|
Lewis Paul
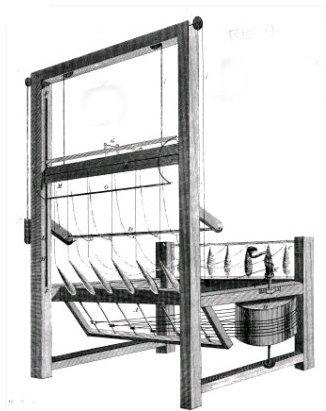
Lewis Paul (died 1759) was the original inventor of roller spinning, the basis of the water frame for spinning cotton in a cotton mill. Life and work Lewis Paul was of Huguenot descent. His father was physician to Lord Shaftesbury. He may have begun work on designing a spinning machine for cotton as early as 1729, but probably did not make practical progress until after 1732 when he met John Wyatt, a carpenter then working in Birmingham for a gun barrel forger. Wyatt had designed a machine, probably for cutting files, in which Paul took an interest. Roller spinning was certainly Paul's idea, and Wyatt built a machine (or model) for him. Paul obtained a patent for this on 24 June 1738. He then set about trying to license his machine, though some licences were granted in satisfaction of debts. In 1741, he set up a machine powered by two asses in the Upper Priory in Birmingham, near his house in Old Square. Mills using the roller spinning patent Edward Cave, a publisher, obta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul 1758 Patent Drawing
Paul may refer to: *Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name) *Paul (surname), a list of people People Christianity *Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Christian missionary and writer *Pope Paul (other), multiple Popes of the Roman Catholic Church *Saint Paul (other), multiple other people and locations named "Saint Paul" Roman and Byzantine empire *Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 BC – 160 BC), Roman general *Julius Paulus Prudentissimus (), Roman jurist *Paulus Catena (died 362), Roman notary *Paulus Alexandrinus (4th century), Hellenistic astrologer *Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (625–690), Greek surgeon Royals *Paul I of Russia (1754–1801), Tsar of Russia *Paul of Greece (1901–1964), King of Greece Other people *Paul the Deacon or Paulus Diaconus (c. 720 – c. 799), Italian Benedictine monk *Paul (father of Maurice), the father of Maurice, Byzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; it had a population of 212,100 in its previous local authority in the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census (225,100 as of 2018 estimates). In its urban area, which includes Boughton, Northamptonshire, Boughton and Moulton, Northamptonshire, Moulton, it had a population of 215,963 as of 2011. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates to the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age, Roman conquest of Britain, Romans and Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxons. In the Middle Ages, the town rose to national significance with the establishment of Northampton Castle, an occasional royal residence which regularly hosted the Parliament of England. Medieval Northampton had many churches, monasteries and the University of Northampton (thirteenth century), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1759 Deaths
In Great Britain, this year was known as the ''Annus Mirabilis'', because of British victories in the Seven Years' War. Events January–March * January 6 – George Washington marries Martha Dandridge Custis. * January 11 – In Philadelphia, the first American life insurance company is incorporated. * January 13 – Távora affair: The Távora family is executed, following accusations of the attempted regicide of Joseph I of Portugal. * January 15 – **Voltaire's satire ''Candide'' is published simultaneously in five countries. ** The British Museum opens at Montagu House in London (after six years of development). * January 27 – Battle of Río Bueno: Spanish forces, led by Juan Antonio Garretón, defeat indigenous Huilliches of southern Chile. * February 12 – Ali II ibn Hussein becomes the new Ruler of Tunisia upon the death of his brother, Muhammad I ar-Rashid. Ali reigns for 23 years until his death in 1782. * February 16 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile Workers
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile Engineering
Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products. Different types of fibres are used to produce yarn. Cotton remains the most widely used and common natural fiber making up 90% of all-natural fibers used in the textile industry. People often use cotton clothing and accessories because of comfort, not limited to different weathers. There are many variable processes available at the spinning and fabric-forming stages coupled with the complexities of the finishing and colouration processes to the production of a wide range of products. History Textile manufacturing in the modern era is an evolved form of the art and craft industries. Until the 18th and 19th centuries, the textile industry was a household work. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Inventors
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Arkwright
Sir Richard Arkwright (23 December 1732 – 3 August 1792) was an English inventor and a leading entrepreneur during the early Industrial Revolution. He is credited as the driving force behind the development of the spinning frame, known as the water frame after it was adapted to use water power; and he patented a rotary carding engine to convert raw cotton to 'cotton lap' prior to spinning. He was the first to develop factories housing both mechanised carding and spinning operations. Arkwright's achievement was to combine power, machinery, semi-skilled labour and the new raw material of cotton to create mass-produced yarn. His organisational skills earned him the accolade "father of the modern industrial factory system," notably through the methods developed in his mill at Cromford, Derbyshire (now preserved as part of the Derwent Valley Mills World Heritage Site). Life and family Richard Arkwright was born in Preston, Lancashire, England on 23 December 1732, the youngest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Highs
Thomas Highs (1718–1803), of Leigh, Lancashire, was a reed-maker and manufacturer of cotton carding and spinning engines in the 1780s, during the Industrial Revolution. He is known for claiming patents on a spinning jenny (invented by James Hargreaves), a carding machine and the throstle (a machine for the continuous twisting and winding of wool). Life and work Thomas Highs, sometimes spelled Thomas Hayes, was born in Leigh, Lancashire in 1718 and lived most of his life there. It is said he was a reed maker. The reed is a comb-like strip attached to the batten of a loom, which keeps the warp threads apart and helps the weaver pack the weft threads tightly on the newly-woven cloth. He married Sarah Moss on 23 February 1747, at Leigh Parish Church. Five years after his marriage, he became interested in cotton-spinning machinery and between 1763 and 1764, he worked to produce a spinning engine with John Kay, a clockmaker,see Retrieved on 3 September 2006. who was a close ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kay (spinning Frame)
John Kay was an English inventor best known for the development of the spinning frame in 1767, which marked an important stage in the development of textile manufacturing during the Industrial Revolution. Born in Warrington in Lancashire, England, Kay was at least the co-constructor of the first spinning frame, and was a claimant to having been its inventor. He is sometimes confused with the unrelated John Kay from Bury, Lancashire, who had invented the flying shuttle, a weaving machine, some thirty years earlier. John Kay and Thomas Highs In 1763, Kay was working as a clockmaker in Leigh. A neighbour of his, Thomas Highs, was an inventor, and the two collaborated in investigations of machinery for the manufacture of textiles, including the spinning of thread by means of rollers. By 1763 weaving was already automated, but spinning was still done by hand. Lewis Paul had made a machine using mechanical rollers in 1738, but this had not been a commercial success. John Kay and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
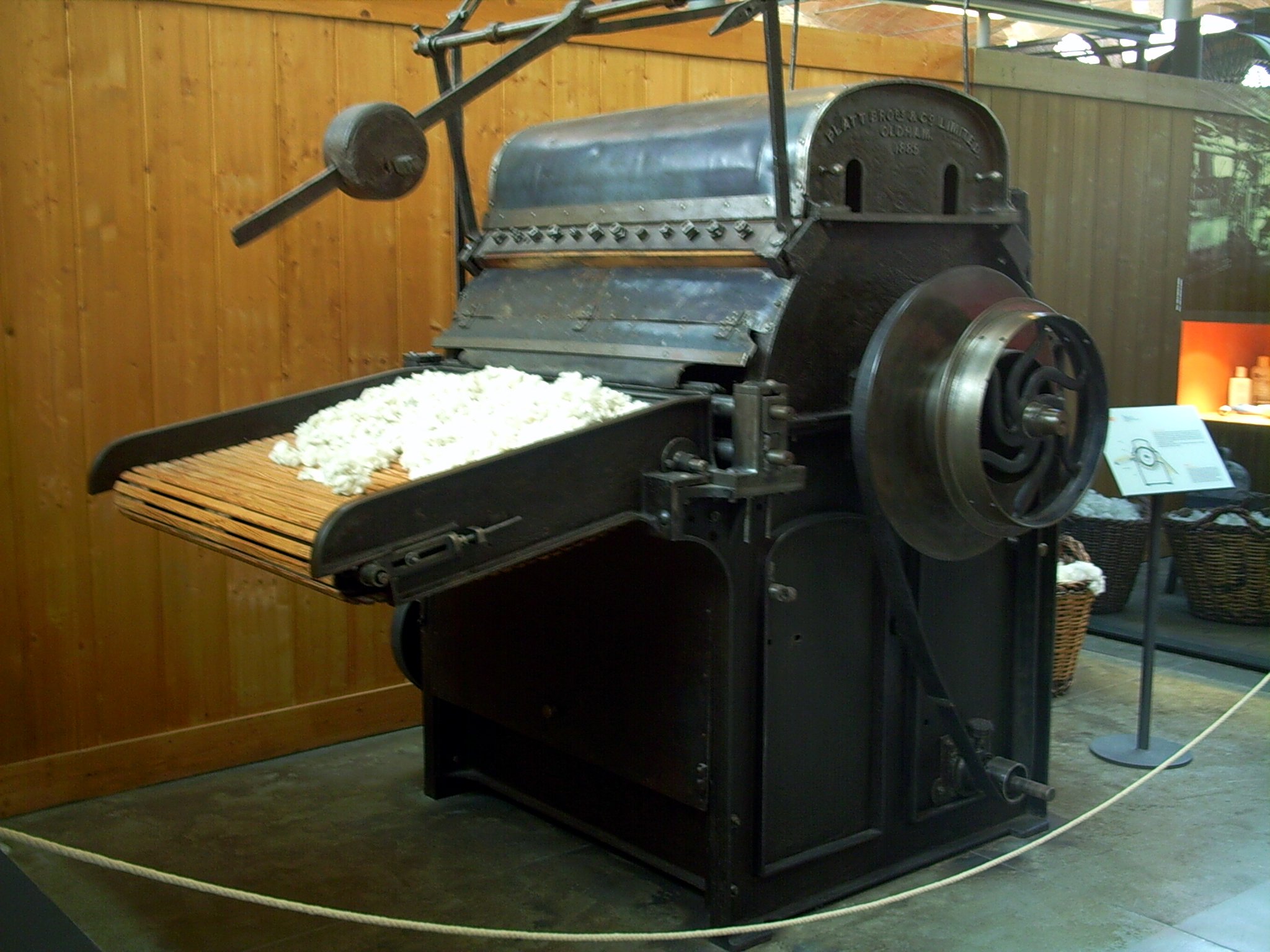
Carding
Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibres to produce a continuous web or sliver (textiles), sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibres between differentially moving surfaces covered with "card clothing", a firm flexible material embedded with metal pins. It breaks up locks and unorganised clumps of fibre and then aligns the individual fibres to be parallel with each other. In preparing wool fibre for spinning, carding is the step that comes after teasing. The word is derived from the Latin meaning thistle or Dipsacus, teasel, as dried vegetable teasels were first used to comb the raw wool before technological advances led to the use of machines. Overview These ordered fibres can then be passed on to other processes that are specific to the desired end use of the fibre: Cotton mill, Cotton, Batting (material), batting, felt, woollen or worsted yarn, etc. Carding can also be used to create blends of dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Bourn
Daniel Bourn was an English inventor, who took out a patent for a carding machine with rotating cylinders in 1748. Though Bourn is thought likely to have had some association with Lancashire, at the time he received the patent he owned a Paul-Wyatt cotton-spinning mill at Leominster in Herefordshire Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouthshire .... References Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown 18th-century English businesspeople English inventors British textile industry businesspeople {{England-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_and_her_daughter_Mary_Anne%2C_by_Joseph_Wright_of_Derby.jpg)