|
Minimalist Program
In linguistics, the minimalist program is a major line of inquiry that has been developing inside generative grammar since the early 1990s, starting with a 1993 paper by Noam Chomsky. Following Imre Lakatos's distinction, Chomsky presents minimalism as a research program, program, understood as a mode of inquiry that provides a conceptual framework which guides the development of linguistic theory. As such, it is characterized by a broad and diverse range of research directions. For Chomsky, there are two basic Minimalist grammar, minimalist questions—What is language? and Why does it have the properties it has?—but the answers to these two questions can be framed in any theory.Boeckx, Cedric ''Linguistic Minimalism. Origins, Concepts, Methods and Aims'', pp. 84 and 115. Conceptual framework Goals and assumptions Minimalism is an approach developed with the goal of understanding the nature of language. It models a speaker's knowledge of language as a computational syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonetic Form
In the field of linguistics, specifically in syntax, phonetic form (PF), also known as phonological form or the articulatory-perceptual (A-P) system, is a certain level of mental representation of a linguistic expression, derived from surface structure, and related to Logical Form. Phonetic form is the level of representation wherein expressions, or sentences, are assigned a phonetic representation, which is then pronounced by the speaker. Phonetic form takes surface structure as its input, and outputs an audible (or visual, in the case of sign languages), pronounced sentence. This is part of the Y- or T-model of grammar within minimalist grammar, wherein the syntactic structure is constructed and then transferred (called spell-out) to both the Phonetic Form and the Logical Form. Operations in this branch of the model (between spell-out and pronunciation), the syntax-phonology interface, affect the pronunciation of the utterance but not its meaning. Within distributed morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalist Program
In linguistics, the minimalist program is a major line of inquiry that has been developing inside generative grammar since the early 1990s, starting with a 1993 paper by Noam Chomsky. Following Imre Lakatos's distinction, Chomsky presents minimalism as a research program, program, understood as a mode of inquiry that provides a conceptual framework which guides the development of linguistic theory. As such, it is characterized by a broad and diverse range of research directions. For Chomsky, there are two basic Minimalist grammar, minimalist questions—What is language? and Why does it have the properties it has?—but the answers to these two questions can be framed in any theory.Boeckx, Cedric ''Linguistic Minimalism. Origins, Concepts, Methods and Aims'', pp. 84 and 115. Conceptual framework Goals and assumptions Minimalism is an approach developed with the goal of understanding the nature of language. It models a speaker's knowledge of language as a computational syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
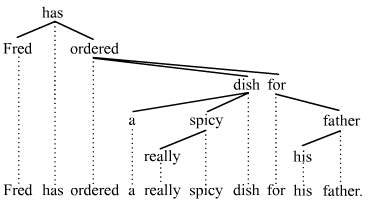
Move α
Move α is a feature of many transformational-generative grammars, first developed in the Revised Extended Standard Theory (REST) by Noam Chomsky in the late 1970s and later part of government and binding theory (GB) in the 1980s and the Minimalist Program of the 1990s. The term refers to the relation between an indexed constituent and its trace ''t'', e.g., the relation of ''whom'' and ''t'' in the example :(1) Whomi do you think you are kidding ti? In (1), the constituent (''whom'') and its trace (''t'') are said to form a "chain". In syntax, Move α is the most general formulation of possible movement permitted by a rule. More specific rules include Move NP and Move wh, which in turn are more general than specific transformations such as those involved in passivization. This marks a shift of attention in transformational grammar around the 1970s, away from focussing on specific rules to underlying principles constraining them, which culminated into the development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merge (linguistics)
Merge is one of the basic operations in the Minimalist Program, a leading approach to generative syntax, when two syntactic objects are combined to form a new syntactic unit (a Set (mathematics), set). Merge also has the property of recursion in that it may be applied to its own output: the objects combined by Merge are either lexical items or sets that were themselves formed by Merge. This recursive property of Merge has been claimed to be a fundamental characteristic that distinguishes language from other cognitive faculties. As Noam Chomsky (1999) puts it, Merge is "an indispensable operation of a recursive system ... which takes two syntactic objects A and B and forms the new object G=" (p. 2). Mechanisms of Merge Within the Minimalist Program, syntax is derivational, and Merge is the structure-building operation. Merge is assumed to have certain formal properties constraining syntactic structure, and is implemented with specific mechanisms. In terms of a merge-base th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government (linguistics)
In grammar and theoretical linguistics, government or rection refers to the relationship between a word and its dependents. One can discern between at least three concepts of government: the traditional notion of case government, the highly specialized definition of government in some generative models of syntax, and a much broader notion in dependency grammars. Traditional case government In traditional Latin and Greek (and other) grammars, government is the control by verbs and prepositions of the selection of grammatical features of other words. Most commonly, a verb or preposition is said to "govern" a specific grammatical case if its complement must take that case in a grammatically correct structure (see: case government). For example, in Latin, most transitive verbs require their direct object to appear in the accusative case, while the dative case is reserved for indirect objects. Thus, the phrase ''I see you'' would be rendered as ''Te video'' in Latin, using the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-bar Theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase structure and a theory of syntactic category formation that proposes a universal schema for how phrases are organized. It suggests that all phrases share a common underlying structure, regardless of their specific category (noun phrase, verb phrase, etc.). This structure, known as the X-bar schema, is based on the idea that every phrase (XP, X phrase) has a Head (linguistics), head, which determines the type (syntactic category) of the phrase (X). The theory was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ''Reading in English Transformational Grammar'', 184–221. Waltham: Ginn. reformulating the ideas of Zellig Harris (1951), and further developed by Ray Jackendoff (1974, 1977a, 1977bJackendoff, Ray (1977b) Constraints on Phrase Structure Rules, in P. W. Culicover, T. Wasow & A. Akmajian (eds.), ''Formal Syntax'', Academic Press, New York, pp. 249– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Structure And Surface Structure
Deep structure and surface structure (also D-structure and S-structure although those abbreviated forms are sometimes used with distinct meanings) are concepts used in linguistics, specifically in the study of syntax in the Chomskyan tradition of transformational generative grammar. The deep structure of a linguistic expression is a theoretical construct that seeks to unify several related structures. For example, the sentences "Pat loves Chris" and "Chris is loved by Pat" mean roughly the same thing and use similar words. Some linguists, Chomsky in particular, have tried to account for this similarity by positing that these two sentences are distinct ''surface forms'' that derive from a common (or very similar) deep structure. Origin Chomsky coined and popularized the terms "deep structure" and "surface structure" in the early 1960s. American linguist Sydney Lamb wrote in 1975 that Chomsky "probably orrowedthe term from Hockett". American linguist Charles Hockett first use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Psychology
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult development, aging, and the entire lifespan. Developmental psychologists aim to explain how thinking, feeling, and behaviors change throughout life. This field examines change across three major dimensions, which are physical development, cognitive development, and social emotional development. Within these three dimensions are a broad range of topics including motor skills, executive functions, moral understanding, language acquisition, social change, personality, emotional development, self-concept, and identity formation. Developmental psychology examines the influences of nature ''and'' nurture on the process of human development, as well as processes of change in context across time. Many researchers are interested in the interactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformational Grammar
In linguistics, transformational grammar (TG) or transformational-generative grammar (TGG) was the earliest model of grammar proposed within the research tradition of generative grammar. Like current generative theories, it treated grammar as a system of formal rules that generate all and only grammatical sentences of a given language. What was distinctive about transformational grammar was that it posited transformation rules that mapped a sentence's deep structure to its pronounced form. For example, in many variants of transformational grammar, the English active voice sentence "Emma saw Daisy" and its passive counterpart "Daisy was seen by Emma" share a common deep structure generated by phrase structure rules, differing only in that the latter's structure is modified by a passivization transformation rule. Basic mechanisms Transformational grammar was a species of generative grammar and shared many of its goals and postulations, including the notion of linguistics as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand De Saussure
Ferdinand Mongin de Saussure (; ; 26 November 185722 February 1913) was a Swiss linguist, semiotician and philosopher. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiotics in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders (together with Charles Sanders Peirce) of semiotics, or ''semiology'', as Saussure called it. One of his translators, Roy Harris, summarized Saussure's contribution to linguistics and the study of "the whole range of human sciences. It is particularly marked in linguistics, philosophy, psychoanalysis, psychology, sociology and anthropology." Although they have undergone extension and critique over time, the dimensions of organization introduced by Saussure continue to inform contemporary approaches to the phenomenon of language. As Leonard Bloomfield stated after reviewing Saussure's work: "he has given us the theoretical basis for a science of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
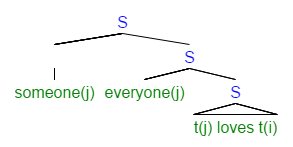
Logical Form (linguistics)
In generative grammar and related approaches, the logical form (LF) of a linguistic expression is the variant of its syntactic structure which undergoes formal semantics (linguistics), semantic interpretation. It is distinguished from ''phonetic form'', the structure which corresponds to a sentence's pronunciation. These separate mental representation, representations are postulated in order to explain the ways in which an expression's meaning can be partially independent of its pronunciation, e.g. scope (formal semantics)#Scope ambiguity, scope ambiguities. LF is the cornerstone of the classic generative view of the syntax-semantics interface. However, it is not used in Lexical Functional Grammar and Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar, as well as some modern variants of the generative approach. Syntax interfacing with semantics The notion of Logical Form was originally invented for the purpose of determining Quantifier (linguistics), quantifier scope. As the theory around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |