|
Leptin
Leptin (from Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small") is a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells and enterocytes in the small intestine that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger, which in turn diminishes fat storage in adipocytes. Leptin is coded for by the ''LEP'' gene. Leptin acts on cell receptors in the arcuate and ventromedial nuclei, as well as other parts of the hypothalamus and dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area, consequently mediating feeding. Although regulation of fat stores is deemed to be the primary function of leptin, it also plays a role in other physiological processes, as evidenced by its many sites of synthesis other than fat cells, and the many cell types beyond hypothalamic cells that have leptin receptors. Many of these additional functions are yet to be fully defined. In obesity, a decreased sensitivity to leptin occurs (similar to insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes), resulting in an ina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptin Receptor
Leptin receptor, also known as LEP-R or OB-R, is a type I cytokine receptor, a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LEPR'' gene. LEP-R functions as a receptor for the fat cell-specific hormone leptin. LEP-R has also been designated as CD295 (cluster of differentiation 295). Its location is the cell membrane, and it has extracellular, trans-membrane and intracellular sections (''protein regions''). History The Leptin Receptor was discovered in 1995 by Louis Tartaglia and his colleagues at Millennium Pharmaceuticals. This same team demonstrated the leptin receptor was expressed by the mouse db gene. Furthermore, in 1996, after co-discovering the Leptin gene with Jeffrey Friedman et al. in 1994, (which involved a reverse genetic/positional cloning strategy to clone ''ob'' and ''db)'', Rudolph Leibel, working with collaborators also at Millennium Pharmaceuticals and colleague Streamson Chua, confirmed cloning of the leptin receptor by demonstrating that an apparent leptin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunger (motivational State)
Hunger is a sensation that motivates the consumption of food. The sensation of hunger typically manifests after only a few hours without eating and is generally considered to be unpleasant. Satiety occurs between 5 and 20 minutes after eating. There are several theories about how the feeling of hunger arises. The desire to eat food, or appetite, is another sensation experienced with regards to eating. The term ''hunger'' is also the most commonly used in social science and policy discussions to describe the condition of people who suffer from a chronic lack of sufficient food and constantly or frequently experience the sensation of hunger, and can lead to malnutrition. A healthy, well-nourished individual can survive for weeks without food intake (see fasting), with claims ranging from three to ten weeks. Satiety is the opposite of hunger; it is the sensation of feeling full. Hunger pangs The physical sensation of hunger is related to contractions of the stomach muscles. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may also include increased hunger, feeling tired, and sores that do not heal. Often symptoms come on slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, strokes, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the limbs which may lead to amputations. The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primarily to type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes. In type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet, physical activity, automation, urbanization, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, economic policies, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. While a majority of obese individuals at any given time are attemptin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ... part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain Metabolism, metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Homeostasis
In biology, energy homeostasis, or the homeostatic control of energy balance, is a biological process that involves the coordinated homeostatic regulation of food intake (energy inflow) and energy expenditure (energy outflow). The human brain, particularly the hypothalamus, plays a central role in regulating energy homeostasis and generating the sense of hunger by integrating a number of biochemical signals that transmit information about energy balance. Fifty percent of the energy from glucose metabolism is immediately converted to heat. Energy homeostasis is an important aspect of bioenergetics. Definition In the US, biological energy is expressed using the energy unit Calorie with a capital C (i.e. a kilocalorie), which equals the energy needed to increase the temperature of 1 kilogram of water by 1 °C (about 4.18 k J). Energy balance, through biosynthetic reactions, can be measured with the following equation: :''Energy intake (from food and fluids) = Energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eating
Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food, typically to provide a heterotrophic organism with energy and to allow for growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive — carnivores eat other animals, herbivores eat plants, omnivores consume a mixture of both plant and animal matter, and detritivores eat detritus. Fungi digest organic matter outside their bodies as opposed to animals that digest their food inside their bodies. For humans, eating is an activity of daily living. Some individuals may limit their amount of nutritional intake. This may be a result of a lifestyle choice, due to hunger or famine, as part of a diet or as religious fasting. Eating practices among humans Many homes have a large kitchen area devoted to preparation of meals and food, and may have a dining room, dining hall, or another designated area for eating. Most societies also have restaurants, food courts, and food vendors so that people may eat whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
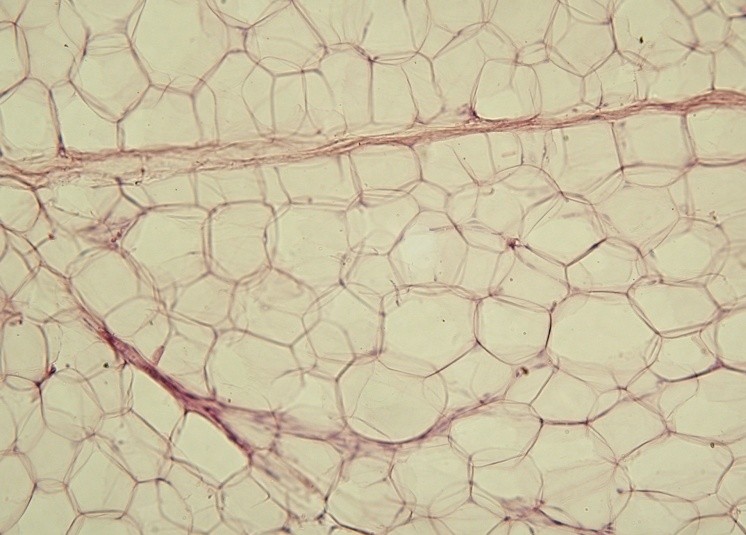
Adipose Cells
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adipose tissue. The fat stored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipocyte
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adipose tissue. The fat stored i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood, but sulfate depletion may be the important factor. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. There are multiple ways to measure insulin resistance such as fasting insulin levels or glucose tolerance tests, but these are not often use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventromedial Nucleus Of The Hypothalamus
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN, also sometimes referred to as the ventromedial hypothalamus, VMH) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. "The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is a distinct morphological nucleus involved in terminating hunger, fear, thermoregulation, and sexual activity." This nuclear region is involved in the recognition of the feeling of fullness. Structure It has four subdivisions: * Anterior (VMHa) * Dorsomedial (VMHdm) * Ventrolateral (VMHvl) * Central (VMHc) These subdivisions differ anatomically, neurochemically, and behaviorally. Function The ventromedial nucleus (VMN) is most commonly associated with satiety. Early studies showed that VMN lesions caused over-eating and obesity in rats. However, the interpretation of these experiments was summarily discredited when Gold's research demonstrated that precision lesioning of the VMN did not result in hyperphagia. Nevertheless, numerous studies have shown that the immediacy of hyperphagia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |