|
Melchisedek
In the Hebrew Bible, Melchizedek was the king of Salem (Bible), Salem and priest of (often translated as 'most high God'). He is first mentioned in Genesis 14:18–20, where he brings out bread and wine and then blesses Abraham, Abraham, and El Elyon or "the Lord, God Most High". Abraham was returning from pursuing the kings who came from the East and gave him a "Tithes in Judaism, tenth of everything". In Christianity, according to the Epistle to the Hebrews, Jesus Christ is identified as "High priest forever in the order of Melchizedek", and so Jesus assumes the role of High Priest of Israel, High Priest once and for all. Chazalic literature – specifically Targum Jonathan, Targum Pseudo-Jonathan, Targum Yerushalmi, and the Talmud, Babylonian Talmud – presents his name () as a nickname for Shem. Joseph Blenkinsopp has suggested that the story of Melchizedek is an informal insertion into the Genesis narration, possibly inserted in order to give validity to the priesthood an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
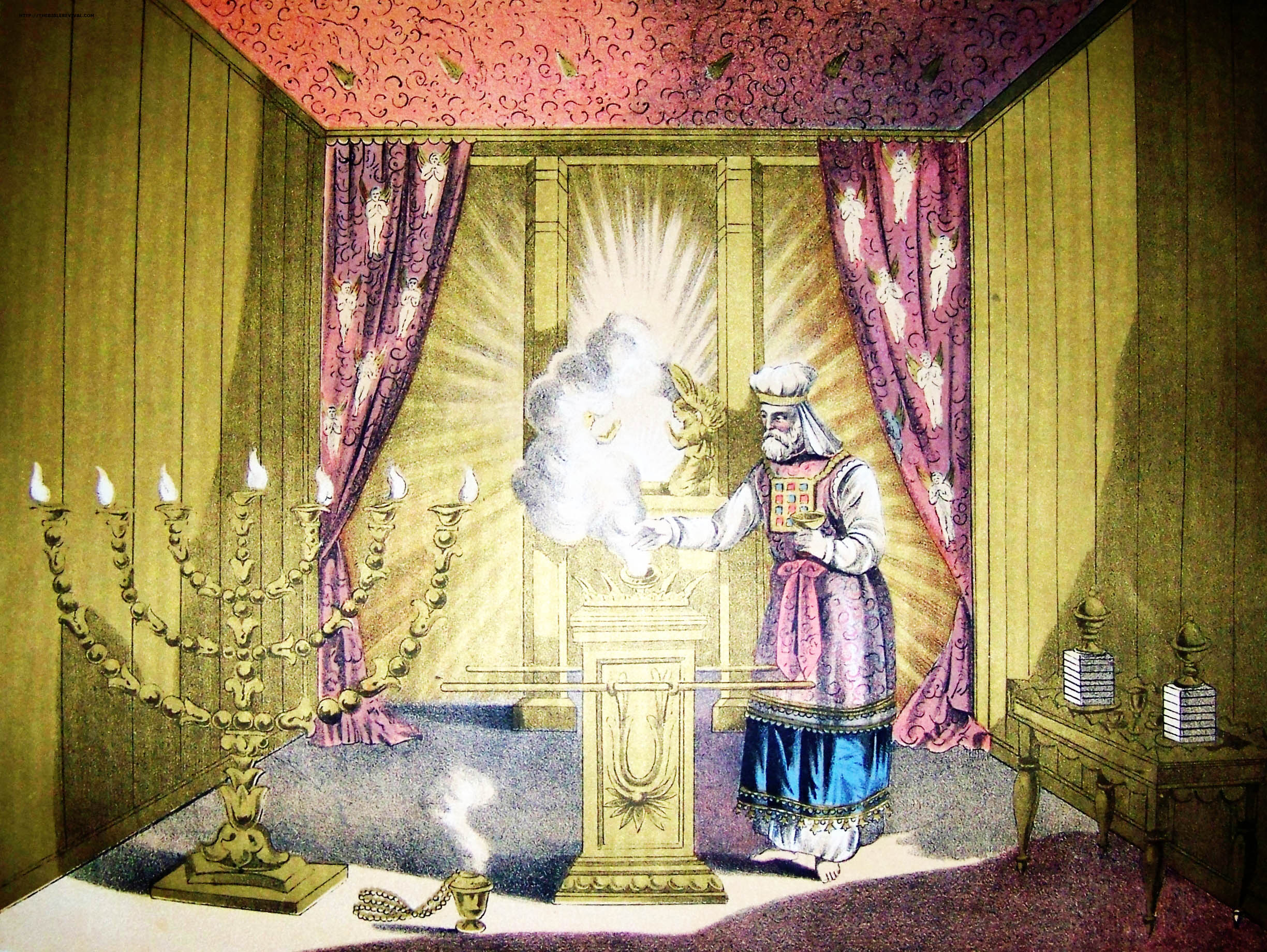
High Priest Of Israel
In Judaism, the High Priest of Israel (, lit. ‘great priest’; Aramaic: ''Kahana Rabba'') was the head of the Israelite priesthood. He played a unique role in the worship conducted in the Tabernacle and later in the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as in some non-ritual matters. Like all priests, he was required to be descended from Aaron (the first biblical priest). But unlike other priests, the high priest followed more restrictive laws, wore unique priestly garments, and was the only priest allowed to perform certain ceremonies. Titles The high priest is referred to by a number of titles in the Hebrew Bible; the title ''kohen gadol'' did not become dominant until well into the Second Temple period. In addition to the title of "great priest" (''kohen gadol'') which later became the standard Hebrew title, the term "head priest" (''kohen harosh''; ) was used, as was "anointed priest" (''kohen mashiach''; )., , The Torah sometimes uses longer descriptions: "the great priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and jurisdictional groups of Christianity, with approximately 230 million baptised members. It operates as a Communion (Christian), communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its Bishop (Orthodox Church), bishops via local Holy Synod, synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the pope of the Catholic Church. Nevertheless, the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognised by them as ''primus inter pares'' (), a title held by the patriarch of Rome prior to 1054. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played an especially prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. Since 2018, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elyon
Elyon or El Elyon ( ''ʼĒl ʻElyōn''), is an epithet that appears in the Hebrew Bible. ' is usually rendered in English as "God Most High", and similarly in the Septuagint as ("God the highest"). The title ' is a common topic of scholarly debate, sometimes interpreted as equal to the Abrahamic God, and otherwise theorized as a reference to a separate deity of its own kind, potentially above that of Yahweh. Outside of biblical context, the term also has mundane uses, such as " upper" (where the ending in both roots is a locative, not superlative or comparative), "top", or "uppermost", referring simply to the position of objects (e.g. applied to a basket in Genesis 40:17 or to a chamber in Ezekiel 42:5). Hebrew Bible ''ʼĒl ʻElyōn'' The compound name ''ʼĒl ʻElyōn'' 'God Most High' occurs in Genesis 14:18–20 as the God whose priest was Melchizedek, king of Salem. The form appears again almost immediately in verse 22, used by Abraham in an oath to the king of Sodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targum Yonathan
The Targum Jonathan () is the Aramaic translation of the Nevi'im section of the Hebrew Bible employed in Lower Mesopotamia ("Babylonia"). It is not to be confused with "Targum Pseudo-Jonathan," an Aramaic translation of the Torah. It is often known as "Targum Jonathan" due to a printer's error or perhaps because it is so stylistically similar to the Targum Jerusalem, which is named "Jonathan" to differentiate the two later translations. Origin Like Targum Onkelos, it originated in the synagogue reading of a translation from the Nevi'im, which was part of the weekly lesson. The Talmud attributes its authorship to Jonathan ben Uzziel, a pupil of Hillel the Elder, in Megillah 3a:4. According to this source, it was composed by Jonathan ben Uzziel "from the mouths of Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachi," implying that it was based on traditions derived from the last prophets. The additional statements that, on this account, the entire land of Israel was shaken and that a voice from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shem
Shem (; ''Šēm''; ) is one of the sons of Noah in the Bible ( Genesis 5–11 and 1 Chronicles 1:4). The children of Shem are Elam, Ashur, Arphaxad, Lud and Aram, in addition to unnamed daughters. Abraham, the patriarch of Jews, Christians, and Muslims, is one of the descendants of Arphaxad. In medieval and early modern European tradition he was considered to be the ancestor of the peoples of Asia, Javakhishvili, Ivane (1950), ''Historical-Ethnological problems of Georgia, the Caucasus and the Near East''. Tbilisi, pp. 130–135 (in Georgian). and he gives his name to the title " Semites" formerly given to West Asian peoples. Islamic literature describes Shem as one of the believing sons of Noah. Some sources even identify Shem as a prophet in his own right and that he was the next prophet after his father. In the Bible Genesis 10 Genesis 10:21 refers to relative ages of Shem and his brother Japheth, but with sufficient ambiguity to have yielded different Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickname
A nickname, in some circumstances also known as a sobriquet, or informally a "moniker", is an informal substitute for the proper name of a person, place, or thing, used to express affection, playfulness, contempt, or a particular character trait. It is distinct from a pseudonym, stage name, or title, although the concepts can overlap. Etymology The compound word ''ekename'', meaning "additional name", was attested as early as 1303. This word was derived from the Old English word ''eac'', meaning "also", related to ''eacian'', meaning "to increase". By the 15th century, the misdivision of the syllables of the phrase "an ekename" led to its rephrasing as "a nekename". Though the spelling has changed, the meaning of the word has remained relatively stable ever since. Various language conventions English nicknames are generally represented in quotes between the bearer's first and last names (e.g., '' Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower'' and '' Daniel Lamont "Bubba" Franks''). I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish culture, Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, Jewish philosophy, philosophy, Jewish customs, customs, Jewish history, history, and Jewish folklore, folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 Masekhet, tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targum Pseudo-Jonathan
Targum Pseudo-Jonathan (also known as the Jerusalem Targum, Targum Yerushalmi, or Targum Jonathan) is an Aramaic translation and interpretation (targum) of the Torah (Pentateuch) traditionally thought to have originated from the land of Israel, although more recently a provenance in 12th-century Italy has been proposed. As a ''targum'', it is not just a translation but incorporates aggadic material collected from various sources as late as the Midrash Rabbah as well as earlier material from the Talmud. So it is a combination of a commentary and a translation. It is also a composite text, involving the Old Palestinian Targum, Targum Onkelos, and a diverse array of other material. Name The original name of Targum Pseudo-Jonathan was Targum Yerushalmi (Jerusalem Targum). However, due to an error in the fourteenth century, it came to be known as the Targum "Jonathan" instead of "Jerusalem" in reference to Jonathan ben Uzziel. Due to the pseudonymous nature of this attribution, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targum Jonathan
The Targum Jonathan () is the Aramaic translation of the Nevi'im section of the Hebrew Bible employed in Lower Mesopotamia ("Babylonia"). It is not to be confused with "Targum Pseudo-Jonathan," an Aramaic translation of the Torah. It is often known as "Targum Jonathan" due to a printer's error or perhaps because it is so stylistically similar to the Targum Jerusalem, which is named "Jonathan" to differentiate the two later translations. Origin Like Targum Onkelos, it originated in the synagogue reading of a translation from the Nevi'im, which was part of the weekly lesson. The Talmud attributes its authorship to Jonathan ben Uzziel, a pupil of Hillel the Elder, in Megillah 3a:4. According to this source, it was composed by Jonathan ben Uzziel "from the mouths of Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachi," implying that it was based on traditions derived from the last prophets. The additional statements that, on this account, the entire land of Israel was shaken and that a voice fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chazal
Chazal or Ḥazal () are the Jewish sages of the Mishnaic and Talmudic eras, spanning from the final 300 years of the Second Temple period until the 7th century, or . Their authority was mostly in the field of ''Halakha'' (Jewish law) and less regarding Jewish theology. Rabbinic eras (eras of ''Halakha'') Chazal are generally divided according to their era and the major written products thereof: * '' Soferim'' ("scribes"): Sages from the period preceding Ezra the scribe and up to the '' Zugot'' era, including the men of the Great Assembly. Traditionally, the era of ''Soferim'' is assumed to have stretched from the '' Matan Torah'' ("giving of the Law"; i.e., the receipt of the Torah by Moses on Mount Sinai) to the era of the earliest ''Halakha'', including the times of Simeon the Just. * '' Zugot'' ("pairs"): Five pairs of sages from consecutive generations who lived during a period of roughly 100 years toward the end of the Second Temple era. (142BCE) * ''Tannaim'' ("t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the Major religious groups, world's largest religion. Most Christians consider Jesus to be the Incarnation (Christianity), incarnation of God the Son and awaited Messiah#Christianity, messiah, or Christ (title), Christ, a descendant from the Davidic line that is prophesied in the Old Testament. Virtually all modern scholars of classical antiquity, antiquity agree that Historicity of Jesus, Jesus existed historically. Accounts of Life of Jesus, Jesus's life are contained in the Gospels, especially the four canonical Gospels in the New Testament. Since the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, Quest for the historical Jesus, academic research has yielded various views on the historical reliability of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistle To The Hebrews
The Epistle to the Hebrews () is one of the books of the New Testament. The text does not mention the name of its author, but was traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle; most of the Ancient Greek manuscripts, the Old Syriac Peshitto and some of the Old Latin manuscripts place the epistle to the Hebrews among Paul's letters. However, doubt on Pauline authorship in the Roman Church is reported by Eusebius. Modern biblical scholarship considers its authorship unknown, with Pauline authorship mostly rejected. A minority view Hebrews as written in deliberate imitation of the style of Paul, with some contending that it was authored by Apollos or Priscilla and Aquila. Scholars of Greek consider its writing to be more polished and eloquent than any other book of the New Testament, and "the very carefully composed and studied Greek of Hebrews is not Paul's spontaneous, volatile contextual Greek." It has been described as an intricate New Testament book.Mackie, Scott D. ''Esch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |