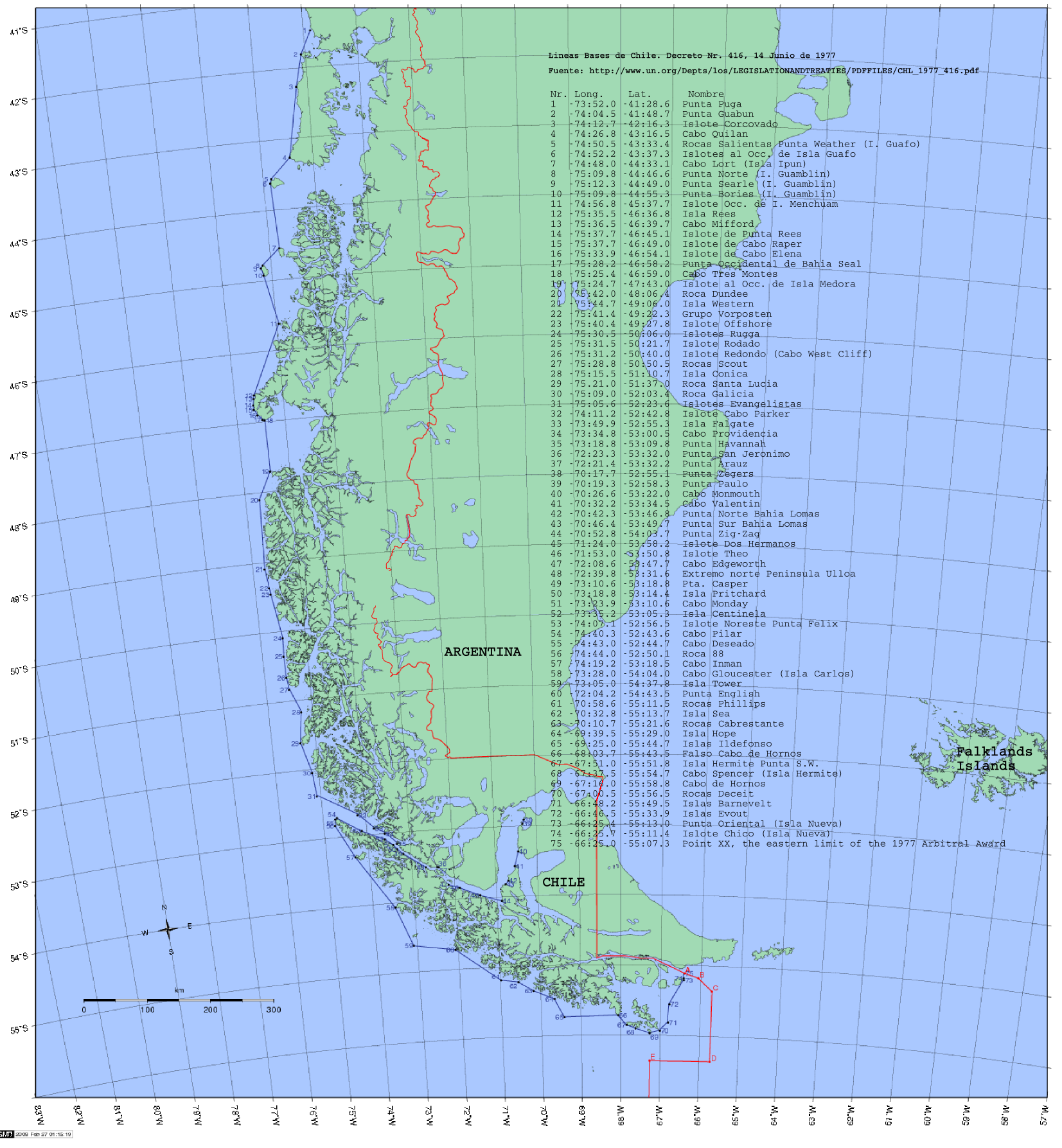
|
Maritime Boundary
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of Earth's water surface areas using physiographical or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boundaries Geodatabase General info retrieved 19 November 2010 encompassing maritime features, limits and zones.Geoscience Australia Maritime definitions retrieved 16 January 2023 Generally, a maritime boundary is delineated at a particular distance from a jurisdiction's coastline. Although in some countries the term ''maritime boundary'' represents borders of a maritime nation that are recognized by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, maritime borders usually serve to identify the edge of international waters. Maritime boundaries exist in the context of territorial waters, contiguous zones, and exclusive economic zones; however, the terminology does not encompass lake or river boundaries, which are considered within the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Zones Under International Law
Maritime may refer to: Geography * Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps * Maritime Region, a region in Togo * Maritime Southeast Asia * The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island * Maritime County, former county of Poland, existing from 1927 to 1939, and from 1945 to 1951 * Neustadt District, Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, known from 1939 to 1942 as ''Maritime District'', a former district of Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Nazi Germany, from 1939 to 1945 * The Maritime republics, Maritime Republics, thalassocratic city-states on the Italian peninsula during the Middle Ages Museums * Maritime museum (sometimes nautical museum), a museum for the display of objects relating to ships and travel on large bodies of water. * Maritime Museum (Belize) * Maritime Museum (Macau), China * Maritime Museum (Malaysia) * Maritime Museum (Stockholm), Sweden Music * Maritime (album), ''Maritime'' (album), a 2005 alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
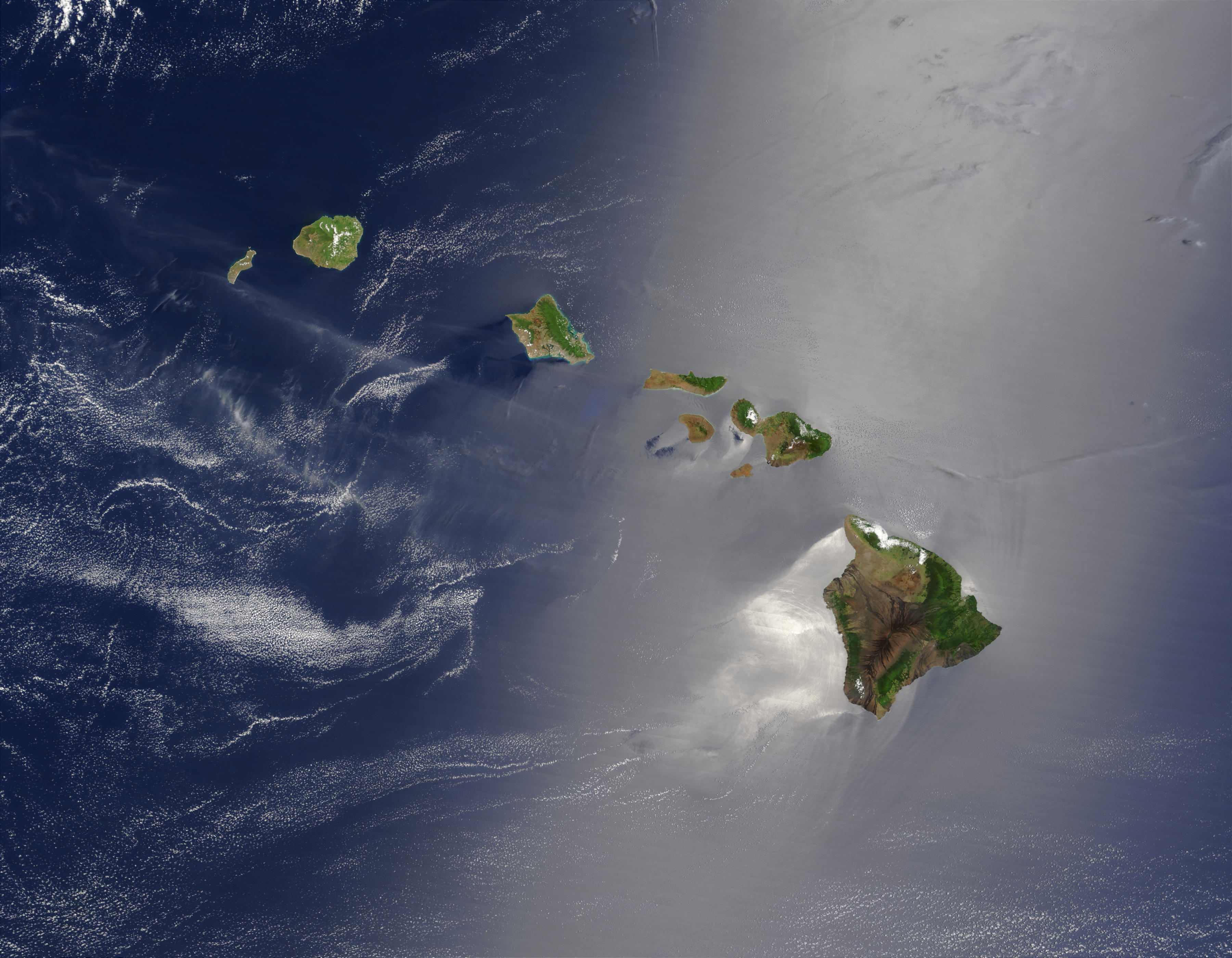
Island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been part of a continent. Oceanic islands can be formed from volcano, volcanic activity, grow into atolls from coral reefs, and form from sediment along shorelines, creating barrier islands. River islands can also form from sediment and debris in rivers. Artificial islands are those made by humans, including small rocky outcroppings built out of lagoons and large-scale land reclamation projects used for development. Islands are host to diverse plant and animal life. Oceanic islands have the sea as a natural barrier to the introduction of new species, causing the species that do reach the island to evolve in isolation. Continental islands share animal and plant life with the continent they split from. Depending on how long ago the continental is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equidistance Principle
The equidistance principle, or principle of equidistance, is a legal concept in maritime boundary claims that a nation's maritime boundaries should conform to a median line that is equidistant from the shores of neighboring nations. The concept was developed in the process of settling disputes in which the borders of adjacent nations were located on a contiguous continental shelf: The equidistance principle represents one aspect of customary international law, but its importance is evaluated in light of other factorsDorinda G. Dallmeyer ''et al.'' (1989). such as history: History The United States used equidistance in the 1805 Act of Congress that divided public lands by measurements as close as possible to "equidistant from those two corners which stand on the same line." One of the most notable historical events regarding equidistance is the Argument between Germany, Netherlands and Denmark. All three countries laid claim to a specific area within the ocean. Germany clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautical Mile
A nautical mile is a unit of length used in air, marine, and space navigation, and for the definition of territorial waters. Historically, it was defined as the meridian arc length corresponding to one minute ( of a degree) of latitude at the equator, so that Earth's polar circumference is very near to 21,600 nautical miles (that is 60 minutes × 360 degrees). Today the international nautical mile is defined as exactly . The derived unit of speed is the knot, one nautical mile per hour. Unit symbol There is no single internationally agreed symbol, with several symbols in use. * NM is used by the International Civil Aviation Organization. * nmi is used by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and the United States Government Publishing Office. * M is used as the abbreviation for the nautical mile by the International Hydrographic Organization. * nm is a non-standard abbreviation used in many maritime applications and texts, including U.S. Government Coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archipelagic Waters
An archipelagic state is an island country that consists of one or more archipelagos. The designation is legally defined by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea of 1982 ( UNCLOS III). The Bahamas, Fiji, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and the Philippines are the five original sovereign states that obtained approval in the UNCLOS signed in Montego Bay, Jamaica on 10 December 1982 and qualified as the archipelagic states. An archipelagic state can designate the waters between the islands as sovereign archipelagic waters. As of 20 June 2015, a total of 22 sovereign states have sought to claim archipelagic status. Some island countries comprise one or more archipelagos in a geographical sense, but chose not to claim the archipelagic state status, including Japan, Malta, New Zealand, Cuba, Iceland, and the United Kingdom. Archipelagic waters Archipelagic states are composed of groups of islands that form a state as a single unit, the islands and the waters within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseline (sea)
A baseline, as defined by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is the line (or curve) along the coast from which the seaward limits of a state's territorial sea and certain other maritime zones of jurisdiction are measured, such as a state's exclusive economic zone. Normally, a sea baseline follows the low-water line of a coastal state. This is either the low-water mark closest to the shore or an unlimited distance from permanently exposed land, provided that some portion of elevations exposed at low tide but covered at high tide (such as mud flats) is within 3 nautical miles (5.6 kilometres; 3+1⁄2 statute miles) of permanently exposed land. When the coast is deeply indented, has fringing islands or is highly unstable, ''straight'' baselines may be used. Measurement of baseline The following methods are used to measure a baseline under United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea 1982. Normal baseline Except where otherwise provided in this Convention, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure made up of line segments connected to form a closed polygonal chain. The segments of a closed polygonal chain are called its '' edges'' or ''sides''. The points where two edges meet are the polygon's '' vertices'' or ''corners''. An ''n''-gon is a polygon with ''n'' sides; for example, a triangle is a 3-gon. A simple polygon is one which does not intersect itself. More precisely, the only allowed intersections among the line segments that make up the polygon are the shared endpoints of consecutive segments in the polygonal chain. A simple polygon is the boundary of a region of the plane that is called a ''solid polygon''. The interior of a solid polygon is its ''body'', also known as a ''polygonal region'' or ''polygonal area''. In contexts where one is concerned only with simple and solid polygons, a ''polygon'' may refer only to a simple polygon or to a solid polygon. A polygonal chain may cross over itself, creating star polyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyline
In geometry, a polygonal chain is a connected series of line segments. More formally, a polygonal chain is a curve specified by a sequence of points (A_1, A_2, \dots, A_n) called its vertices. The curve itself consists of the line segments connecting the consecutive vertices. Variations Simple A simple polygonal chain is one in which only consecutive segments intersect and only at their endpoints. Closed A closed polygonal chain is one in which the first vertex coincides with the last one, or, alternatively, the first and the last vertices are also connected by a line segment. A simple closed polygonal chain in the plane is the boundary of a simple polygon. Often the term "polygon" is used in the meaning of "closed polygonal chain", but in some cases it is important to draw a distinction between a polygonal area and a polygonal chain. A space closed polygonal chain is also known as a skew "polygon". Monotone A polygonal chain is called ''monotone'' if there is a straig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outlying Territory
An outlying territory or separate area is a state territory geographically separated from its parent territory and lies beyond Exclusive Economic Zone of its parent territory. The tables below are lists of outlying territories which are marked by distinct, non- contiguous maritime boundaries or land boundaries: Outlying geographical regions Outlying territories outside the continent Outlying uninhabited dependent territories Outlying dependent territories and areas of special sovereignty Notes * ''1. Enclaves are not included''. * ''2. Disputed outlying territories in the Spratly Islands are not included''. See also * List of sovereign states The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership with ... * List of dependent territories External links Maritime bound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Prolongation
The natural prolongation principle or principle of natural prolongation is a legal concept introduced in maritime claims submitted to the United Nations. The phrase denotes a concept of political geography and international law that a nation's maritime boundary should reflect the 'natural prolongation' of where its land territory reaches the coast. Oceanographic descriptions of the land mass under coastal waters became conflated and confused with criteria that are deemed relevant in border delimitation. The concept was developed in the process of settling disputes if the borders of adjacent nations were located on a contiguous continental shelf. An unresolved issue is whether a natural prolongation defined scientifically, without reference to equitable principles, is to be construed as a "natural prolongation" for the purpose of maritime border delimitation or maritime boundary disputes. History The phrase ''natural prolongation'' was established as a concept in the ''North S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |