|
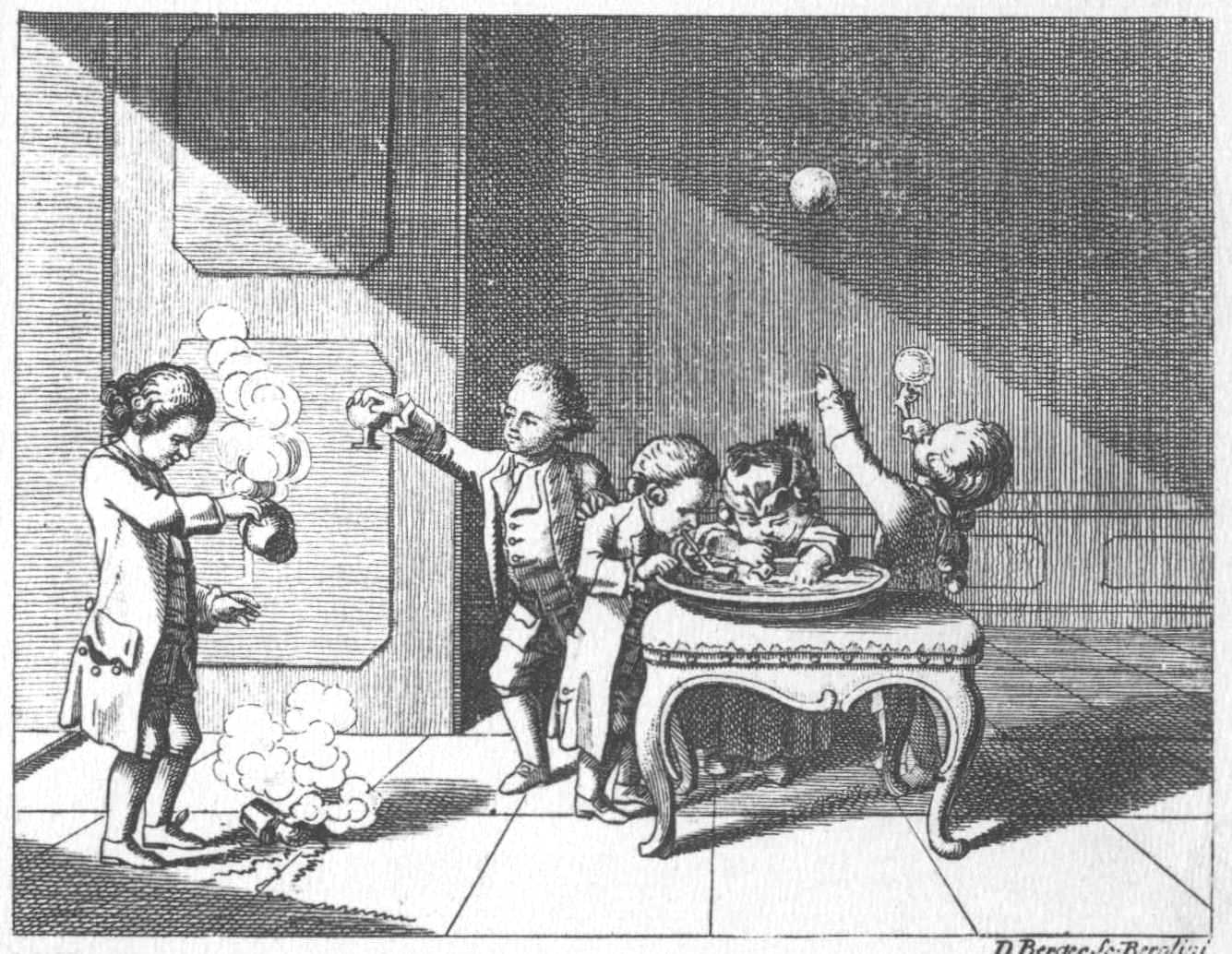
Microscale Chemistry
Microscale chemistry (often referred to as small-scale chemistry, in German: Chemie im Mikromaßstab) is an analytical method and also a teaching method widely used at school and at university levels, working with small quantities of chemical substance A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be com ...s. While much of traditional chemistry teaching centers on multi-gramme preparations, milligrammes of substances are sufficient for microscale chemistry. In universities, modern and expensive lab glassware is used and modern methods for detection and characterization of the produced substances are very common. In schools and in many countries of the Southern hemisphere, small-scale working takes place with low-cost and even no-cost material. There has always been a place for small-sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative inorganic analysis, Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while Quantitative analysis (chemistry), quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemistry, wet chemical methods and modern analytical techniques. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as Precipitation (chemistry), precipitation, Extraction (chemistry), extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teaching Method
A teaching method is a set of principles and methods used by teachers to enable student learning. These strategies are determined partly by the subject matter to be taught, partly by the relative expertise of the learners, and partly by constraints caused by the learning environment. For a particular teaching method to be appropriate and efficient it has to take into account the learner, the nature of the subject matter, and the type of learning it is supposed to bring about. The approaches for teaching can be broadly classified into teacher-centered and student-centered, but in practice teachers will often adapt instruction by moving back and forth between these methodologies depending on learner prior knowledge, learner expertise, and the desired learning objectives. In a teacher-centered approach to learning, teachers are the main authority figure in this model. Students are viewed as "empty vessels" whose primary role is to passively receive information (via lectures and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsory education, compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools that can be built and operated by both government and private organization. The names for these schools vary by country (discussed in the ''School#Regional terms, Regional terms'' section below) but generally include primary school for young children and secondary school for teenagers who have completed primary education. An institution where higher education is taught is commonly called a university college or university. In addition to these core schools, students in a given country may also attend schools before and after primary (elementary in the U.S.) and secondary (middle scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church, Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or field observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context. Qualitative research is often used to explore complex phenomena or to gain insight into people's experiences and perspectives on a particular topic. It is particularly useful when researchers want to understand the meaning that people attach to their experiences or when they want to uncover the underlying reasons for people's behavior. Qualitative methods include ethnography, grounded theory, discourse analysis, and interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative research methods have been used in sociology, anthropology, political science, psychology, communication studies, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteur Pipette
An eye dropper, also called Pasteur pipette or simply dropper, is a device used to transfer small quantities of liquids. They are used in the laboratory and also to dispense small amounts of liquid medicines. A very common use is to dispense eye drops into the eye. The commonly recognized form is a glass tube tapered to a narrow point (a pipette) and fitted with a rubber bulb at the top, although many styles of both plastic and glass droppers exist. The combination of the pipette and rubber bulb has also been referred to as a teat pipette. The ''Pasteur pipette'' name is from the French scientist Louis Pasteur, who used a variant of them extensively during his research. In the past, there was no equipment to transfer a chemical solution without exposing it to the external environment. The hygiene and purity of chemical compounds is necessary for the expected result of each experiment. The eye dropper, both glass and plastic types, can be sterilized and plugged with a rubber bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microanalysis
Microanalysis is the chemical identification and quantitative analysis of very small amounts of chemical substances (generally less than 10 mg or 1 ml) or very small surfaces of material (generally less than 1 cm2). One of the pioneers in the microanalysis of chemical elements was the Slovenian-Austrian Nobel Prize winner Fritz Pregl.http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1923/index.html ''The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1923''. Nobelprize.org. Retrieved 2014-08-06 Methods The most known methods used in microanalysis include: * Most of the spectroscopy methods: ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray fluorescence, Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry * Most of the chromatography methods : high-performance liquid chromatography, Gel permeation chromatography; * Some thermal analysis methods: differential scanning calorimetry, thermogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microreactor
A microreactor or microstructured reactor or microchannel reactor is a device in which chemical reactions take place in a confinement with typical lateral dimensions below 1 mm; the most typical form of such confinement are microchannels. Microreactors are studied in the field of micro process engineering, together with other devices (such as micro heat exchangers) in which physical processes occur. The microreactor is usually a continuous flow reactor (contrast with/to a batch reactor). Microreactors can offer many advantages over conventional scale reactors, including improvements in energy efficiency, reaction speed and yield, safety, reliability, scalability, on-site/on-demand production, and a much finer degree of process control. History Gas-phase microreactors have a long history but those involving liquids started to appear in the late 1990s. One of the first microreactors with embedded high performance heat exchangers were made in the early 1990s by the Central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry Education
Chemistry education (or chemical education) is the study of teaching and learning chemistry. It is one subset of STEM education or discipline-based education research (DBER). Topics in chemistry education include understanding how students learn chemistry and determining the most efficient methods to teach chemistry. There is a constant need to improve chemistry curricula and learning outcomes based on findings of chemistry education research (CER). Chemistry education can be improved by changing teaching methods and providing appropriate training to chemistry instructors, within many modes, including classroom lectures, demonstrations, and laboratory activities. Importance Chemistry education is important because the field of chemistry is fundamental to our world. The universe is subject to the laws of chemistry, while human beings depend on the orderly progress of chemical reactions within their bodies. Described as the central science, chemistry connects physical sciences w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |