|
Magdeburg Hemispheres
The Magdeburg hemispheres are a pair of large copper hemispheres with mating rims that were used in a famous 1654 experiment to demonstrate the power of atmospheric pressure. When the rims were sealed with grease and the air was pumped out, the sphere contained a vacuum and could not be pulled apart by teams of horses. Once the valve was opened, air rushed in and the hemispheres were easily separated. The Magdeburg hemispheres were invented by German scientist and mayor of Magdeburg, Otto von Guericke, to demonstrate the air pump that he had invented and the concept of atmospheric pressure. Speculation varied about the contents of the sphere. Many thought it was simply empty, while others argued the vacuum contained air or some finer aerial substance. Sound did not transmit through the sphere, indicating that sound needed a medium in order to be heard, while light did not. The first artificial vacuum had been produced a few years earlier by Evangelista Torricelli and inspired Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; ) is the Capital city, capital of the Germany, German States of Germany, state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is on the Elbe river. Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archbishopric of Magdeburg, was buried in the city's Magdeburg Cathedral, cathedral after his death. Magdeburg's version of German town law, known as Magdeburg rights, spread throughout Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. In the Late Middle Ages, Magdeburg was one of the largest and most prosperous German cities and a notable member of the Hanseatic League. One of the most notable people from the city was Otto von Guericke, famous for his experiments with the Magdeburg hemispheres. Magdeburg has experienced three major devastations in its history. In 1207 the first catastrophe struck the city, with a fire burning down large parts of the city, including the Magdeburg Cathedral#Previous building, Ottonian cathedral. The Catholic League (German), Catholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire)
The Imperial Diet (; ) was the deliberative body of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not a legislative body in the contemporary sense; its members envisioned it more like a central forum where it was more important to negotiate than to decide. Its members were the Imperial Estates, divided into three colleges. The Diet (assembly), diet as a permanent, regularized institution evolved from the ''Hoftage'' (court assemblies) of the Middle Ages. From 1663 until the end of the empire in 1806, it was in Perpetual Diet of Regensburg, permanent session at Regensburg. All Imperial Estates enjoyed Imperial immediacy, immediacy and, therefore, they had no authority above them besides the Holy Roman Emperor himself. While all the estates were entitled to a seat and vote, only the higher temporal and spiritual princes of the College of Princes enjoyed an individual vote (''Virilstimme''), while lesser estates such as imperial counts and imperial abbots, were merely entitled to a collective vote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horror Vacui (physics)
In philosophy and early physics, ''horror vacui'' ( Latin: ''horror of the vacuum'') or plenism ()—commonly stated as "nature abhors a vacuum", for example by Spinoza—is a hypothesis attributed to Aristotle, later criticized by the atomism of Epicurus and Lucretius, that nature contains no vacuums because the denser surrounding material continuum would immediately fill the rarity of an incipient void. Aristotle also argued against the void in a more abstract sense: since a void is merely nothingness, following his teacher Plato, nothingness cannot rightly be said to exist. Furthermore, insofar as a void would be featureless, it could neither be encountered by the senses nor could its supposition lend additional explanatory power. Hero of Alexandria challenged the theory in the first century AD, but his attempts to create an artificial vacuum failed. The theory was debated in the context of 17th-century fluid mechanics, by Thomas Hobbes and Robert Boyle, among ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
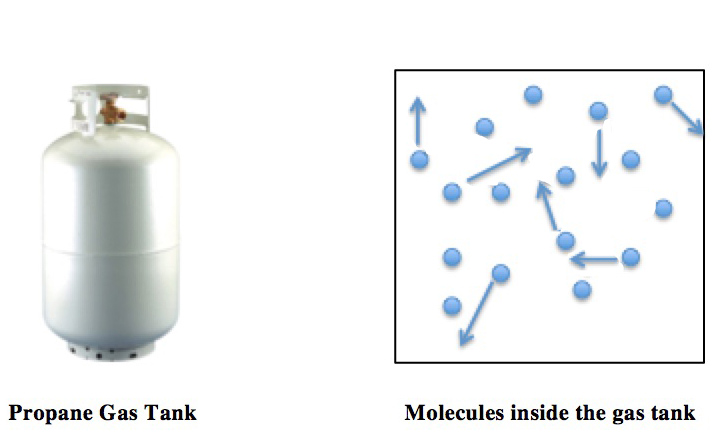
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyle's Law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an empirical gas laws, gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as: The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of substance, amount of gas remain unchanged within a closed system.Levine (1978) p. 12 gives the original definition. Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as: or where is the pressure of the gas, is the volume of the gas, and is a Constant (mathematics), constant for a particular temperature and amount of gas. Boyle's law states that when the temperature of a given mass of confined gas is constant, the product of its pressure and volume is also constant. When comparing the same substance under two different sets of conditions, the law can be expressed as: P_1 V_1 = P_2 V_2. showi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living things at microscopic scale in 1665, using a compound microscope that he designed. Hooke was an impoverished scientific inquirer in young adulthood who went on to become one of the most important scientists of his time. After the Great Fire of London in 1666, Hooke (as a surveyor and architect) attained wealth and esteem by performing more than half of the Boundary (real estate), property line surveys and assisting with the city's rapid reconstruction. Often vilified by writers in the centuries after his death, his reputation was restored at the end of the twentieth century and he has been called "England's Leonardo da Vinci, Leonardo [da Vinci]". Hooke was a Fellow of the Royal Society and from 1662, he was its first Curator of Experimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, Alchemy, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. He is best known for Boyle's law, which describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system. Among his works, ''The Sceptical Chymist'' is seen as a cornerstone book in the field of chemistry. He was a devout and pious Anglican and is noted for his works in theology. Biography Early years Boyle was born at Lismore Castle in County Waterford, in the far south of Ireland, the seventh son and fourteenth child of Richard Boyle, 1st Earl of Cork, the 1st Earl of Cork ("the Great Earl of Cork") and Catherine Fenton Boyle, Catherine Fenton. Lord Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer World
Barometer World was the world's only barometer museum, and was located in the village of Merton, near Great Torrington, Devon, England. Barometer World makes, sells and restores barometers of a variety of types. It was established in 1979 by Philip Collins. In March 2022, Barometer World closed its museum and premises in Merton, Devon. It is now an online-only business. History In 1987 Barometer World moved from The Old Smithy in Merton to its current location at Quicksilver Barn. An exhibition of barometers was opened by Peter Negretti in 1990 and replaced by a new one now on display, the current premises comprises a shop, workshop, and the exhibition. Visitors are advised to e-mail or phone before turning up. The museum's curator is Philip Collins. He started learning the craft of barometer repair in Bideford at the age of 19, and in 1979 established a barometer specialist company. He is an author of barometer books having written numerous books on barometers and restora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Torrington
Great Torrington (often abbreviated to Torrington, though the villages of Little Torrington and Black Torrington are situated in the same region) is a market town in Devon, England. Parts of it are sited on high ground with steep drops down to the River Torridge below, with the lower-lying parts of the town prone to occasional flooding. Torrington is in the centre of Tarka Country, a landscape captured by Henry Williamson in his novel ''Tarka the Otter'' in 1927. Great Torrington has one of the most active volunteering communities in the United Kingdom. In July 2019, Great Torrington was reported to be the healthiest place to live in Britain. Researchers from the University of Liverpool found that the area had low levels of pollution, good access to green space and health services, along with few retail outlets. History There were Iron Age and medieval castles and forts in Torrington, located on the Castle Hill, Torrington, Castle Hill. Great Torrington had strategic sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William, Elector Of Brandenburg
Frederick William (; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he is popularly known as "the Great Elector" (') because of his military and political achievements. Frederick William was a staunch pillar of the Calvinist faith, associated with the rising commercial class. He saw the importance of trade and promoted it vigorously. His shrewd domestic reforms gave Prussia a strong position in the post-Westphalian political order of Northern-Central Europe, setting up Prussia for elevation from duchy to kingdom, achieved under his son and successor. Biography Elector Frederick William was born in Berlin to George William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Elisabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate. His inheritance consisted of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, the Duchy of Cleves, the County of Mark, and the Duchy of Prussia. Owing to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, highest population within its city limits of any city in the European Union. The city is also one of the states of Germany, being the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country by area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.6 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region, as well as the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, fifth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspar Schott
Gaspar Schott (German language, German: ''Kaspar'' (or ''Caspar'') ''Schott''; Latin: ''Gaspar Schottus''; 5 February 1608 – 22 May 1666) was a Germans, German Jesuit and scientist, specializing in the fields of physics, mathematics and natural philosophy, and known for his industry. Biography He was born at Bad Königshofen im Grabfeld. It is probable, but not certain, that his early education was at the Jesuit College at Würzburg. In any case, at the age of 19 he joined the Society of Jesus, entering the novitiate at Trier on 30 October 1627. After two years of novitiate training, he matriculated at the University of Würzburg on 6 November 1629 to begin a three-year study of Philosophy, following the normal academic path prescribed for Jesuit seminarians. Owing to the Swedish invasion of Würzburg in October 1631, the Jesuit community fled the city. Schott went, first to the Jesuit seminary of Tournai in Belgium, and subsequently, in 1633, to Caltagirone in Sicily, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |