|
Model Engine
A model engine is a small internal combustion engine typically used to power a radio-controlled aircraft, radio-controlled car, radio-controlled boat, free flight, control line aircraft, or ground-running tether car model. Because of the square–cube law, the behaviour of many engines does not always scale up or down at the same rate as the machine's size; usually at best causing a dramatic loss of power or efficiency, and at worst causing them not to work at all. Methanol and nitromethane are common fuels. Overview The fully functional, albeit small, engines vary from the most common single-cylinder two-stroke to the exotic single and multiple-cylinder four-stroke, the latter taking shape in boxer, v-twin, inline and radial form, a few Wankel engine designs are also used. Most model engines run on a blend of methanol, nitromethane, and lubricant (either castor or synthetic oil). Two-stroke model engines, most often designed since 1970 with Schnuerle por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Old Cox Babe Bee Engine Dissasembled
Old or OLD may refer to: Places *Old, Baranya, Hungary *Old, Northamptonshire, England *Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD) *OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Maine, United States People *Old (surname) Music *OLD (band), a grindcore/industrial metal group *Old (Danny Brown album), ''Old'' (Danny Brown album), a 2013 album by Danny Brown *Old (Starflyer 59 album), ''Old'' (Starflyer 59 album), a 2003 album by Starflyer 59 *Old (song), "Old" (song), a 1995 song by Machine Head *"Old", a 1982 song by Dexys Midnight Runners from ''Too-Rye-Ay'' Other uses *Old (film), ''Old'' (film), a 2021 American thriller film *''Oxford Latin Dictionary'' *Online dating *Over-Locknut Distance (or Dimension), a measurement of a Bicycle wheel#Construction, bicycle wheel and frame See also *Old age *List of people known as the Old *''Old LP'', a 2019 album by That Dog * * *Olde, a list of people with the surna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
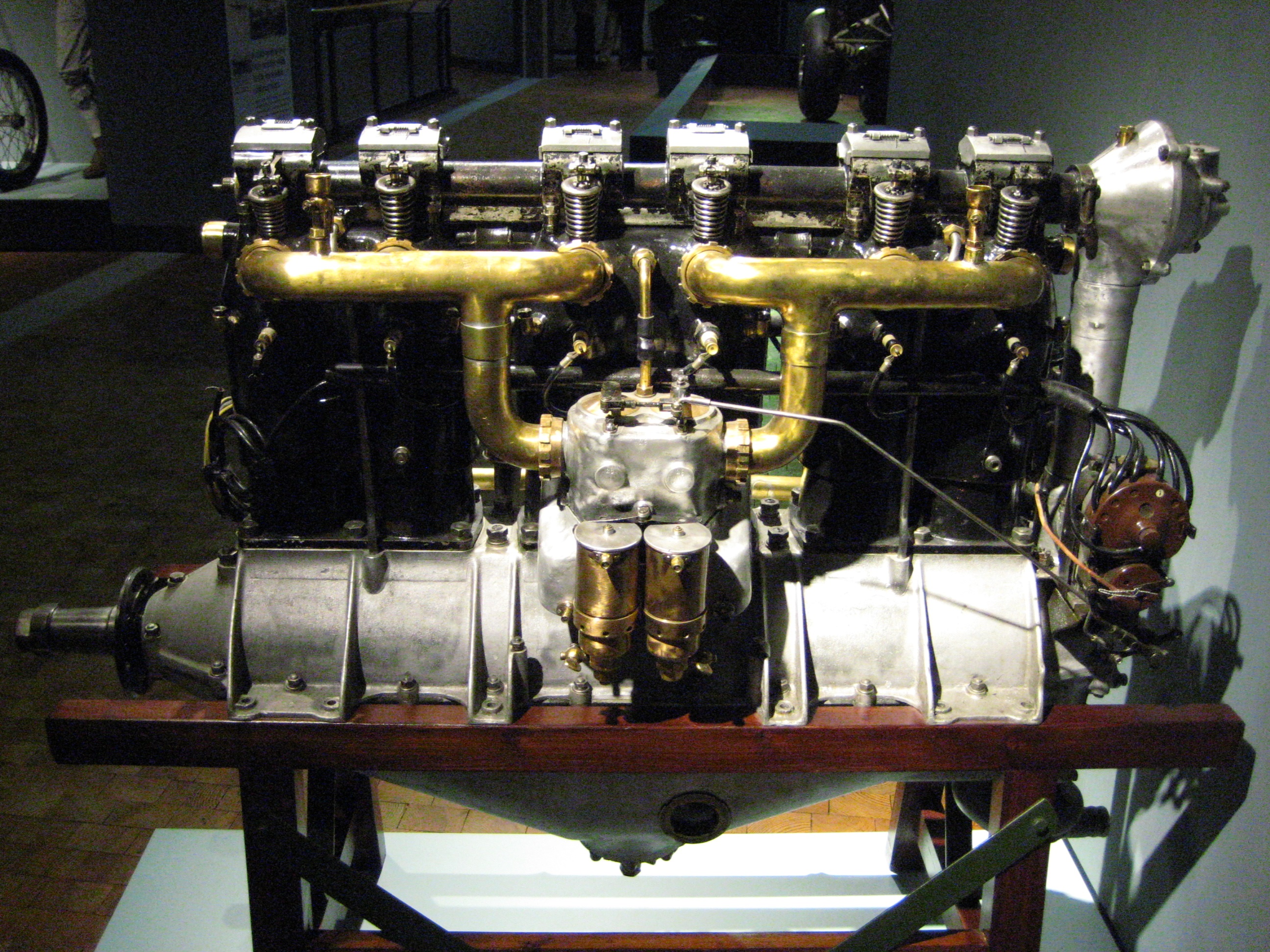
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating engine, reciprocating type internal combustion engine, internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinder (engine), cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized Star polygon, star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Glow Fuel
Glow fuel is a fuel source used in model engines – generally the same or similar fuels can be used in model airplanes, helicopters, cars and boats. Glow fuel can be burned by very simple two-stroke engines or by more complicated four-stroke engines, and these engines can provide impressive amounts of power for their very small size. Glow fuel is primarily for two-stroke engines with the need for oil mixed in the fuel and limited exhaust and fuel/air between cycles. Top Fuel race cars with 4-stroke engines may also use glow fuel, but in this case it does not contain appreciable oil. Name Other commonly used names are nitro or just model fuel. Note that the nitro name is generally inaccurate, as nitromethane is usually not the primary ingredient, and in fact many glow fuels, especially the so-called "FAI" type, named for the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, which requires such fuel in some forms of aeromodeling competition, contain no nitromethane at all. Ingredients Glo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Inline Engine (aeronautics)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ;Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Boxer Engine
A flat engine is a Internal combustion engine#Reciprocating engines, piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, whereby each cylinder has two pistons sharing a central combustion chamber. The most common configuration of flat engines is the #Boxer configuration, boxer engine configuration, in which the pistons of each opposed pair of cylinders move inwards and outwards at the same time. The other configuration is effectively a V engine with a 180-degree angle between the cylinder banks: in this configuration each pair of cylinders shares a single crankpin, so that as one piston moves inward, the other moves outward. The first flat engine (Benz Contramotor) was built in 1897 by Karl Benz. Flat engines have been used in aviation, motorcycle and automobile applications. They are now less common in car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Single-cylinder
A single-cylinder engine, sometimes called a thumper, is a piston engine with one cylinder. This engine is often used for motorcycles, motor scooters, motorized bicycles, go-karts, all-terrain vehicles, radio-controlled vehicles, power tools and garden machinery (such as chainsaws, lawn mowers, cultivators, and string trimmers). Single-cylinder engines are made both as 4-strokes and 2-strokes. Characteristics Compared with multi-cylinder engines, single-cylinder engines are usually simpler and compact. Due to the greater potential for airflow around all sides of the cylinder, air cooling is often more effective for single cylinder engines than multi-cylinder engines. This reduces the weight and complexity of air-cooled single-cylinder engines, compared with liquid-cooled engines. Drawbacks of single-cylinder engines include a more pulsating power delivery through each cycle and higher levels of vibration. The uneven power delivery means that often a single-cylinder engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Four-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: #Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing a partial vacuum (negative pressure) in the cylinder through its downward motion. #Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage. #Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work (physics), energy transfer. The watt is named in honor of James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776, which became fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. \mathrm. In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the imperial horsepower as in "hp" or "bhp" which is about , and the metric horsepower as in "cv" or "PS" which is approximately . The electric horsepower "hpE" is exactly , while the boiler horsepower is 9809.5 or 9811 watts, depending on the exact year. The term was adopted in the late 18th century by Scottish engineer James Watt to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses. It was later expanded to include the output power of other power-generating machinery such as piston engines, turbines, and electric motors. The definition of the unit varied among geographical regions. Most countries now use the SI unit watt for measurement of power. With the implementation of the EU Directive 80/181/EEC on 1 January 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Schnuerle Porting
Schnuerle porting is a system to improve efficiency of a valveless two-stroke engine by giving better scavenging. The intake and exhaust ports cut in the cylinder wall are shaped to give a more efficient transfer of intake and exhaust gases. Description Gas flow within the two-stroke engine is even more critical than for a four-stroke engine, as the exhaust flow exits the chamber as the intake enters simultaneously. A well-defined flow pattern is required, avoiding any turbulent mixing. The efficiency of the two-stroke engine depends on effective scavenging, the more complete replacement of the old spent charge with a fresh charge. Apart from large diesels with separate superchargers, two-stroke engines are generally piston-ported and use their crankcase beneath the piston for compression. The cylinder has a transfer port (inlet from crankcase to cylinder) and an exhaust port cut into it. These are opened, as the piston moves downwards past them; with the higher exhaust po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston, one up and one down, in one revolution of the crankshaft in contrast to a four-stroke engine which requires four strokes of the piston in two crankshaft revolutions to complete a power cycle. During the stroke from bottom dead center to top dead center, the end of the exhaust/intake (or scavenging) is completed along with the compression of the mixture. The second stroke encompasses the combustion of the mixture, the expansion of the burnt mixture and, near bottom dead center, the beginning of the scavenging flows. Two-stroke engines often have a higher power-to-weight ratio than a four-stroke engine, since their power stroke occurs twice as often. Two-stroke engines can also have fewer moving parts, and thus be cheaper to manufacture and weigh less. In countries and regions with stringent emissions regulation, two-stroke engines have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Synthetic Oil
Synthetic oil is a lubricant consisting of chemical compounds that are artificially modified or synthesised. Synthetic oil is used as a substitute for petroleum-refined oils when operating in extreme temperature, in metal stamping to provide environmental and other benefits, and to lubricate pendulum clocks. There are various types of synthetic oils. Advantages of using synthetic motor oils include better low-and high-temperature viscosity performance, better (higher) viscosity index (VI), and chemical and shear stability, while disadvantages are that synthetics are substantially more expensive (per volume) than mineral oils and have potential decomposition problems. Description Synthetic oil lubricant comprises chemical compounds that are artificially modified or synthesised. Synthetic lubricants can be manufactured using chemically modified petroleum components rather than whole crude oil, but can also be synthesized from other raw materials. The base material, however, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |