|
Lupus In Chinese Astronomy
According to traditional Chinese uranography, the modern constellation Lupus is located within the eastern quadrant of the sky, which is symbolized as the Azure Dragon of the East (東方青龍, ''Dōng Fāng Qīng Lóng''). The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is 豺狼座 (''chái láng zuò''), meaning "the dhole constellation". Stars The map of Chinese constellation in constellation Lupus area consists of: See also *Traditional Chinese star names Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of ... * Chinese constellations References {{reflist External linksLupus – Chinese associations香港太空館https://web.archive.org/web/20120813070951/http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/Research/c_index.htm 研究資源] *中國星區、星官及星名英譯表 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz Kög ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Lupi
Epsilon Lupi, Latinized from ε Lup, is a multiple star system in the southern constellation of Lupus. At an apparent visual magnitude of 3.41, Epsilon Lupi can be readily viewed from the southern hemisphere with sufficiently dark skies. It is the fifth-brightest star or star system in the constellation. Parallax measurements give a distance to this system of roughly . This system is what astronomers term a double-lined spectroscopic binary. When the spectrum is examined, the absorption line features of both stars can be viewed. As a result of the Doppler effect, these lines shift back and forth in frequency as the two stars orbit around each other. This allows some of their orbital elements to be deduced, even though the individual stars have not been resolved with a telescope. The pair share a close, elliptical orbit with a period of 4.55970 days. The orbital eccentricity is 0.277, which means that at the separation at closest approach, or periapsis, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart (Chinese Constellation)
The Heart mansion (; also called ) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellation Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenisti ...s. It is one of the eastern mansions of the Azure Dragon. Its prominent figure is the star Alpha Scorpii. Asterisms References {{DEFAULTSORT:Heart (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psi1 Lupi
Psi1 Lupi, which is Latinized from ψ1 Lupi, is a single star in the southern constellation of Lupus. It has a yellow-white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.66. The star is located at a distance of approximately 207 light years from the Sun based on parallax. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −23 km/s, and is predicted to come to within in 2.8 million years. This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of G8/K0 III. With the hydrogen exhausted at its core, the star has cooled and expanded to 11 times the radius of the Sun. It is a red clump giant, which indicates it is on the horizontal branch and is generating energy through core helium fusion. The star has an estimated 2.4 times the Sun's mass and is radiating 62 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,939 K. The star is surrounded by a cold circumstellar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Lupi
Chi Lupi (Chi Lup, χ Lupi, χ Lup) is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation of Lupus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of approximately 3.957. The primary star in the binary is a mercury-manganese star of spectral type B9.5V; the secondary is a metallic-lined star of type A2Vm. This system is a proper motion member of the Upper Scorpius sub-group in the Scorpius–Centaurus OB association, the nearest such co-moving association of massive stars to the Sun. The Upper Scorpius subgroup contains thousands of stars with an average age of 11 million years old at mean distances of 145 parsec The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, an ...s (470 light years). References {{Stars of Lupus Lupus (constellation) B-type main-sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psi2 Lupi
Psi2 Lupi (ψ2 Lup) is a triple star system in the constellation Lupus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 4.75. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.97 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 360 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction factor of due to interstellar dust. This system is a member of the Upper Centaurus–Lupus subgroup of the Scorpius–Centaurus association. The inner pair of stars in this system form a double-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 12.26 days and an eccentricity of 0.19. The two components are described as similar in appearance. They have the spectrum of a B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B5 V. The luminosity has a micro-variability with a frequency of 0.94483 cycles per day and an amplitude of 0.0067 in magnitude. The third component is a magnitude 10 star at an angular separati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room (Chinese Constellation)
The Room mansion (房宿, pinyin: Fáng Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellation Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" (Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic t ...s. It is one of the eastern mansions of the Azure Dragon. Asterisms {{DEFAULTSORT:Room (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa1 Lupi
Kappa1 Lupi is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Lupus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.86, and forms a double star with Kappa2 Lupi. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 18.12 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 180 light years from the Sun. Both Kappa1 Lupi and its neighbor Kappa2 Lupi are members of the Hyades Stream, which is a moving group that is coincident with the proper motions of the Hyades cluster. This is a B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B9.5 Vne. The 'n' suffix indicates the spectrum shows "nebulous" absorption lines due to rapid rotation, while the 'e' means this is a Be star that displays Balmer series emission lines. With an estimated age of 195 million years, it is about 75% of the way through its life span on the main sequence. The star is rotating with a projected rotational velocity of 191 km/s. This rate of spin is giving the star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Lupi
Sigma Lupi, Latinized from σ Lupi, is a star in the southern constellation of Lupus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.4. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.67 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 580 light years from the Sun. It is a member of the Upper Centaurus–Lupus subgroup of the nearby Sco OB2 association. This is a B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B1/B2 V. Sigma Lupi is a Helium strong star with an enhanced abundance nitrogen and an underabundance of carbon. Jerzykiewicz and Sterken (1992) showed a small amplitude variability with a period of 3.02 days. This suggests it is a close binary system forming a rotating ellipsoidal variable, although other causes such as rotational modulation can not be ruled out. There is a higher frequency photometric variability with a rate of 10.93482 per day and an amplitude of 0.0031 in visual magnitude, but the cause of this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Lupi
Rho Lupi, Latinized from ρ Lupi, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Lupus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.05. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.32 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 316 light years from the Sun. It is a member of the Upper Centaurus–Lupus subgroup of the nearby Scorpius–Centaurus association. This is a B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B3/4 V. It is a microvariable with a period of 10.7 hours and an amplitude of 0.0046 in magnitude. With an age of just 44 million years, the star is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 166 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is an estimated 6% larger than the polar radius. It has an estimated 4.66 times the mass of the Sun and about 3.4 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 365 times the solar luminosity The solar luminosity (), is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Lupi
ζ Lupi (Latinised as Zeta Lupi) is the brighter component of a wide double star in the constellation Lupus, consisting of an orange-hued primary and a fainter secondary with a golden-yellow hue. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.41. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 27.80 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 117.3 light-years from the Sun. This is a probable binary star system. As of 2013, the pair had an angular separation of 71.20 arcseconds along a position angle of 249°. The primary, component A, is an evolved G-type giant star with a visual magnitude of 3.50 and a stellar classification of G7 III. This is a red clump star, indicating that it is generating energy through the thermonuclear fusion of helium in its core region. Its measured angular diameter is , which, at the estimated distance of Zeta Lupi, yields a physical size of about 10 times the radius of the Sun Solar radius is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
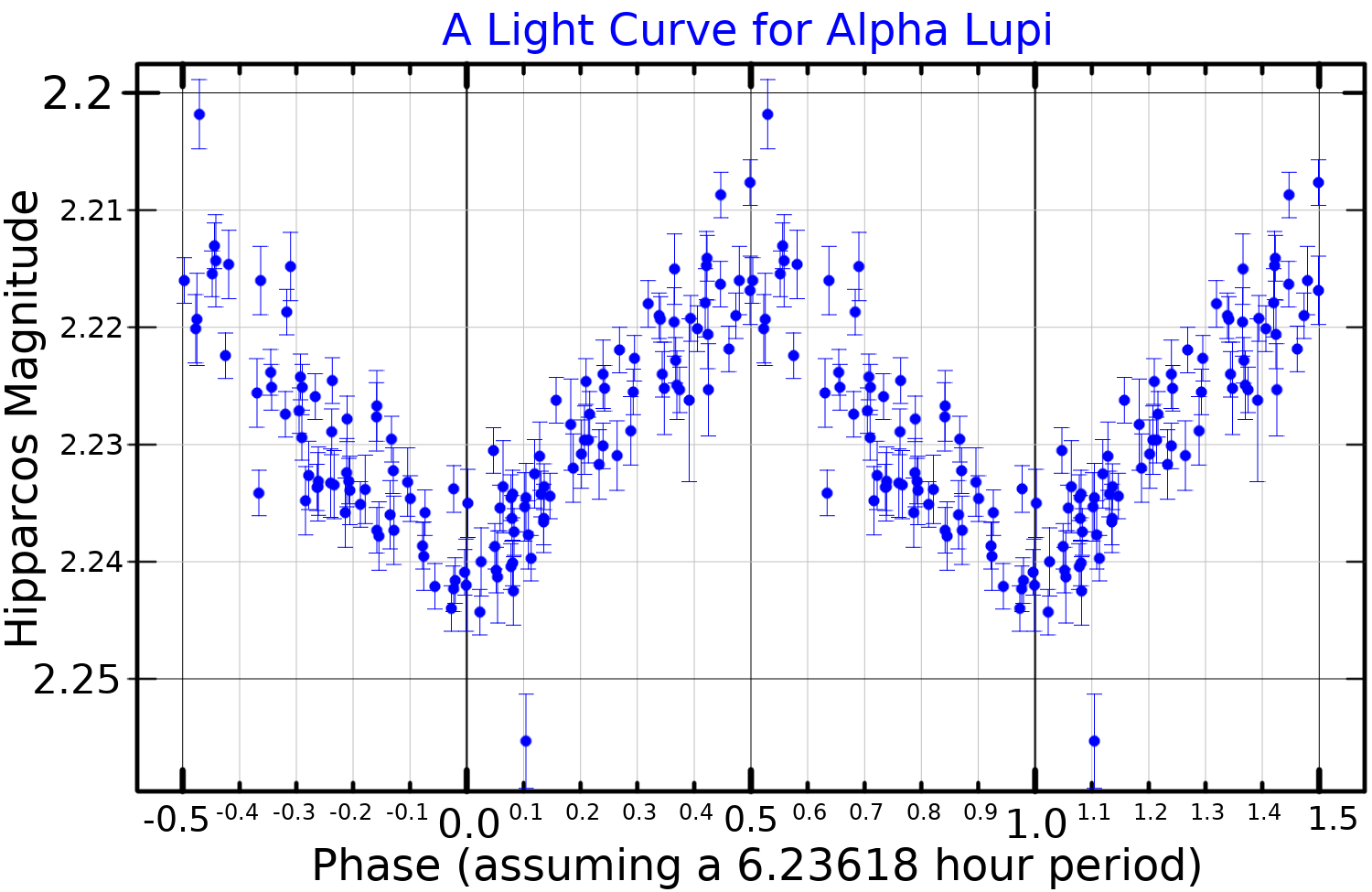
Alpha Lupi
Alpha Lupi (α Lupi, α Lup) is a blue giant star, and the brightest star in the southern constellation of Lupus. According to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, its apparent visual magnitude of 2.3 makes it readily visible to the naked eye even from highly light-polluted locales. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, the star is around from the solar system. It is one of the nearest supernova candidates. Characteristics Alpha Lupi is a giant star with a stellar classification of B1.5 III. It has about ten times the mass of the sun (~) yet is radiating 25,000 times the Sun's luminosity. The outer atmosphere has an effective temperature of 21,820 K, which gives it the blue-white glow of a B-type star. In 1956 it was identified as a Beta Cephei variable by Bernard Pagel and colleagues, which means it undergoes periodic changes in luminosity because of pulsations in the atmosphere. The variability period is 0.29585 days, or just over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |