|
Mixed Oxides Of Nitrogen
Mixed oxides of nitrogen (MON) are solutions of dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3) in dinitrogen tetroxide/nitrogen dioxide (N2O4 and NO2). It may be used as an oxidizing agent in rocket propulsion systems. Mixed oxides of nitrogen are produced by dissolving nitric oxide (NO) gas in liquid dinitrogen tetroxide. Nitric oxide reacts with nitrogen dioxide, present in dinitrogen tetroxide, to from dinitrogen trioxide. Resulting mixture is greenish blue, while dinitrogen tetroxide is colorless or brownish yellow. Liquid phase of MON contains no nitric oxide. A broad range of compositions is available, and can be denoted as MON''i'', where ''i'' represents the percentage of nitric oxide in the mixture (e.g. MON3 contains 3% nitric oxide, MON25 25% nitric oxide). An upper limit is MON40 (40% by weight). In Europe MON 1.3 is mostly used for rocket propulsion systems, while NASA seems to prefer MON 3. A higher percentage of NO decreases the corrosiveness of the liquid, but decreases oxidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
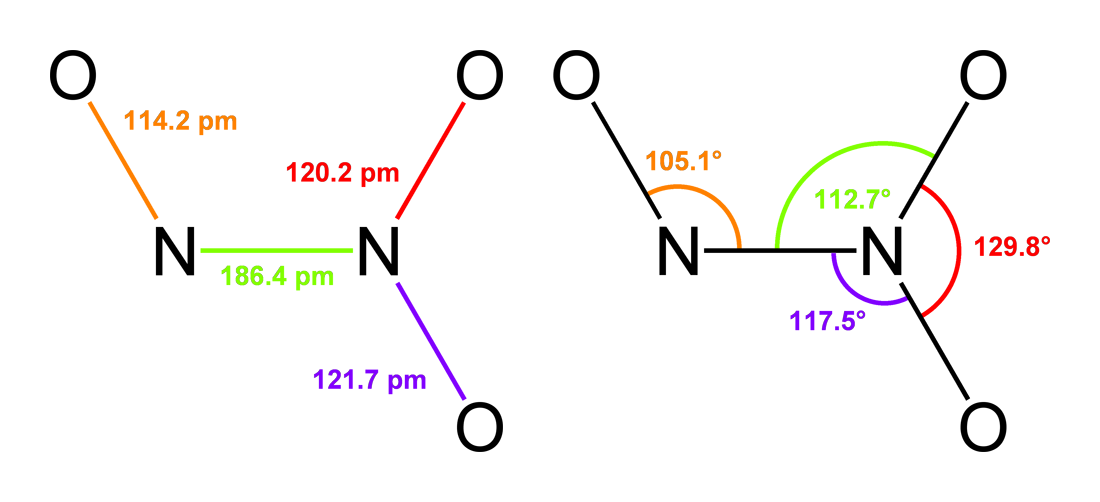
Dinitrogen Trioxide
Dinitrogen trioxide (also known as nitrous anhydride) is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a nitrogen oxide. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21°C (−6°F): : + Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures (i.e., in the liquid and solid phases). In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color. At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with ''KD'' = 193 kPa (25°C). This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical . Structure and bonding Dinitrogen trioxide molecule contains an N–N bond. One of the numerous resonant structures of the molecule of dinitrogen trioxide is , which can be described as a nitroso group attached to a nitro group by a single bond between the two nitrogen atoms. This isomer is considered as the "anhydride" of the unstable nitrous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russian rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. Its molar mass is 92.011 g/mol. Dinitrogen tetroxide is a powerful oxidizer that is hypergolic (spontaneously reacts) upon contact with various forms of hydrazine, which has made the pair a common bipropellant for rockets. Structure and properties Dinitrogen tetroxide could be regarded as two nitro groups (-NO2) bonded together. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. The molecule is planar with an N-N bond distance of 1.78Å and N-O distances of 1.19Å. The N-N distance corresponds to a weak bond, since it is significantly longer than the average N-N single bond length of 1.45Å. This exceptionally weak σ bond (amounting to overlapping of the ''sp''2 hybrid orbitals of the two NO2 uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, is an intermediate in the synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year, primarily for the production of fertilizers. Nitrogen dioxide is poisonous and can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Cooking with a gas stove produces nitrogen dioxide which causes poorer indoor air quality. Combustion of gas can lead to increased concentrations of nitrogen dioxide throughout the home environment which is linked to respiratory issues and diseases. The LC50 ( median lethal dose) for humans has been estimated to be 174 ppm for a 1-hour exposure. It is also included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above and becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizing Agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Propulsion
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to Acceleration, accelerate without using any surrounding Atmosphere of Earth, air. A rocket engine produces thrust by Reaction (physics), reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from rocket propellant, propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with Airbreathing jet engine, airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, Reaction control system, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, Reaction wheel, momentum wheels, Thrust vectoring, deflection of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Technical Information Center
The Defense Technical Information Center (DTIC, ) is the repository for research and engineering information for the United States Department of Defense (DoD). DTIC's services are available to DoD personnel, federal government personnel, federal contractors and selected academic institutions. The general public can access unclassified information through its public website. History The DTIC traces its history to the June 1945 formation of the Air Documents Research Center (ADRC), a joint effort of the US Army Air Force, US Navy and Royal Air Force to build a single collection of captured German aeronautical research, based in London. The ADRC was initially tasked with the sorting of the document collection into three broad groups; documents that would assist the war in the Pacific theater, documents of immediate intelligence interest to the United States or British forces and documents of interest for future research. With the ending of the war in 1945, the ADRC moved to Wrig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the " Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Its impact extends beyond biology, with applications in medicine, such as the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metal in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen, hydrogen, or hydroxide. Rusting, the formation of red-orange iron oxides, is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion. This type of corrosion typically produces oxides or salts of the original metal and results in a distinctive coloration. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as ceramics or polymers, although in this context, the term "degradation" is more common. Corrosion degrades the useful properties of materials and structures including mechanical strength, appearance, and permeability to liquids and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freezing Point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilibrium, equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at a Standard temperature and pressure, standard pressure such as 1 Atmosphere (unit), atmosphere or 100 Pascal (unit), kPa. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point. Because of the ability of substances to Supercooling, supercool, the freezing point can easily appear to be below its actual value. When the "characteristic freezing point" of a substance is determined, in fact, the actual methodology is almost always "the principle of observing the disappearance rather than the formation of ice, that is, the #Melting point measurements, melting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Mixtures
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bonded to a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Compounds
The chemical element nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements in the universe and can form many compounds. It can take several oxidation states; but the most common oxidation states are −3 and +3. Nitrogen can form nitride and nitrate ions. It also forms a part of nitric acid and nitrate salts. Nitrogen compounds also have an important role in organic chemistry, as nitrogen is part of proteins, amino acids and adenosine triphosphate. Dinitrogen complexes The first example of a dinitrogen complex to be discovered was u(NH3)5(N2)sup>2+ (see figure at right), and soon many other such complexes were discovered. These complexes, in which a nitrogen molecule donates at least one lone pair of electrons to a central metal cation, illustrate how N2 might bind to the metal(s) in nitrogenase and the catalyst for the Haber process: these processes involving dinitrogen activation are vitally important in biology and in the production of fertilisers. Dinitrogen is able to coordinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Oxides
In atmospheric chemistry, is shorthand for nitric oxide () and nitrogen dioxide (), the nitrogen oxides that are most relevant for air pollution. These gases contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, as well as affecting tropospheric ozone. gases are usually produced from the reaction between nitrogen and oxygen during combustion of fuels, such as hydrocarbons, in air; especially at high temperatures, such as in car engines. In areas of high motor vehicle traffic, such as in large cities, the nitrogen oxides emitted can be a significant source of air pollution. gases are also produced naturally by lightning. does not include nitrous oxide (), a fairly inert oxide of nitrogen that contributes less severely to air pollution, notwithstanding its involvement in ozone depletion and high global warming potential. is the class of compounds comprising and the compounds produced from the oxidation of which include nitric acid, nitrous acid (HONO), din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |