|
List Of Communications Satellite Firsts
Milestones in the history of communications satellite A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth ...s. See also * Timeline of first artificial satellites by country * First images of Earth from space References {{DEFAULTSORT:Communications satellite firsts *Firsts Lists of firsts in space Satellite firsts Technology-related lists Lists of satellites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this honor was subsequently passed to Helsinki due to Japan's invasion of China, before ultimately being cancelled due to World War II. Tokyo was chosen as the host city during the 55th IOC Session in West Germany on 26 May 1959. The 1964 Summer Games were the first Olympics held in Asia, and marked the first time South Africa was excluded due to the use of its apartheid system in sports. Until 1960, South Africa had fielded segregated teams, conforming to the country's racial classifications; for the 1964 Games the International Olympic Committee demanded a multi-racial delegation to be sent, and after South Africa refused, they were excluded from participating. The country was, however, allowed to compete at the 1964 Summer Paralympics, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
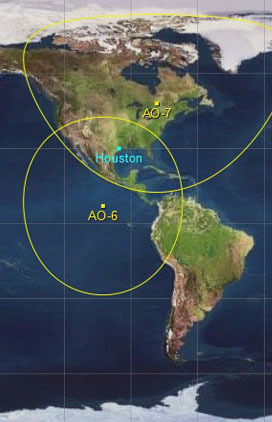
AMSAT-OSCAR 7
AMSAT-OSCAR 7, or AO-7, is the second Phase 2 amateur radio satellite constructed by the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation or AMSAT. It was launched into Low Earth Orbit on November 15, 1974 and remained operational until a battery failure in 1981. Then after 21 years of apparent silence, the satellite was heard again on June 21, 2002 – 27 years after launch. At that time the public learned that the satellite had remained intermittently functional and was used surreptitiously for communication by the anticommunist opposition Fighting Solidarity during martial law in Poland. AO-7 is the oldest amateur satellite still in use, and is one of the oldest operational communications satellites. It carries two amateur radio transponders. Its "Mode A" transponder has an uplink on the 2-meter band and a downlink on the 10-meter band. The "Mode B" transponder has an uplink on the 70-centimeter band and a downlink on the 2-meter band. The satellite also carries four beacons which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphonie
The Symphonie satellites (2 satellites orbited) were the first communications satellites built by France and Germany (and the first to use three-axis stabilization in geostationary orbit with a bipropellant propulsion system) to provide geostationary orbit injection and station-keeping during their operational lifetime. After the launch of the second flight model, they comprised the first complete telecommunications satellite system (including an on-orbit spare and a dedicated ground control segment). They were the result of a program of formal cooperation between France and Germany. 1963–1970: Beginnings * January 22, 1963: Signing by President Charles de Gaulle and Chancellor Konrad Adenauer of the Élysée Treaty, an agreement for Franco-German cooperation. Start of preliminary studies in France (SAROS project) and in Germany (Olympia project) of communications satellites. * June 1967: Both countries sign an intergovernmental convention concerning the launch and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Broadcast Satellite
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver then decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Modern systems signals are relayed from a communications satellite on the X band (8–12 GHz) or Ku band (12–18 GHz) frequencies requiring only a small dish less than a meter in diameter. The first satellite TV systems were an obsolete type now known as television receive-only. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-axis Stabilized
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle/satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires sensors to measure vehicle orientation, actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on (1) sensor measurements of the current attitude and (2) specification of a desired attitude. The integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called guidance, navigation and control (GNC). Overview A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It is often needed so that the spacecraft high-gain antenna may be accurately pointed to Earth for communications, so that onboard experiments may accomplish precise pointing for accurate collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATS-6
ATS-6 (Applications Technology Satellite-6) was a NASA experimental satellite, built by Fairchild Space and Electronics Division It has been called the world's first educational satellite as well as world's first experimental Direct Broadcast Satellite as part of the Satellite Instructional Television Experiment between NASA and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was launched May 30, 1974, and decommissioned July 1979. At the time of launch, it was the most powerful telecommunication satellite in orbit. ATS-6 carried no fewer than 23 different experiments, and introduced several breakthroughs. It was the first 3-axis stabilized spacecraft in geostationary orbit. It was also the first to use experimentally with some success electric propulsion in geostationary orbit. It also carried several particle physics experiments, including the first heavy ion detector in geostationary orbit. During its five-year life, ATS-6 transmitted connection programming to various c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anik 1
The Anik satellites are a series of geostationary communications satellites launched for Telesat Canada for television, voice and data in Canada and other parts of the world, from 1972 through 2013. Some of the later satellites in the series remain operational in orbit, while others have been retired to a graveyard orbit. The naming of the satellite was determined by a national contest, and was won by Julie-Frances Czapla of Saint-Léonard, Québec. In Inuktitut, ''Anik'' means "little brother". Satellites Anik A The Anik A satellites were the world's first national domestic satellites. (Prior to Anik A1's launch, all geosynchronous communications satellites were transcontinental, i.e. Intelsat I and others.) The Anik A fleet of three satellites gave CBC the ability to reach the Canadian North for the first time. Each of the satellites was equipped with 12 C-band transponders, and thus had the capacity for 12 colour television channels. Three channels were allocate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimbus Program
The Nimbus satellites were second-generation U.S. robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1978 used for meteorological research and development. The spacecraft were designed to serve as stabilized, Earth-oriented platforms for the testing of advanced systems to sense and collect atmospheric science data. Seven Nimbus spacecraft have been launched into near-polar, sun-synchronous orbits beginning with Nimbus 1 on August 28, 1964. On board the Nimbus satellites are various instrumentation for imaging, sounding, and other studies in different spectral regions. The Nimbus satellites were launched aboard Thor-Agena rockets (Nimbus 1–4) and Delta rockets (Nimbus 5–7). Over a 20-year period from the launch of the first satellite, the Nimbus series of missions was the United States' primary research and development platform for satellite remote sensing of the Earth. The seven Nimbus satellites, launched over a fourteen-year period, shared their space-based observations of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver then decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Modern systems signals are relayed from a communications satellite on the X band (8–12 GHz) or Ku band (12–18 GHz) frequencies requiring only a small dish less than a meter in diameter. The first satellite TV systems were an obsolete type now known as television receive-only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |