|
Local Government In New Zealand
New Zealand has a unitary system of government in which the authority of the central government defines sub-national entities. Local government in New Zealand has only the powers conferred upon it by the New Zealand Parliament. In general, local authorities are responsible for enabling democratic local decision-making and promoting the social, economic, environmental, and cultural well-being of their communities, as well as more specific functions for which they have delegated authority. , seventy-eight local authorities cover all areas of New Zealand. Local authorities are positioned within a two-tier structure of territorial authorities (district and city councils) and superimposed regional councils. In addition, district health boards are locally-elected bodies with responsibilities for oversight of health and disability services within a specified area, although these boards are not generally considered to be local authorities in the conventional sense. History The mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago Province
The Otago Province was a province of New Zealand until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. The capital of the province was Dunedin. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the province again in 1870. Area and history Otago Province was one of the six original provinces established in New Zealand in 1853. It covered the lower third of the South Island. Its northern neighbour was the Canterbury Province, and the boundary was the Waitaki River from the Pacific Ocean to its source in the Southern Alps, and from there a straight line to Awarua Bay (now known as Big Bay) on the west coast. The inland area of the Waitaki catchment was unexplored in 1853 and dispute later arose over which branch of the Waitaki should form the boundary. The boundary was delineated in 1861 as following the Ohau River to Lake Ohau and from there a straight line to Mount Aspiring and Awarua Bay. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Labour Government Of New Zealand
The Fourth Labour Government of New Zealand governed New Zealand from 26 July 1984 to 2 November 1990. It was the first Labour government to win a second consecutive term since the First Labour Government of 1935 to 1949. The policy agenda of the Fourth Labour Government differed significantly from that of previous Labour governments: it enacted major social reforms (such as legalising homosexual relations) and economic reforms (including corporatisation of state services and reform of the tax system). The economic reforms became known as "Rogernomics", after Finance Minister Roger Douglas. According to one political scientist: The Labour government also enacted nuclear-free legislation, which led to the United States suspending its treaty obligations to New Zealand under the ANZUS alliance. David Lange led the government for most of its two three-year terms in office. Lange and Douglas had a falling out that divided the party. The government suffered a defeat at the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
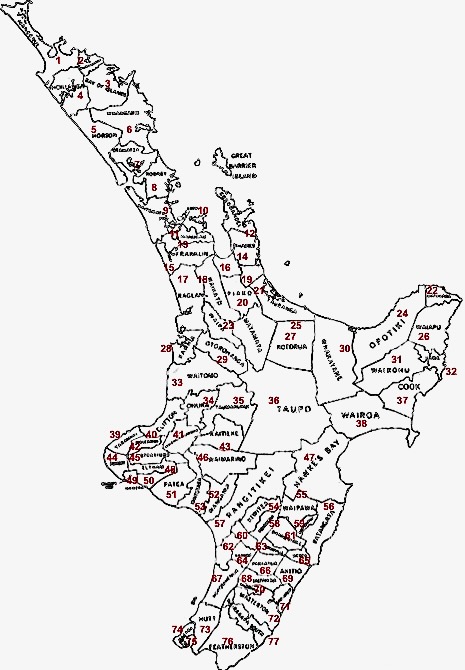
Counties Of New Zealand
A system of counties of New Zealand was instituted after the country dissolved its provinces in 1876, and these counties were similar to other countries' systems, lasting with little change (except mergers and other localised boundary adjustments) until 1989, when they were reorganised into district and city councils within a system of larger regions. History The Counties Bill of 1876 was initiated to merge 314 road boards into 39 counties. However, as a result of lobbying the number of counties had grown to 63 by the time the bill was enacted. They had chairmen, not mayors as boroughs and cities had; many legislative provisions (such as burial and land subdivision control) were different for the counties. By 1966, there were 112 counties. During the second half of the 20th century, many counties received overflow population from nearby cities. The result was often a merger of the two into a "district" (e.g., Rotorua) or a change of name to "district" (e.g., Waimairi) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Holidays In New Zealand
Public holidays in New Zealand (also known as statutory holidays) consist of a variety of cultural, national, and religious holidays that are legislated in New Zealand. Workers can get a maximum of 12 public holidays (eleven national holidays plus one provincial holiday) and a minimum of 20 annual leave days a year. History Bank Holidays in New Zealand originated with a celebration of St Andrew's Day in 1857. Nationwide public holidays began with the Bank Holidays Act 1873, which was based on the UK Bank Holidays Act 1871. Initially there was some resistance to it. Anniversary Days celebrated, from as early as 1843, the first arrivals of settlers in each province. By 1846 the Wellington Anniversary Day was described as having the appearance of an English Fair. A "one off" national public holiday was declared by the Prime Minister for 26 September 2022 to allow people to pay their respects for the passing of Queen Elizabeth II, the longest-reigning monarch of New Zealand. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliamentary Sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty, also called parliamentary supremacy or legislative supremacy, is a concept in the constitutional law of some parliamentary democracies. It holds that the legislative body has absolute sovereignty and is supreme over all other government institutions, including executive or judicial bodies. It also holds that the legislative body may change or repeal any previous legislation and so it is not bound by written law (in some cases, not even a constitution) or by precedent. In some countries, parliamentary sovereignty may be contrasted with separation of powers, which limits the legislature's scope often to general law-making and makes it subject to external judicial review, where laws passed by the legislature may be declared invalid in certain circumstances. Many states have sovereign legislatures, including the United Kingdom, New Zealand, the Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Barbados, Jamaica, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Vogel
Sir Julius Vogel (24 February 1835 – 12 March 1899) was the eighth premier of New Zealand. His administration is best remembered for the issuing of bonds to fund railway construction and other public works. He was the first Jewish prime minister of New Zealand. Historian Warwick R. Armstrong assesses Vogel's strengths and weaknesses: Early life Born in London, Vogel received his early education at University College School in University College, Gower St London. He later studied chemistry and metallurgy at the Royal School of Mines (later part of Imperial College London). He emigrated to Victoria, Australia in 1852, being editor of several newspapers on the goldfields, including the ''Inglewood'' ''Advertiser'' and the ''Maryborough and Dunolly Advertiser''. After an unsuccessful attempt to enter the Victorian Parliament in the Avoca district in August 1861 (he lost to James Macpherson Grant and Benjamin George Davies), he moved to Otago in October 1861, where he b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington City Council
Wellington City Council is a territorial authority in New Zealand, governing the country's capital city Wellington, and ''de facto'' second-largest city (if the commonly considered parts of Wellington, the Upper Hutt, Porirua, Lower Hutt and often the Kapiti Coast, are taken into account; these, however have independent councils rather than a supercity governance like Auckland, and so Wellington City is legally only third-largest city by population, behind Auckland and Christchurch). It consists of the central historic town and certain additional areas within the Wellington metropolitan area, extending as far north as Linden and covering rural areas such as Mākara and Ohariu. The city adjoins Porirua in the north and Hutt City in the north-east. It is one of nine territorial authorities in the Wellington Region. Wellington attained city status in 1886. The settlement had become the colonial capital and seat of government by 1865, replacing Auckland. Parliament official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria University Of Wellington
Victoria University of Wellington ( mi, Te Herenga Waka) is a university in Wellington, New Zealand. It was established in 1897 by Act of Parliament, and was a constituent college of the University of New Zealand. The university is well known for its programmes in law, the humanities, and some scientific disciplines, and offers a broad range of other courses. Entry to all courses at first year is open, and entry to second year in some programmes (e.g. law, criminology, creative writing, architecture, engineering) is restricted. Victoria had the highest average research grade in the New Zealand Government's Performance Based Research Fund exercise in both 2012 and 2018, having been ranked 4th in 2006 and 3rd in 2003. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Corporation
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally owned corporations. Municipal corporation as local self-government Municipal incorporation occurs when such municipalities become self-governing entities under the laws of the state or province in which they are located. Often, this event is marked by the award or declaration of a municipal charter. A city charter or town charter or municipal charter is a legal document establishing a municipality, such as a city or town. Canada In Canada, charters are granted by provincial authorities. India The Corporation of Chennai is the oldest Municipal Corporation in the world outside the United Kingdom. Ireland The title "corporation" was used in boroughs from soon after the Norman conquest until the Local Government Act 2001. Under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westland Province
The Westland Province was a province of New Zealand from 1873 until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. The capital was Hokitika. Area and history The area was part of Canterbury Province when the provinces were created in 1853. By 1868, triggered by the population growth associated with the West Coast Gold Rush, the West Coast region was separated from Canterbury Province with the formation of the County of Westland. The boundary to Canterbury was defined as the crest of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana. This county was not a true province, as it had all the administrative powers of a provincial council, but saw the legislative powers remain with Parliament in Wellington. Members of Parliament were not happy with having to spend their time on local legislation, and in 1873 the government elevated the county to full provincial status – the last of the 10 New Zealand provinces to be established. The province covered an area roughly the same as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southland Province
The Southland Province was a Provinces of New Zealand, province of New Zealand from March 1861, when it split from Otago Province, until 1870, when it rejoined Otago. History Following the passage of the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 by the British Parliament, New Zealand was divided into six new provinces in 1853, the southern part of the South Island was part of the Otago Province. Settlers in Murihiku, the southernmost part of the South Island purchased from Māori people, Māori in 1853 by Walter Mantell, petitioned the government for separation from Otago. Petitioning started in 1857. The central government's New Zealand Parliament, General Assembly passed the New Provinces Act in 1858, and the Province of Southland was proclaimed in 1861. It was named Southland despite the wishes of many settlers and Māori, who preferred Murihiku. The province started to accumulate debt, whereas Otago prospered due to the Central Otago Gold Rush. By the late 1860s, most settlers wante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |