|
Merlin M4000
The BT Merlin M4000 was a Personal computer sold by British Telecom during the 1980s as part of the Merlin range of electronic machinery for businesses. It was not developed by BT but was a rebadged Logica VTS-2300 Kennet, and a completely different machine from the Merlin Tonto which was a rebadged ICL OPD. Merlin M4000 was designed as a general purpose computer but was not IBM PC compatible, and so could not run the major business applications around at the time as these were tied to the IBM PC hardware. Hardware Merlin M4000 computers were packaged inside a substantial and heavy steel desktop case weighing approximately 12 kg. Inside the case was the main board, power supply, floppy and hard drives, and expansion cards. The design was reasonably modular as the case and main board were able to accommodate expansion cards and additional memory. A separate keyboard with 114 keys connected to the main unit using a reversed British telephone plug with the clip on the lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit computing, 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit Bus (computing), data bus (allowing the use of cheaper and fewer supporting Integrated circuit, ICs),Fewer TTL buffers, latches, multiplexers (although the amount of TTL logic was not drastically reduced). It also permits the use of cheap 8080-family ICs, where the 8254 CTC, Intel 8255, 8255 PIO, and 8259 PIC were used in the IBM PC design. In addition, it makes PCB layout simpler and boards cheaper, as well as demanding fewer (1- or 4-bit wide) DRAM chips. and is notable as the processor used in the original IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC design. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture, which eventually became Intel's most successful line of processors. On June 5, 2018, Intel released a limited-edition CPU celebrating the 40th anniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Fibre
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data transfer rates) than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are immune to electromagnetic interference. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, such as fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers. Glass optical fibers are typically made by drawing, while plastic fibers can be made either by drawing or by extrusion. Optical fibers typically include a core surrounded by a transparent cladding material with a lower index of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COBOL
COBOL (; an acronym for "common business-oriented language") is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is an imperative, procedural, and, since 2002, object-oriented language. COBOL is primarily used in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments. COBOL is still widely used in applications deployed on mainframe computers, such as large-scale batch and transaction processing jobs. Many large financial institutions were developing new systems in the language as late as 2006, but most programming in COBOL today is purely to maintain existing applications. Programs are being moved to new platforms, rewritten in modern languages, or replaced with other software. COBOL was designed in 1959 by CODASYL and was partly based on the programming language FLOW-MATIC, designed by Grace Hopper. It was created as part of a U.S. Department of Defense effort to create a portable programming language for data pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Language
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book '' The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switchboard Operator
In the early days of telephony, companies used manual telephone switchboards, and switchboard operators connected calls by inserting a pair of phone plugs into the appropriate jacks. They were gradually phased out and replaced by automated systems, first those allowing direct dialing within a local area, then for long-distance and international direct dialing. Description A typical manual telephone switchboard has a vertical panel containing an array of jacks with a desk in front. The desk has a row of switches and two rows of plugs attached to cables that retract into the desk when not in use. Each pair of plugs was part of a cord circuit with a switch associated that let the operator participate in the call or ring the circuit for an incoming call. Each jack had a light above it that lit when the customer's telephone receiver was lifted (the earliest systems required the customer to hand-crank a magneto to alert the central office and, later, to "ring off" the completed ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Off The Shelf
Commercial-off-the-shelf or commercially available off-the-shelf (COTS) products are packaged or canned (ready-made) hardware or software, which are adapted aftermarket to the needs of the purchasing organization, rather than the commissioning of custom-made, or bespoke, solutions. A related term, Mil-COTS, refers to COTS products for use by the U.S. and Canadian militaries. In the context of the U.S. government, the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) has defined "COTS" as a formal term for commercial items, including services, available in the commercial marketplace that can be bought and used under government contract. For example, Microsoft is a COTS software provider. Goods and construction materials may qualify as COTS but bulk cargo does not. Services associated with the commercial items may also qualify as COTS, including installation services, training services, and cloud services. COTS purchases are alternatives to custom software or one-off developments – governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Custom Software
Custom software (also known as bespoke software or tailor-made software) is software that is developed specifically for some specific organization or other user. As such, it can be contrasted with the use of out-of-the-box software packages developed for the mass market, such as commercial off-the-shelf software, or existing free software. Considerations Since custom software is developed for a single customer it can accommodate that customer's particular preferences and expectations, which may not be the case for commercial off-the-shelf software. Custom software may be developed in an iterative processes, allowing all nuances and possible hidden risks to be taken into account, including issues which were not mentioned in the original requirement specifications (which are, as a rule, never perfect). In particular, the first phase in the software development process may involve many departments, including marketing, engineering, research and development and general management.Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wordstar
WordStar is a discontinued word processor application for microcomputers. It was published by MicroPro International and originally written for the CP/M-80 operating system (OS), with later editions added for MS-DOS and other 16-bit computing, 16-bit PC OSes. Rob Barnaby was the sole author of the early versions of the program. Starting with WordStar 4.0, the program was built on new code written principally by Peter Mierau. WordStar dominated the market in the early and mid-1980s, succeeding the market leader Electric Pencil. WordStar was written with as few assumptions as possible about the operating system and machine hardware, allowing it to be easily ported across the many platforms that proliferated in the early 1980s. Because all of these versions had relatively similar commands and controls, users could move between platforms with equal ease. It was already popular when its inclusion with the Osborne 1 portable computer made the program the ''de facto'' standard for mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DOS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent DOS
Multiuser DOS is a real-time multi-user multi-tasking operating system for IBM PC-compatible microcomputers. An evolution of the older Concurrent CP/M-86, Concurrent DOS and Concurrent DOS 386 operating systems, it was originally developed by Digital Research and acquired and further developed by Novell in 1991. Its ancestry lies in the earlier Digital Research 8-bit operating systems CP/M and MP/M, and the 16-bit single-tasking CP/M-86 which evolved from CP/M. When Novell abandoned Multiuser DOS in 1992, the three master value-added resellers (VARs) DataPac Australasia, Concurrent Controls and Intelligent Micro Software were allowed to take over and continued independent development into Datapac Multiuser DOS and System Manager, CCI Multiuser DOS, and IMS Multiuser DOS and REAL/32. The FlexOS line, which evolved from Concurrent DOS 286 and Concurrent DOS 68K, was sold off to Integrated Systems, Inc. (ISI) in July 1994. Concurrent CP/M-86 The initial version of CP/M-86 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
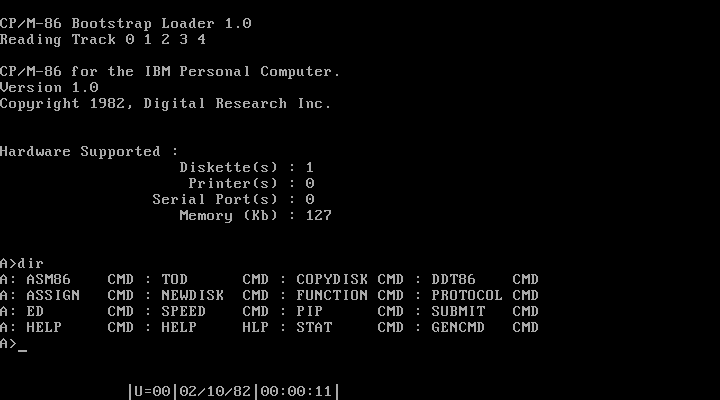
CP/M-86
CP/M-86 is a discontinued version of the CP/M operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086 and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well. History Digital Research's CP/M-86 was originally announced to be released in November 1979, but was delayed repeatedly. When IBM contacted other companies to obtain components for the IBM PC, the as-yet unreleased CP/M-86 was its first choice for an operating system because CP/M had the most applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape Drive
A tape drive is a data storage device that reads and writes data on a magnetic tape. Magnetic-tape data storage is typically used for offline, archival data storage. Tape media generally has a favorable unit cost and long archival stability. A tape drive provides sequential access storage, unlike a hard disk drive, which provides direct access storage. A disk drive can move to any position on the disk in a few milliseconds, but a tape drive must physically wind tape between reels to read any one particular piece of data. As a result, tape drives have very large average access times. However, tape drives can stream data very quickly off a tape when the required position has been reached. For example, Linear Tape-Open (LTO) supports continuous data transfer rates of up to 360 MB/s, a rate comparable to hard disk drives. Design Magnetic-tape drives with capacities of less than one megabyte were first used for data storage on mainframe computers in the 1950s. , capac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |