|
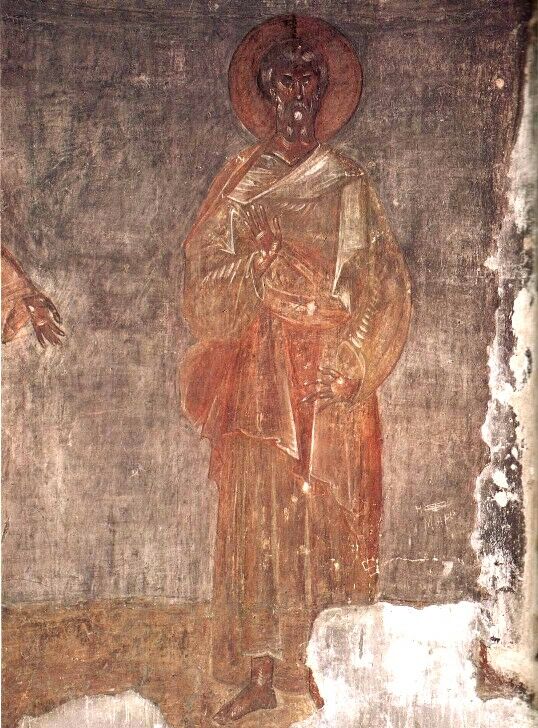
Methuselah
Methuselah (; ''Məṯūšélaḥ'', in pausa ''Məṯūšālaḥ'', "His death shall send" or "Man of the javelin" or "Death of sword"; ''Mathousalas'') was a biblical patriarch and a figure in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He is claimed to have lived the longest life, dying at 969 years of age. According to the Book of Genesis, Methuselah was the son of Enoch, the father of Lamech, and the grandfather of Noah. Elsewhere in the Bible, Methuselah is mentioned in genealogies in 1 Chronicles and the Gospel of Luke. His life is described in further detail in other texts such as the Book of Enoch, Slavonic Enoch, and the Book of Moses. Bible commentators have offered various explanations as to why the Book of Genesis describes him as having died at such an advanced age; some believe that Methuselah's age is the result of a mistranslation, while others believe that his age is used to give the impression that part of Genesis takes place in a very distant past. Methusel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogies Of Genesis
The genealogies of Genesis provide the framework around which the Book of Genesis is structured. Beginning with Adam, genealogical material in Genesis 4, 5, 10, 11, 22, 25, 29–30, 35–36, and 46 moves the narrative forward from the creation to the beginnings of the Israelites' existence as a people. Adam's lineage in Genesis contains two branches: Chapter 4 giving the descendants of Cain, and Chapter 5 that for Seth that is then continued in later chapters. Chapter 10 gives the Generations of Noah (also called the Table of Nations) that records the populating of the Earth by Noah's descendants, and is not strictly a genealogy but an ethnography. Genesis 5 and Genesis 11 include the age at which each patriarch had the progeny named as well as the number of years he lived thereafter. Many of the ages given in the text are long, but could have been considered modest in comparison to the ages given in other works (for instance, the Sumerian King List). The ages include patterns s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogies In The Bible
There are various genealogies described in the Bible. Genesis The book of Genesis records the descendants of Adam and Eve. The enumerated genealogy in chapters 4, 5, and 11, reports the lineal male descent to Abraham, including the age at which each patriarch fathered his named son and the number of years he lived thereafter. The genealogy for Cain is given in chapter 4, and the genealogy for Seth is in chapter 5. The genealogy in chapter 10, recording the male descendants of Noah, is known as the ''Table of Nations''. Family tree of Adam Table of Nations The Table of Nations is an extensive list of descendants of Noah found in chapter 10 of the Book of Genesis, representing an ethnology from an Iron Age Levantine perspective. Family tree of Abraham Family tree of Levi Genealogy of Jesus in the New Testament The New Testament provides two accounts of the genealogy of Jesus, one in the Gospel of Matthew and another in the Gospel of Luke. Matthew starts with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamech (father Of Noah)
Lamech (; ''Lemeḵ'', in pausa ''Lāmeḵ''; ''Lámekh'') was a patriarch in the genealogies of Adam in the Book of Genesis. He is part of the genealogy of Jesus in Luke 3:36. Lamech (Arabic: لامك, romanized: ''Lāmik'') is also mentioned in Islam in the various collections of tales of the prophets who preceded Muhammad, which mentions him in an identical manner. Bible narrative Biblical genealogy Lamech is the eighth-generation descendant of Adam (), the son of Methuselah, and the father of Noah (), in the genealogy of Seth in Genesis 5. In Genesis 5:12-25, Lamech was a son of Methuselah, who was a grandson of Jared, who was a grandson of Kenan descended from Adam. Genesis 5:28–31 records that Lamech was 182 (according to the Masoretic Text; 188 according to the Septuagint) years old at the birth of Noah and lived for another 595 years, attaining an age at death of 777 years, five years before the Flood in the Masoretic chronology. With such numbers in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Enoch
The Book of Enoch (also 1 Enoch; Hebrew language, Hebrew: סֵפֶר חֲנוֹךְ, ''Sēfer Ḥănōḵ''; , ) is an Second Temple Judaism, ancient Jewish Apocalyptic literature, apocalyptic religious text, ascribed by tradition to the Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Enoch who was the father of Methuselah and the great-grandfather of Noah..Barker, Margaret. (2005) [1998]. ''The Lost Prophet: The Book of Enoch and Its Influence on Christianity''. London: SPCK; Sheffield Phoenix Press. The Book of Enoch contains unique material on the origins of demons and Nephilim, why some fallen angel, angels fell from heaven, an explanation of why the Genesis flood narrative, Genesis flood was morally necessary, and a prophetic exposition of the Millennialism, thousand-year reign of the Messiah. Three books are traditionally attributed to Enoch, including the distinct works 2 Enoch and 3 Enoch. 1 Enoch is not considered to be Biblical canon, canonical scripture by most Jewish or Christian chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Book Of Enoch
The Second Book of Enoch (abbreviated as 2 Enoch and also known as Slavonic Enoch, Slavic Enoch, or the Secrets of Enoch) is a pseudepigraphic text in the apocalyptic genre. It describes the ascent of the patriarch Enoch, ancestor of Noah, through ten heavens of an Earth-centered cosmos. The Slavonic edition and translation of 2 Enoch is of Christian origin in the 8th century but is based on an earlier work. 2 Enoch is distinct from the Book of Enoch, known as 1 Enoch, and there is also an unrelated 3 Enoch, although none of the three books are considered canonical scripture by the majority of Jewish or Christian bodies. The numbering of these texts has been applied by scholars to distinguish each from the others. The cosmology of 2 Enoch corresponds closely with beliefs of the Early Middle Ages about the metaphysical structure of the universe. It may have been influential in shaping them. The text was lost for several centuries, then recovered and published at the end of the ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Moses
The Book of Moses, dictated by Joseph Smith, is part of the scriptural canon for some denominations in the Latter Day Saint movement. The book begins with the "Visions of Moses", a prologue to the story of the creation and the fall of man (Moses chapter 1), and continues with material corresponding to the Joseph Smith Translation of the Bible's (JST) first six chapters of the Book of Genesis (Moses chapters 2–5, 8), interrupted by two chapters of "extracts from the prophecy of Enoch" (Moses chapters 6–7). The Book of Moses begins with Moses speaking with God "face to face" and seeing a vision of all existence. Moses is initially overwhelmed by the immensity of the cosmos and humanity's smallness in comparison, but God then explains that he made the earth and heavens to bring humans to eternal life. The book subsequently provides an enlarged account of the Genesis creation narrative which describes God having a corporeal body, followed by a rendering of the fall of Adam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoch (ancestor Of Noah)
Enoch ( ; ''Henṓkh'') is a biblical figure and patriarch prior to Noah's flood, and the son of Jared and father of Methuselah. He was of the Antediluvian period in the Hebrew Bible. The text of the Book of Genesis says Enoch lived 365 years before he was taken by God. The text reads that Enoch "walked with God: and he was no more; for God took him" (), which is interpreted as Enoch entering heaven alive in some Jewish and Christian traditions, and interpreted differently in others. Enoch is the subject of many Jewish and Christian traditions. He was considered the author of the Book of Enoch and also called the scribe of judgement. In the New Testament, the Gospel of Luke, the Epistle to the Hebrews, and the Epistle of Jude all reference Enoch, the last of which also quotes from the Book of Enoch. In the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Oriental Orthodoxy, he is venerated as a Saint. Etymology Several etymologies have been proposed for the name Enoch ( ''Ḥănō� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarchs (Bible)
The patriarchs ( ''Ab (Semitic), ʾAvot'', "fathers") of the Bible, when narrowly defined, are Abraham, his son Isaac, and Isaac's son Jacob, also named Israel, the ancestor of the Israelites. These three figures are referred to collectively as "the patriarchs", and the period in which they lived is known as the patriarchal age. Judaism, Christianity, and Islam hold that the patriarchs, along with their primary wives, known as the #Matriarchs, matriarchs (Sarah, Rebekah and Leah), are entombed at the Cave of the Patriarchs, a site held holy by the three religions. Rachel, Jacob's other wife, is said to be buried separately at what is known as Rachel's Tomb, near Bethlehem, at the site where she is believed to have died in childbirth. More widely, the term patriarchs can be used to refer to the twenty male ancestor-figures between Adam and Abraham. The first ten of these are called the antediluvian patriarchs, because they came before Genesis flood narrative, the Flood. By the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoch
Enoch ( ; ''Henṓkh'') is a biblical figure and Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch prior to Noah's flood, and the son of Jared (biblical figure), Jared and father of Methuselah. He was of the Antediluvian period in the Hebrew Bible. The text of the Book of Genesis says Enoch lived 365 years before he was taken by God. The text reads that Enoch "walked with God: and he was no more; for God took him" (), which is interpreted as Enoch entering heaven alive in some Jewish and Christian traditions, and interpreted differently in others. Enoch is the subject of many Jewish and Christian traditions. He was considered the author of the Book of Enoch and also called the scribe of judgement. In the New Testament, the Gospel of Luke, the Epistle to the Hebrews, and the Epistle of Jude all reference Enoch, the last of which also quotes from the Book of Enoch. In the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Oriental Orthodoxy, he is venerated as a Saint. Etymology Several etymologies have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Luke
The Gospel of Luke is the third of the New Testament's four canonical Gospels. It tells of the origins, Nativity of Jesus, birth, Ministry of Jesus, ministry, Crucifixion of Jesus, death, Resurrection of Jesus, resurrection, and Ascension of Jesus, ascension of Jesus. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-volume work which scholars call Luke–Acts, accounting for 27.5% of the New Testament. The combined work divides the Christianity in the 1st century, history of first-century Christianity into three stages, with the gospel making up the first two of these – the life of Jesus the messiah (Christ (title), Christ) from his birth to the beginning of his mission in the meeting with John the Baptist, followed by his ministry with events such as the Sermon on the Plain and its Beatitudes, and his Passion of Jesus, Passion, death, and resurrection. Most modern scholars agree that the main sources used for Luke were (1) the Gospel of Mark; (2) a hypothetical col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Revised Standard Version
The New Revised Standard Version (NRSV) is a translation of the Bible in American English. It was first published in 1989 by the National Council of Churches, the NRSV was created by an ecumenical committee of scholars "comprising about thirty members". The NRSV is considered a revision of the Revised Standard Version, and relies on recently published critical editions of the original Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek texts. It is thus a revision in a series of English translations that has been identified as beginning with the King James Version. A major revision of the NRSV, the New Revised Standard Version Updated Edition (NRSVue), was released in 2021. Used broadly among biblical scholars, the NRSV was intended as a translation to serve the devotional, liturgical, and scholarly needs of the broadest possible range of Christian religious adherents. The full 84 book translation includes the Protestant enumeration of the Old Testament, the Apocrypha, and the New Testament; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam). According to Christianity, Adam sinned in the Garden of Eden by eating from the tree of the knowledge of good and evil. This action introduced death and sin into the world. This sinful nature infected all his descendants, and led humanity to be expelled from the Garden. Only through the crucifixion of Jesus, humanity can be redeemed. In Islam, Adam is considered '' Khalifa'' (خليفة) (successor) on earth. This is understood to mean either that he is God's deputy, the initiation of a new cycle of sentient life on earth, or both. Similar to the Biblical account, the Quran has Adam placed in a garden where he sins by taking from the Tree of Immortality, so loses his abode in the garden. When Adam repents from his sin, he is forgiven by God. This is seen as a guidan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |