|
List Of Stars In Dorado ...
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Dorado, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also *Lists of stars by constellation References * * * * * * {{Dorado *List Dorado Dorado () is a constellation in the southern sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the dolphinfish (''Coryphaena hippurus''), which is known as ''dorado'' in Spanish, altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
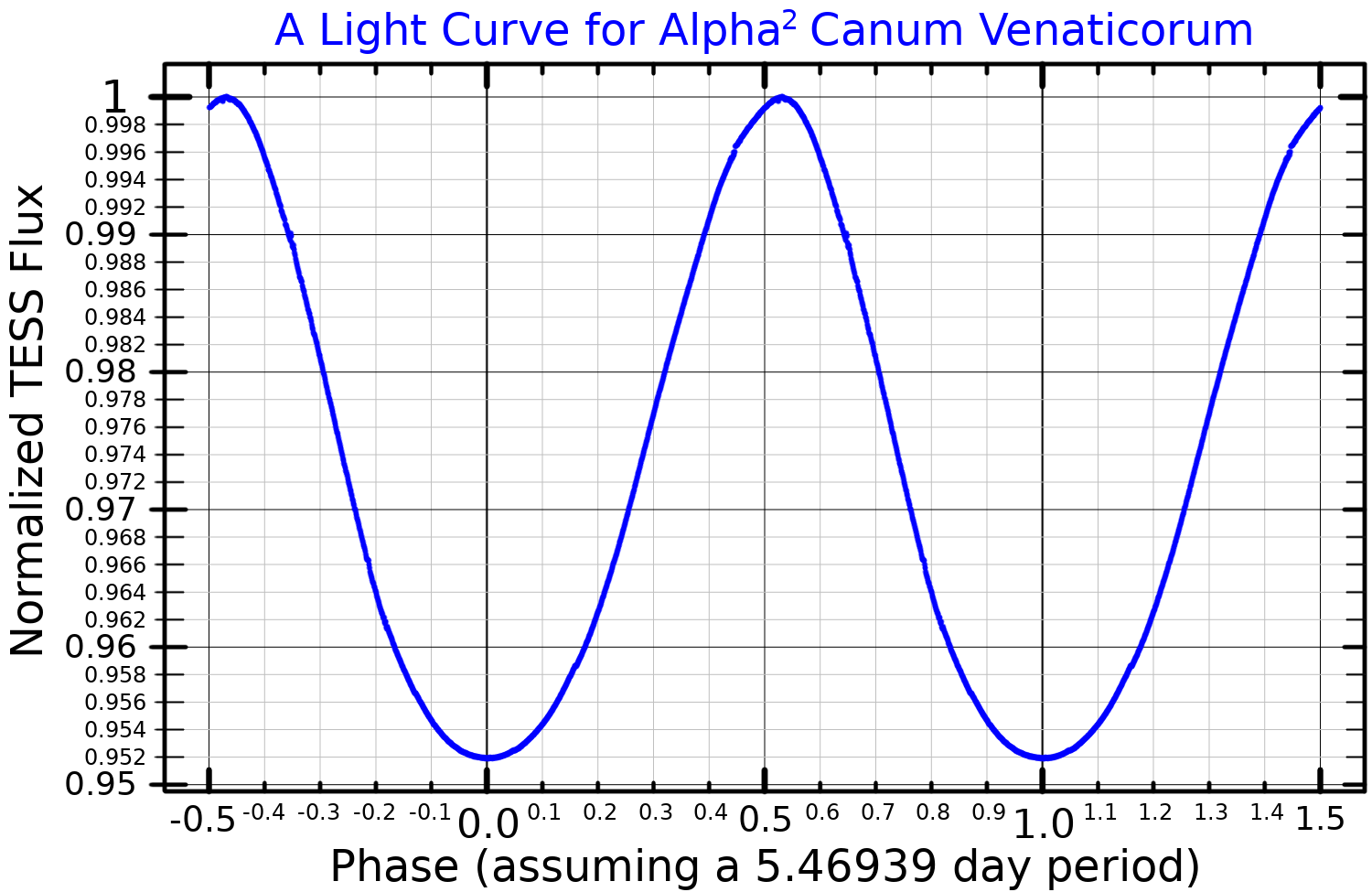
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum Variable
An Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of variable star. These stars are chemically peculiar main sequence stars of spectral class B8p to A7p. They have strong magnetic fields and strong silicon, strontium, or chromium spectral lines. Their brightness typically varies by 0.01 to 0.1 magnitudes over the course of 0.5 to 160 days. In addition to their intensities, the intensities and profiles of the spectral lines of α2 CVn variables also vary, as do their magnetic fields. The periods of these variations are all equal and are believed to equal the period of rotation of the star. It is thought that they are caused by an inhomogeneous distribution of metals in the atmospheres of these stars, so that the surface of the star varies in brightness from point to point. The type-star which this class is named after is α² Canum Venaticorum, a star in the binary system of Cor Caroli, which is in the northern constellation A constellation is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Doradus
Epsilon Doradus, Latinzied from ε Doradus, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation of Dorado. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.11. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.68 mas as measured from Earth, it is located roughly 570 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.09 due to interstellar dust. This is a B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B6 V. It is a slowly pulsating B-type star with a mean longitudinal magnetic field strength of . With 4.31 times the mass of the Sun and 3.8 times the Sun's radius, it is about 85% of the way through its main sequence lifetime. The star is an estimated 210 million years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 17 km/s. Epsilon Doradus radiates 556 times the solar luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Doradus
Nu Doradus, Latinized from ν Doradus, is a single, blue-white hued star in the southern constellation of Dorado. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.06. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.88 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 300 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction of 0.07 due to interstellar dust. It is moving further from the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of +17.5 km/s. This is an ordinary B-type main-sequence star, as indicated by its stellar classification of B8 V. It is an estimated 118 million years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 98 km/s. The star has 2.7 times the mass of the Sun and about 3.2 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 107 times the Sun's luminosity from its photoshere at an effective temperature of 11,381 K. No infrared excess An infrared excess is a measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiregular Variable
In astronomy, a semiregular variable star, a type of variable star, is a giant or supergiant of intermediate and late (cooler) spectral type showing considerable periodicity in its light changes, accompanied or sometimes interrupted by various irregularities. Periods lie in the range from 20 to more than 2000 days, while the shapes of the light curves may be rather different and variable with each cycle. The amplitudes may be from several hundredths to several magnitudes (usually 1-2 magnitudes in the V filter). Classification The semiregular variable stars have been sub-divided into four categories for many decades, with a fifth related group defined more recently. The original definitions of the four main groups were formalised in 1958 at the tenth general assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) has updated the definitions with some additional information and provided newer reference stars where old examples such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta2 Doradus
Eta2 Doradus, Latinized from η2 Doradus, is a star in the southern constellation of Dorado. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, reddish star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.01 It is about 580 light years from the Sun as shown by parallax, and its net movement is one of receding, having a radial velocity of +34.5 km/s. It is circumpolar south of latitude S. This object is an M-type giant star, with its stellar classification being M2.5III. It has left the main sequence after exhausting its core hydrogen and expanded to around . The star is radiating about 1200 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere, at an effective temperature of 3726 K. References External links * 2004. Starry Night Pro, Version 5.8.4. Imaginova Imaginova Corporation is a U.S. digital commerce company based in Watsonville, California. The company, which was started in 1999 as "Space.com" by CNN business anchor Lou Dobbs, later became known as Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Doradus
Theta Doradus, Latinized from θ Doradus, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Dorado. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 6.64 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 490 light years from the Sun. With an apparent visual magnitude of +4.82, the star is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. This is an evolved orange-hued K-type giant star with a stellar classification of , where the suffix indicates it is a chemically peculiar star with a strong CN band. With an age of around 1.17 billion years, it has an estimated 2.23 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to about 16 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 426.6 times the solar luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Doradus
Zeta Doradus, Latinized from ζ Doradus, is a young star system that lies approximately 38 light-years away. The system consists of two widely separated stars, with the primary being bright enough to be observed with the naked eye but the secondary being much a much fainter star that requires telescopic equipment to be observed. Components Zeta Doradus A is a bright, high proper motion star with a spectral type of F7V, meaning that it is a main sequence star that is hotter and brighter than the Sun. With an apparent magnitude of 4.82, it is approximately the eighth brightest star in the constellation of Dorado. Though it has been known that Zeta Doradus B is a nearby star since at least the Gliese Catalogue of Nearby Stars, the connection that it is a common proper motion companion to Zeta Doradus A was only made much more recently thanks to Hipparcos satellite data. The two stars form a wide binary, with a physical separation between the components of about 0.018 par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 40409
HD 40409 is a suspected astrometric binary star system in the southern constellation of Dorado. It is a faint system but visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.65. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located 88 light years away from the Sun. It is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +25 km/s. The system has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of per year along a position angle of 14.51°. Based on the stellar classification of K2 III assigned by Gray et al. (2006), the visible component is a K-type giant star. In contrast, Keenan and McNeil (1989) gave it a somewhat less evolved classification of K2 III–IV. It is about eight billion years old with 12% more mass than the Sun, and has expanded to 4.8 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 11 times the Sun's luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Doradus
δ Doradus (often Latinised to Delta Doradus, abbreviated to δ Dor or delta Dor) is a star in the southern constellation of Dorado. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 21.80 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 150 light years from the Sun. The star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.34. This is an A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A7 V. The star is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 172 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is 12% larger than the polar radius. Although A-type stars are not expected to harbor a magnetic dynamo needed to power X-ray emission, an X-ray flux of has been detected at these coordinates. This may indicate that the star has an unseen companion. δ Doradus displays an infrared excess suggesting it may be a Vega-like star with an orbiting debris disk. Currently this star is the Moon's south pole st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Doradus Variable
Gamma Doradus variables are variable stars which display variations in luminosity due to non-radial pulsations of their surface. The stars are typically young, early F or late A type main sequence stars, and typical brightness fluctuations are 0.1 magnitudes with periods on the order of one day. This class of variable stars is relatively new, having been first characterized in the second half of the 1990s, and details on the underlying physical cause of the variations remains under investigation. The star 9 Aurigae was first noticed to be variable in 1990. However, none of the currently-accepted explanations were adequate: it pulsated too slowly and was outside of the Delta Scuti instability strip, and there was no evidence for any eclipsing material, although Gamma Doradus and HD 96008 were noted to be similar. These three stars, as well as HD 224638, were soon hypothesized to belong to a new class of variable stars in which variability was produced by g-mode pulsations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |