|
Modal Adverbs
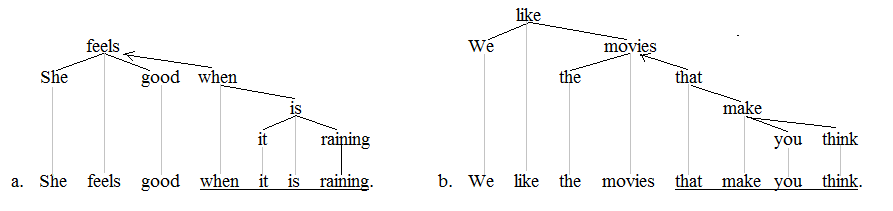
Modal adverbs are adverbs, such as ''probably'', ''necessarily'', and ''possibly'' that express modality, i.e., possibility, necessity, or contingency. In English ''The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language'' provides the following non-exhaustive list of modal adverbs at different levels of strength. Strong: ''assuredly'', ''certainly'', ''clearly'', ''definitely'', ''incontestably'', ''indubitably'', ''ineluctably'', ''inescapably'', ''manifestly'', ''necessarily'', ''obviously'', ''patently'', ''plainly'', ''surely'', ''truly'', ''unarguably'', ''unavoidably'', ''undeniably'', ''undoubtedly'', ''unquestionably'' Quasi-strong: ''apparently'', ''doubtless'', ''evidently'', ''presumably'', ''seemingly'' Medium: ''arguably'', ''likely'', ''probably'' Weak: ''conceivably'', ''maybe'', ''perhaps'', ''possibly'' Syntax and meaning Modal adverbs often appear as clause-initial adjuncts, and have scope over the whole clause, as in (1) with the adverb in bold. # ''Probably, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverb
An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by answering questions such as ''how'', ''in what way'', ''when'', ''where'', ''to what extent''. This is called the adverbial function and may be performed by an individual adverb, by an adverbial phrase, or by an adverbial clause. Adverbs are traditionally regarded as one of the parts of speech. Modern linguists note that the term ''adverb'' has come to be used as a kind of "catch-all" category, used to classify words with various types of syntactic behavior, not necessarily having much in common except that they do not fit into any of the other available categories (noun, adjective, preposition, etc.). Functions The English word ''adverb'' derives (through French) from Latin ''adverbium'', from ''ad-'' ('to'), ''verbum'' ('word', 'ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modality (linguistics)
In linguistics and philosophy, modality refers to the ways language can express various relationships to reality or truth. For instance, a modal expression may convey that something is likely, desirable, or permissible. Quintessential modal expressions include modal auxiliaries such as "could", "should", or "must"; modal adverbs such as "possibly" or "necessarily"; and modal adjectives such as "conceivable" or "probable". However, modal components have been identified in the meanings of countless natural language expressions, including counterfactuals, propositional attitudes, evidentials, habituals, and generics. Modality has been intensely studied from a variety of perspectives. Within linguistics, typological studies have traced crosslinguistic variation in the strategies used to mark modality, with a particular focus on its interaction with tense–aspect–mood marking. Theoretical linguists have sought to analyze both the propositional content and discourse effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cambridge Grammar Of The English Language
''The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language'' (''CamGEL''The abbreviation ''CamGEL'' is less commonly used for the work than is ''CGEL'' (and the authors themselves use ''CGEL'' in their other works), but ''CGEL'' is ambiguous because it has also often been used for the earlier work ''A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language''. This article uses the unambiguous form.) is a descriptive grammar of the English language. Its primary authors are Rodney Huddleston and Geoffrey K. Pullum. Huddleston was the only author to work on every chapter. It was published by Cambridge University Press in 2002 and has been cited more than 8,000 times. Background In 1988, Huddleston published a very critical review of the 1985 book ''A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language''. He wrote: [T]here are some respects in which it is seriously flawed and disappointing. A number of quite basic categories and concepts do not seem to have been thought through with sufficient care; this re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjunct (grammar)
In linguistics, an adjunct is an optional, or ''structurally dispensable'', part of a sentence, clause, or phrase that, if removed or discarded, will not structurally affect the remainder of the sentence. Example: In the sentence ''John helped Bill in Central Park'', the phrase ''in Central Park'' is an adjunct.See Lyons (1968). A more detailed definition of the adjunct emphasizes its attribute as a modifying form, word, or phrase that depends on another form, word, or phrase, being an element of clause structure with adverbial function. An adjunct is not an argument (linguistics), argument (nor is it a predicative expression), and an argument is not an adjunct. The argument–adjunct distinction is central in most theories of syntax and semantics. The terminology used to denote arguments and adjuncts can vary depending on the theory at hand. Some dependency grammars, for instance, employ the term ''circonstant'' (instead of ''adjunct''), following Lucien Tesnière, Tesnière (195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scope (formal Semantics)
In formal semantics (linguistics), formal semantics, the scope of a semantic operator is the semantic object to which it applies. For instance, in the sentence "''Paulina doesn't drink beer but she does drink wine''," the proposition that Paulina drinks beer occurs within the scope of negation, but the proposition that Paulina drinks wine does not. Scope can be thought of as the semantic order of operations. One of the major concerns of research in formal semantics is the relationship between operators' syntax, syntactic positions and their semantic scope. This relationship is not transparent, since the scope of an operator need not directly correspond to its Deep structure and surface structure, surface position and a single surface form can be semantic ambiguity, semantically ambiguous between different scope construals. Some theories of scope posit a level of syntactic structure called Logical form (linguistics), logical form, in which an item's syntactic position corresponds t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Adjective
Modal adjectives are adjectives, such as ''likely'', ''probable'' and ''necessary'', that express modality, i.e., possibility, necessity, or contingency. In English Modal adjectives can express modality regarding a situation or a participant in that situation. With situations, some usual syntactic patterns include an extraposed subject, such as the underlined elements in the following examples with the modal adjective in bold. Here the modal adjective is analyzed semantically as a sentential modal operator. # ''It's possible that some of them are broken.'' # ''It's likely that they will come.'' # ''It is necessary'' (''for us'') ''to make a choice''''.'' For participants, however, the usual syntactic construction has the adjective phrase in attributive modifier function, as in the following examples, where the modal adjective is again in bold and this time the participant in underlined. # ''We've found a potential replacement.'' # ''They need to file the necessary papers.'' # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb ( abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause. An example is the verb ''have'' in the sentence ''I have finished my lunch.'' Here, the auxiliary ''have'' helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, ''finished''. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or (verbal) auxiliaries. Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Basic examples Below are some sentences that contain representative auxiliary verbs from English, Spanish, German and French, with the auxiliary verb marked in bold: ::a. Do you want tea? – ''do'' is an auxiliary accompanying the infinitive, ''want'', used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Verb
In linguistics a lexical verb or main verb is a member of an open class of verbs that includes all verbs except auxiliary verbs. Lexical verbs typically express action, state, or other predicate meaning. In contrast, auxiliary verbs express grammatical meaning. The verb phrase of a sentence is generally headed by a lexical verb. Lexical verbs are categorized into five categories: copular, intransitive, transitive, ditransitive, and ambitransitive. The descriptor ''lexical'' is applied to the words of a language's lexicon A lexicon (plural: lexicons, rarely lexica) is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Greek word () ..., often to indicate a content word, as distinct from a function word. See also * Light verb References {{lexical categories, state=collapsed Verb types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Word
Modal words are words in a language that express modality, i.e., possibility, necessity, or contingency. One kind of modal word is the modal verb A modal verb is a type of verb that contextually indicates a modality such as a ''likelihood'', ''ability'', ''permission'', ''request'', ''capacity'', ''suggestion'', ''order'', ''obligation'', ''necessity'', ''possibility'' or ''advice''. Modal v ... (''should'', ''can'', ''might'', and ''ought'', as well as ''oblige'', ''need'', and ''require''). Other types of modal words in English include modal adjectives (''likely'', ''probable'', ''necessary''), modal adverbs (''probably'', ''perhaps'', ''certainly''), modal prepositions (''despite'', ''unless'', ''if''), and modal nouns (''possibility'', ''probability'', ''certainty''). References Linguistics Semantics Words {{authority control, qid=Q123236362 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |