of the scientific community as a public critic of religion. As a proponent of New Atheism, he is often cited with atheists such as Richard Dawkins and Sam Harris. He is the author of the book '' Faith Versus Fact''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Synthesis (20th Century)
The modern synthesis was the early 20th-century synthesis of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's ideas on Mendelian inheritance, heredity into a joint mathematical framework. Julian Huxley coined the term in his 1942 book, ''Evolution: The Modern Synthesis''. The synthesis combined the ideas of natural selection, Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, and population genetics. It also related the broad-scale macroevolution seen by paleontology, palaeontologists to the small-scale microevolution of local population, populations. The synthesis was defined differently by its founders, with Ernst Mayr in 1959, G. Ledyard Stebbins in 1966, and Theodosius Dobzhansky in 1974 offering differing basic postulates, though they all include natural selection, working on heritable variation supplied by mutation. Other major figures in the synthesis included E. B. Ford, Bernhard Rensch, Ivan Schmalhausen, and George Gaylord Simpson. An early event in the modern synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Weismann
August Friedrich Leopold Weismann (; 17 January 18345 November 1914) was a German evolutionary biology, evolutionary biologist. Fellow German Ernst Mayr ranked him as the second most notable evolutionary theorist of the 19th century, after Charles Darwin. Weismann became the Director of the Zoological Institute and the first Professor of Zoology at University of Freiburg, Freiburg. His main contribution involved germ plasm theory, at one time also known as Weismannism,Romanes, George John. ''An examination of Weismannism''. The Open court publishing company in Chicago 189/ref> according to which inheritance (in a multicellular animal) only takes place by means of the germ cells—the gametes such as egg cells and sperm cells. Other cells of the body—somatic cells—do not function as agents of heredity. The effect is one-way: germ cells produce somatic cells and are not affected by anything the somatic cells learn or therefore any ability an individual acquires during its life. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
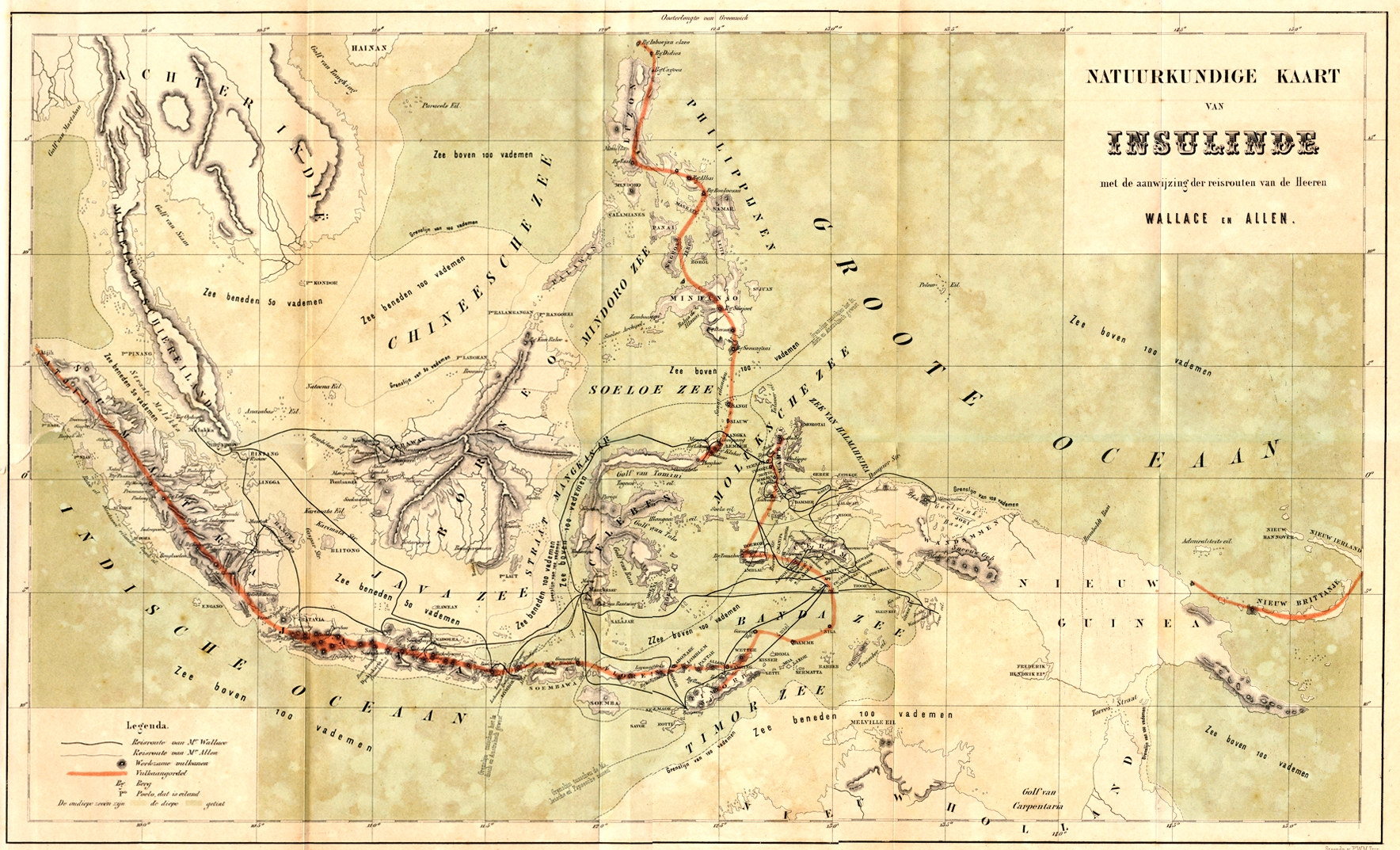
Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 paper on the subject was published that year On the Tendency of Species to form Varieties; and on the Perpetuation of Varieties and Species by Natural Means of Selection, alongside extracts from Charles Darwin's earlier writings on the topic. It spurred Darwin to set aside the Natural Selection (manuscript), "big species book" he was drafting and to quickly write an Abstract (summary), abstract of it, which was published in 1859 as ''On the Origin of Species''. Wallace did extensive fieldwork, starting in the Amazon River basin. He then did fieldwork in the Malay Archipelago, where he identified the faunal divide now termed the Wallace Line, which separates the Indonesian archipelago into two distinct parts: a western portion in which the ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a Common descent, common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental scientific concept. In a joint presentation with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this Phylogenetics, branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding.. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by Burials and memorials in Westminster Abbey, burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh Medical Schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Founder Effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using existing theoretical work by those such as Sewall Wright. As a result of the loss of genetic variation, the new population may be distinctively different, both genotypically and phenotypically, from the parent population from which it is derived. In extreme cases, the founder effect is thought to lead to the speciation and subsequent evolution of new species. In the figure shown, the original population has nearly equal numbers of blue and red individuals. The three smaller founder populations show that one or the other color may predominate (founder effect), due to random sampling of the original population. A population bottleneck may also cause a founder effect, though it is not strictly a new population. The founder effect o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |