|
Mandrillus Leucophaeus
The drill (''Mandrillus leucophaeus'') is a primate of the family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys), related to baboons and even more closely to the mandrill. Description The drill is a short-tailed monkey up to long, similar in appearance to the mandrill, but lacks the bright blue and red on the face of that species. It has high sexual dimorphism in weight, with males weighing up to and females up to .ARKive Drill (''Mandrillus leucophaeus'') The body is overall a dark grey-brown. Mature males have a pink lower lip and white chin on a dark grey to black face with raised grooves on the nose. The rump is pink, mauve and blue. Female drills lack the pink chin. Taxonomy Two subspecies of drill are accepted by some authorities, but are not considered distinct by others:Primate Info NetDrill/ref> * Mainland drill, ''Mandrillus leucophaeus leucophaeus'' * Bioko drill, ''Mandrillus leucophaeus poensis'' Their closest relative is the mandrill (''Mandrillus sphinx''), found from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandrillus Leucophaeus 01 MWNH 297
''Mandrillus'' is a genus of large Old World monkeys distributed throughout central and southern Africa, consisting of two species: ''M. sphinx'' and ''M. leucophaeus'', the mandrill and drill, respectively. ''Mandrillus'', originally placed under the genus ''Papio'' as a type of baboon, is closely related to the genus ''Cercocebus''. They are characterised by their large builds, elongated snouts with furrows on each side, and stub tails. Both species occupy the west central region of Africa and live primarily on the ground. They are frugivores, consuming both meat and plants, with a preference for plants. ''M. sphinx'' is classified as vulnerable and ''M. leucophaeus'' as endangered on the ''IUCN Red List of Threatened Species''. Taxonomy ''Mandrillus'' is a genus within the tribe Papionini, which in turn is under the subfamily Cercopithecinae. This subfamily is classified under the family of Old World monkeys (Cercopithecidae) within the infraorder Simiiformes. The Papioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandrillus
''Mandrillus'' is a genus of large Old World monkeys distributed throughout Central Africa, central and southern Africa, consisting of two species: ''M. sphinx'' and ''M. leucophaeus'', the mandrill and drill (animal), drill, respectively. ''Mandrillus'', originally placed under the genus ''Papio'' as a type of baboon, is closely related to the genus ''white-eyelid mangabey, Cercocebus''. They are characterised by their large builds, elongated snouts with furrows on each side, and stub tails. Both species occupy the west central region of Africa and live primarily terrestrial animal, on the ground. They are frugivores, consuming omnivore, both meat and plants, with a preference for plants. ''M. sphinx'' is classified as vulnerable species, vulnerable and ''M. leucophaeus'' as endangered species, endangered on the ''IUCN Red List of threatened species, Threatened Species''. Taxonomy ''Mandrillus'' is a genus within the tribe Papionini, which in turn is under the subfamily Cercopi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of and a population of million people. There are coastal plains, mountains (the Crystal Mountains (Africa), Cristal Mountains and the Chaillu Massif in the centre), and a savanna in the east. Libreville is the country's capital and largest city. Gabon's original inhabitants were the African Pygmies, Bambenga. In the 14th century, Bantu expansion, Bantu migrants also began settling in the area. The Kingdom of Orungu was established around 1700. France colonised the region in the late 19th century. Since its independence from France in 1960, Gabon has had four President of Gabon, presidents. In the 1990s, it introduced a multi-party system and a democratic constitution that aimed for a more tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Equatorial Guinea
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primates Of Africa
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers and simians (monkeys and apes). Primates arose 74–63 million years ago first from small terrestrial animal, terrestrial mammals, which adapted for life in tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to the challenging environment among Canopy (biology), tree tops, including large brain sizes, binocular vision, color vision, Animal communication, vocalizations, shoulder girdles allowing a large degree of movement in the upper limbs, and opposable thumbs (in most but not all) that enable better grasping and dexterity. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide. Humans contribute to habitat destruction through the use of natural resources, agriculture, industrial production and urbanization (urban sprawl). Other activities include mining, logging and trawling. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introduction of invasive species, ecosystem nutrient depletion, water and noise pollution are some examples. Loss of habitat can be preceded by an initial habitat fragmentation. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropical rainforests or temperate rainforests, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic community, biotic species being Indigenous (ecology), indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the "medicine chest (idiom), world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to #Deforestation, deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and air pollution, pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforests are cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
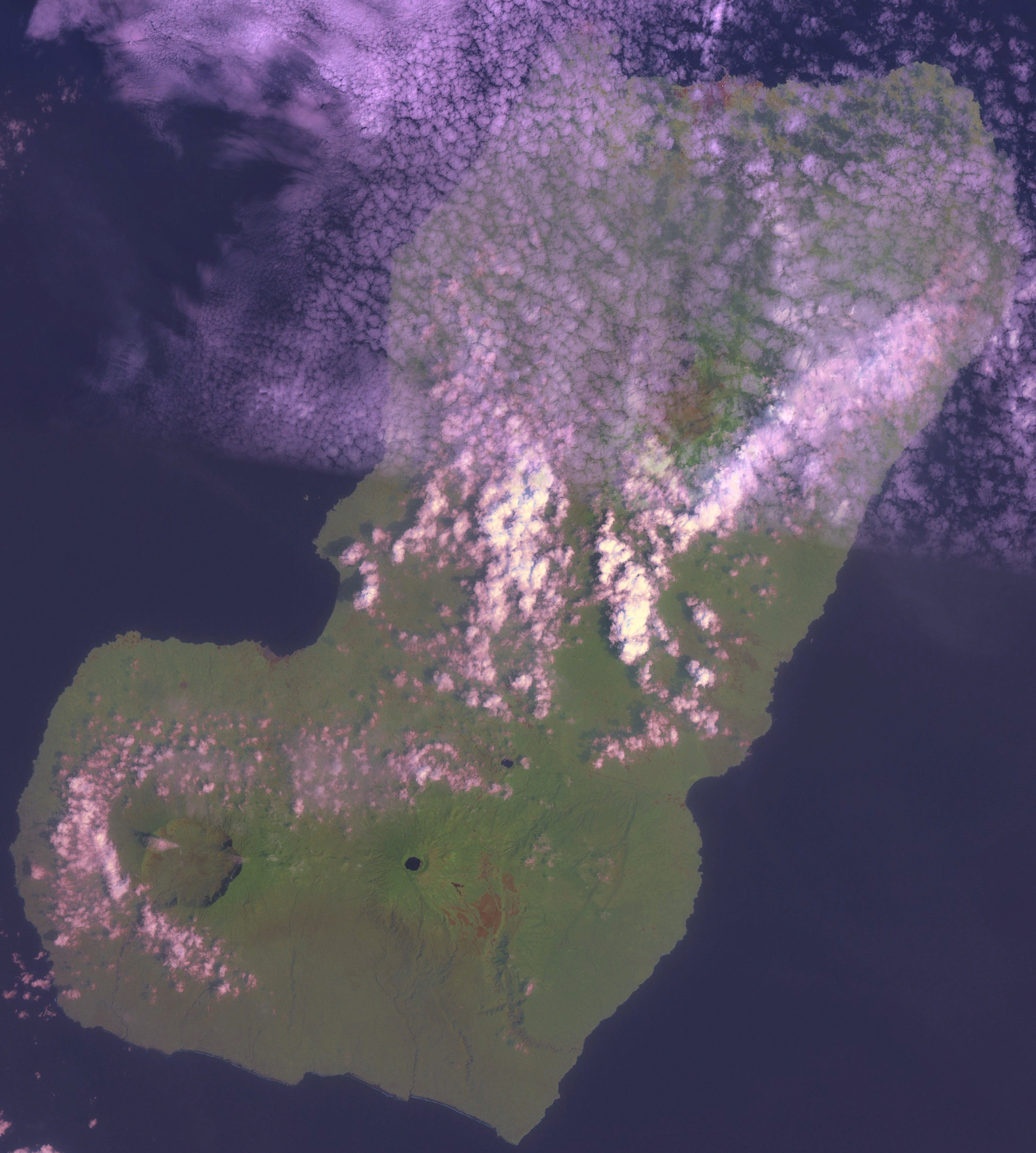
Bioko
Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó, ) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located south of the coast of Cameroon, and northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Bioko's population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá a Ëri'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Pó'' (; ), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then-president of Equatorial Guinea. The current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanaga River
The Sanaga River (formerly ) is the largest river in Cameroon located in East Region (Cameroon), East Region, Centre Region (Cameroon), Centre Region and Littoral Region (Cameroon), Littoral Region. Its length is about from the confluence of Djérem and Lom River. The total length of Sanaga-Djérem River system is about . Djerem is the longest source of Sanaga River with a total length of 464.5 km. Course The Sanaga River has its source at the Adamawa Plateau. It is formed by the confluence of the Djérem River, Djérem and Lom River (Cameroon), Lom Rivers in the north of the East Region (Cameroon), East Region. Djérem River has a total length of and Lom River, Cameroon, Lom River a total length of . Apart from these originating rivers, the largest tributary of Sanaga is Mbam River with a total length of . Climate The Sanaga River forms a boundary between two tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical moist forest ecoregions. The Cross-Sanaga-Bioko coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, a population of more than 230 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising 36 States of Nigeria, states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where its capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria by population is Lagos, one of the largest List of largest cities, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |