|
Mathematical Discussion Of Rangekeeping
In naval gunnery, when long-range guns became available, an enemy ship would move some distance after the shells were fired. It became necessary to figure out where the enemy ship, the target, was going to be when the shells arrived. The process of keeping track of where the ship was likely to be was called rangekeeping, because the distance to the target—the range—was a very important factor in aiming the guns accurately. As time passed, train (also called bearing), the direction to the target, also became part of rangekeeping, but tradition kept the term alive. Rangekeeping is an excellent example of the application of analog computing to a real-world mathematical modeling problem. Because nations had so much money invested in their capital ships, they were willing to invest enormous amounts of money in the development of rangekeeping hardware to ensure that the guns of these ships could put their projectiles on target. This article presents an overview of the rangekeeping as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Gunnery
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines. Origins The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era. Julius Caesar indicates the use of ship-borne catapults against Britons ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and fire-throwers. From the late Middle Ages onwards, warships began to carry cannons of various calibres. The Mongol invasion of Java introduced cannons to be used in naval warfare (e.g. Cetbang by the Majapahit). The Battle of Arnemuiden, fought between England and France in 1338 at the start of the Hundred Years' War, was the first recorded European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Searchlights
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a particular direction. It is usually constructed so that it can be swiveled about. Military use The first use of searchlights using carbon arc technology occurred during the Siege of Paris during the Franco-Prussian War. The Royal Navy used searchlights in 1882 to dazzle and prevent Egyptian forces from manning artillery batteries at Alexandria. Later that same year, the French and British forces landed troops under searchlights. By 1907 the value of searchlights had become widely recognized. One recent use was to assist attacks by torpedo boats by dazzling gun crews on the ships being attacked. Other uses included detecting enemy ships at greater distances, as signaling devices, and to assist landing parties. Searchlights were also used by battles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistics
Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially ranged weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets or the like; the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance. A ballistic body is a free-moving body with momentum which can be subject to forces such as the forces exerted by pressurized gases from a gun barrel or a propelling nozzle, normal force by rifling, and gravity and air drag during flight. A ballistic missile is a missile that is guided only during the relatively brief initial phase of powered flight and the trajectory is subsequently governed by the laws of classical mechanics; in contrast to (for example) a cruise missile which is aerodynamically guided in powered flight like a fixed-wing aircraft. History and prehistory The earliest known ballistic projectiles were stones and spears, and the throwing stic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude ( digital signals). Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions. Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were typically much faster, but they started to become obsolete as early as the 1950s and 1960s, although they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
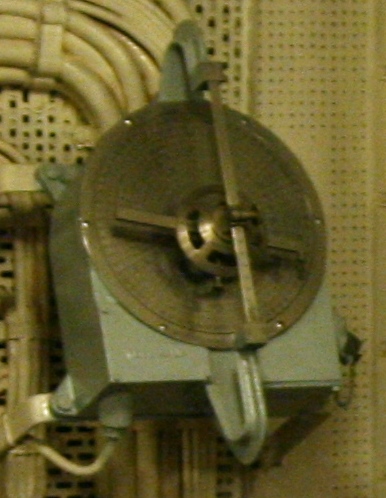
Dumaresq
The Dumaresq is a mechanical calculating device invented around 1902 by Lieutenant John Dumaresq of the Royal Navy. It is an analogue computer that relates vital variables of the fire control problem to the movement of one's own ship and that of a target ship. It was often used with other devices, such as a Vickers range clock, to generate range and deflection data so the gun sights of the ship could be continuously set. A number of versions of the Dumaresq were produced of increasing complexity as development proceeded. Geometric principle The dumaresq relies on sliding and rotating bars and dials to represent the motion of the two ships. Normally the motion of the ship carrying the dumaresq is represented by a metal bar running above the instrument. Below the bar is a round metal plate inscribed with a coordinate plot, and an angle scale around its outer rim. The fixed bar is mounted on a bearing that allows it to be turned to represent the direction of motion of the ship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dazzle Camouflage
Dazzle camouflage, also known as razzle dazzle (in the U.S.) or dazzle painting, is a family of ship camouflage that was used extensively in World War I, and to a lesser extent in World War II and afterwards. Credited to the British marine artist Norman Wilkinson (artist), Norman Wilkinson, though with a rejected prior claim by the zoology, zoologist John Graham Kerr, it consisted of complex patterns of geometric shapes in contrasting colours interrupting and intersecting each other. Unlike other forms of camouflage, the intention of dazzle is not to crypsis, conceal but to make it difficult to estimate a target's range, speed, and heading. Norman Wilkinson explained in 1919 that he had intended dazzle primarily to mislead the enemy about a ship's course and so cause them to take up a poor firing position. Dazzle was adopted by the British Admiralty, Admiralty in the UK, and then by the United States Navy. Each ship's dazzle pattern was unique to avoid making classes of ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Tender
A submarine tender is a type of depot ship that supplies and supports submarines. Development Submarines are small compared to most oceangoing vessels, and generally do not have the ability to carry large amounts of food, fuel, torpedoes, and other supplies, nor to carry a full array of maintenance equipment and personnel. The tender carries all these, and either meets submarines at sea to replenish them or provides these services while docked at a port near the area where the submarines are operating. In some navies, the tenders were equipped with workshops for maintenance, and as floating dormitories with relief crews. With the increased size and automation of modern submarines, plus in some navies the introduction of nuclear power, tenders are no longer as necessary for fuel as they once were. Canada Canada's first Submarine Depot Ship was . Chile The term used in the Chilean Navy is "submarine mother ship", as for example the BMS (buque madre de submarinos) ''Almirant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazy Susan
A Lazy Susan is a turntable (rotating tray) placed on a table or countertop to aid in distributing food. Lazy Susans may be made from a variety of materials but are usually glass, wood, or plastic. They are circular and placed in the centre of a table to share dishes easily among diners. Although they are common in Chinese restaurants, the Lazy Susan is a Western invention. Owing to the nature of Chinese cuisine, especially dim sum, they are common at formal Chinese restaurants both in mainland China and abroad. In Chinese, they are known as ( t. 餐桌轉盤) ( p ''cānzhuō zhuànpán'') or "dinner-table turntables". History It is likely that the explanation of the term Lazy Susan has been lost to history.Quinion, Michael. ''World Wide Words'':lazy Susan. 24 Apr 2010. Accessed 11 Aug 2013.Lazy Susan.What’s in a name? The origins of Lazy Susan. 27 Sep 2010. Accessed 11 Aug 2013. Folk etymologies claim it as an American invention. According to lore, Thomas Jefferson in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle On The Bow
Target angle is the relative bearing of the observing station from the vehicle being observed. It may be used to compute point-of-aim for a fire-control problem when vehicle range and speed can be estimated from other information. Target angle may be best explained from the example of a submarine preparing to launch a straight-run (non-homing) torpedo at a moving target ship. Since the torpedo travels relatively slowly, the torpedo course must be set not toward the target, but toward where the target will be when the torpedo reaches it. Target angle is used to estimate target course. The submarine observer estimating target angle pictures himself on the target ship looking back at the submarine. Relative bearing of the submarine is the clockwise angle in degrees from the heading of the target ship to a straight line drawn from the target ship to the submarine. When target angle is 0° (or 360° ) the target ship is coming directly toward the submarine. Target ang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_cropped.jpg)


