|
List Of Spherical Symmetry Groups
Finite spherical symmetry groups are also called point groups in three dimensions. There are five fundamental symmetry classes which have triangular fundamental domains: dihedral, cyclic, tetrahedral, octahedral, and icosahedral symmetry. This article lists the groups by Schoenflies notation, Coxeter notation, orbifold notation, and order. John Conway uses a variation of the Schoenflies notation, based on the groups' quaternion algebraic structure, labeled by one or two upper case letters, and whole number subscripts. The group order is defined as the subscript, unless the order is doubled for symbols with a plus or minus, "±", prefix, which implies a central inversion. Hermann–Mauguin notation (International notation) is also given. The crystallography groups, 32 in total, are a subset with element orders 2, 3, 4 and 6.Sands, 1993 Involutional symmetry There are four involutional groups: no symmetry (C1), reflection symmetry (Cs), 2-fold rotational symmetry (C2), and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Groups In Three Dimensions
In geometry, a point group in three dimensions is an isometry group in three dimensions that leaves the origin fixed, or correspondingly, an isometry group of a sphere. It is a subgroup of the orthogonal group O(3), the group of all isometries that leave the origin fixed, or correspondingly, the group of orthogonal matrices. O(3) itself is a subgroup of the Euclidean group E(3) of all isometries. Symmetry groups of geometric objects are isometry groups. Accordingly, analysis of isometry groups is analysis of possible symmetries. All isometries of a bounded (finite) 3D object have one or more common fixed points. We follow the usual convention by choosing the origin as one of them. The symmetry group of an object is sometimes also called its full symmetry group, as opposed to its proper symmetry group, the intersection of its full symmetry group with E+(3), which consists of all ''direct isometries'', i.e., isometries preserving orientation. For a bounded object, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbifold Notation
In geometry, orbifold notation (or orbifold signature) is a system, invented by the mathematician William Thurston and promoted by John Conway, for representing types of symmetry groups in two-dimensional spaces of constant curvature. The advantage of the notation is that it describes these groups in a way which indicates many of the groups' properties: in particular, it follows William Thurston in describing the orbifold obtained by taking the quotient of Euclidean space by the group under consideration. Groups representable in this notation include the point groups on the sphere (S^2), the frieze groups and wallpaper groups of the Euclidean plane (E^2), and their analogues on the hyperbolic plane (H^2). Definition of the notation The following types of Euclidean transformation can occur in a group described by orbifold notation: * reflection through a line (or plane) * translation by a vector * rotation of finite order around a point * infinite rotation around a line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group C2v
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is the sphere's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihedral Group
In mathematics, a dihedral group is the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, which includes rotations and reflections. Dihedral groups are among the simplest examples of finite groups, and they play an important role in group theory, geometry, and chemistry. The notation for the dihedral group differs in geometry and abstract algebra. In geometry, or refers to the symmetries of the -gon, a group of order . In abstract algebra, refers to this same dihedral group. This article uses the geometric convention, . Definition Elements A regular polygon with n sides has 2n different symmetries: n rotational symmetries and n reflection symmetries. Usually, we take n \ge 3 here. The associated rotations and reflections make up the dihedral group \mathrm_n. If n is odd, each axis of symmetry connects the midpoint of one side to the opposite vertex. If n is even, there are n/2 axes of symmetry connecting the midpoints of opposite sides and n/2 axes of symmetry connecting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group C2h
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group S4
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is the sphere's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
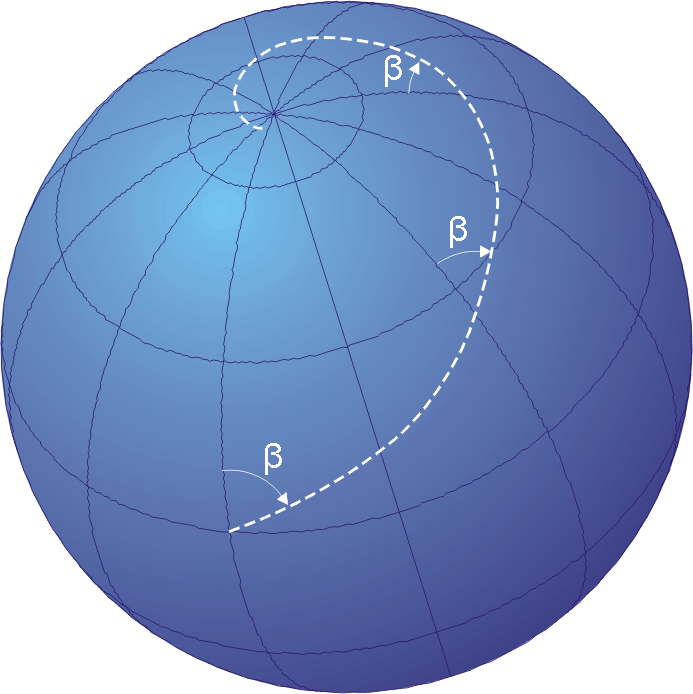
Cyclic Symmetries
In three dimensional geometry, there are four infinite series of point groups in three dimensions (''n''≥1) with ''n''-fold rotational or reflectional symmetry about one axis (by an angle of 360°/''n'') that does not change the object. They are the finite symmetry groups on a cone. For ''n'' = ∞ they correspond to four frieze groups. Schönflies notation is used. The terms horizontal (h) and vertical (v) imply the existence and direction of reflections with respect to a vertical axis of symmetry. Also shown are Coxeter notation in brackets, and, in parentheses, orbifold notation. Types ;Chiral: *''Cn'', sup>+, (''nn'') of order ''n'' - ''n''-fold rotational symmetry - acro-n-gonal group (abstract group ''Zn''); for ''n''=1: no symmetry ( trivial group) ;Achiral: *''Cnh'', +,2 (''n''*) of order 2''n'' - prismatic symmetry or ortho-n-gonal group (abstract group ''Zn'' × ''Dih1''); for ''n''=1 this is denoted by ''Cs'' (1*) and called reflection symmetry, also bil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group Cs
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group Ci
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group C2
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Group
In group theory, a branch of abstract algebra in pure mathematics, a cyclic group or monogenous group is a group, denoted C''n'', that is generated by a single element. That is, it is a set of invertible elements with a single associative binary operation, and it contains an element ''g'' such that every other element of the group may be obtained by repeatedly applying the group operation to ''g'' or its inverse. Each element can be written as an integer power of ''g'' in multiplicative notation, or as an integer multiple of ''g'' in additive notation. This element ''g'' is called a '' generator'' of the group. Every infinite cyclic group is isomorphic to the additive group of Z, the integers. Every finite cyclic group of order ''n'' is isomorphic to the additive group of Z/''n''Z, the integers modulo ''n''. Every cyclic group is an abelian group (meaning that its group operation is commutative), and every finitely generated abelian group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Symmetry Group C1
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is the sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |