|
Legionella Jordanis
''Legionella jordanis'' is a Gram-negative bacterium from the genus '' Legionella'' which was isolated from the Jordan River in Bloomington, Indiana and from the sewage in DeKalb County, Georgia. ''L. jordanis'' is a rare human pathogen and can cause respiratory tract infections. History ''Legionella jordanis'' strain BL-540 was first isolated from water samples taken at the Jordan River in Bloomington, Indiana by Cherry et al. in 1978. Another strain characterized as ABB-9 was discovered in 1980 from sewage collected in DeKalb County, Georgia. The specific epithet ''jordanis'' was derived from the name of the river in which was discovered. The two strains were both Gram-stained. The Sudan black B fat stain for lipids and the Wirtz-Conklin method were used to demonstrate spore formation. Acid-fast staining was used, as well. The cultures were streaked onto trypticase soy agar (TSA) and charcoal yeast extract (CYE) agar slants, and were left to incubate around 36 °C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Encapsulation
Cell encapsulation is a possible solution to graft rejection in tissue engineering applications. Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane. It permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells, regarding them as foreign invaders. Cell encapsulation could reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects. History In 1933 Vincenzo Bisceglie made the first attempt to encapsulate cells in polymer membranes. He demonstrated that tumor cells in a polymer structure transplanted into pig abdominal cavity remained viable for a long period without being rejected by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nosocomial Infections
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is sometimes instead called a healthcare–associated infection. Such an infection can be acquired in hospital, nursing home, rehabilitation facility, outpatient clinic, diagnostic laboratory or other clinical settings. Infection is spread to the susceptible patient in the clinical setting by various means. Health care staff also spread infection, in addition to contaminated equipment, bed linens, or air droplets. The infection can originate from the outside environment, another infected patient, staff that may be infected, or in some cases, the source of the infection cannot be determined. In some cases the microorganism originates from the patient's own skin microbiota, becoming opportunistic after surgery or other procedures that compromi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK or MSKCC) is a cancer treatment and research institution in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, founded in 1884 as the New York Cancer Hospital. MSKCC is one of 52 National Cancer Institute–designated Comprehensive Cancer Centers. Its main campus is located at 1275 York Avenue, between 67th and 68th streets, in Manhattan. According to U.S. News & World Report 2021-2022 Best Hospitals, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) has been ranked as the number two hospital for cancer care in the nation. History New York Cancer Hospital (1884–1934) Memorial Hospital was founded on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in 1884 as the New York Cancer Hospital by a group that included John Jacob Astor III and his wife Charlotte. The hospital appointed as an attending surgeon William B. Coley, who pioneered an early form of immunotherapy to eradicate tumors. Rose Hawthorne, daughter of author Nathaniel Hawthorne, trained there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Fluorescent Antibody
A direct fluorescent antibody (DFA or dFA), also known as "direct immunofluorescence", is an antibody that has been tagged in a direct fluorescent antibody test. Its name derives from the fact that it directly tests the presence of an antigen with the tagged antibody, unlike western blotting, which uses an indirect method of detection, where the primary antibody binds the target antigen, with a secondary antibody directed against the primary, and a tag attached to the secondary antibody. Commercial DFA testing kits are available, which contain fluorescently labelled antibodies, designed to specifically target unique antigens present in the bacteria or virus, but not present in mammals ( Eukaryotes). This technique can be used to quickly determine if a subject has a specific viral or bacterial infection. In the case of respiratory viruses, many of which have similar broad symptoms, detection can be carried out using nasal wash samples from the subject with the suspected infecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum (blood)
Serum () is the fluid and solute component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum includes all proteins not used in blood clotting; all electrolytes, antibodies, antigens, hormones; and any exogenous substances (e.g., drugs or microorganisms). Serum does not contain white blood cells ( leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), platelets, or clotting factors. The study of serum is serology. Serum is used in numerous diagnostic tests as well as blood typing. Measuring the concentration of various molecules can be useful for many applications, such as determining the therapeutic index of a drug candidate in a clinical trial. To obtain serum, a blood sample is allowed to clot (coagulation). The sample is then centrifuged to remove the clot and blood cells, and the resulting liquid supernatant is serum. Clinical and laboratory uses The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
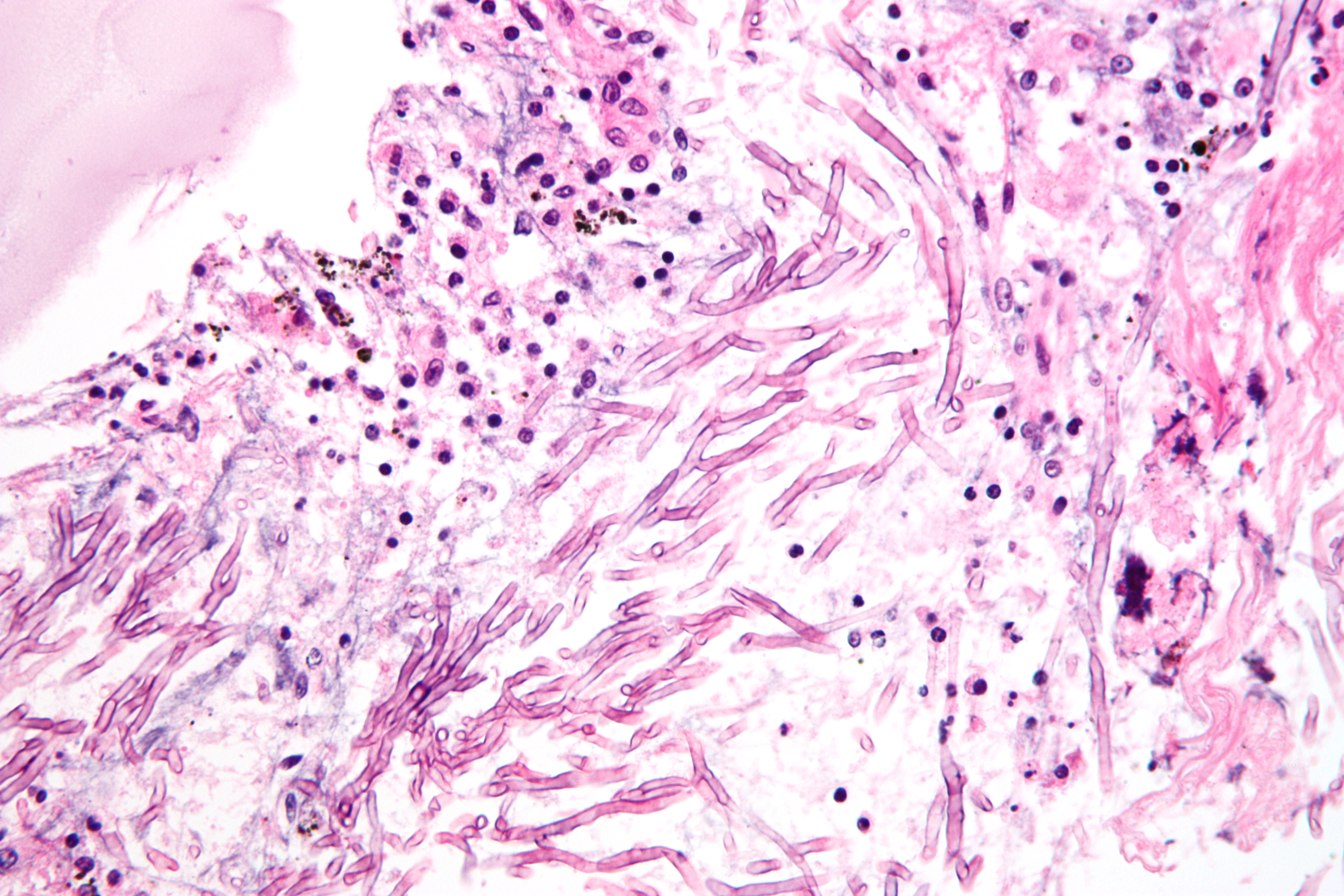
Aspergillus
'''' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. ''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Micheli was reminded of the shape of an '' aspergillum'' (holy water sprinkler), from Latin ''spargere'' (to sprinkle), and named the genus accordingly. Aspergillum is an asexual spore-forming structure common to all ''Aspergillus'' species; around one-third of species are also known to have a sexual stage. While some species of ''Aspergillus'' are known to cause fungal infections, others are of commercial importance. Taxonomy Species ''Aspergillus'' consists of 837 species of fungi. Growth and distribution ''Aspergillus'' is defined as a group of conidial fungi—that is, fungi in an asexual state. Some of them, however, are known to have a teleomorph (sexual state) in the Ascomycota. With DNA evidence, all members of the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionnaires' Disease
Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of '' Legionella'' bacteria, quite often ''Legionella pneumophila''. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, muscle pains, and headaches. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may also occur. This often begins 2–10 days after exposure. A legionellosis is any disease caused by ''Legionella'', including Legionnaires' disease (a pneumonia), Pontiac fever (a nonpneumonia illness), and Pittsburgh pneumonia, but Legionnaires' disease is the most common, so mentions of legionellosis often refer to Legionnaires' disease. The bacterium is found naturally in fresh water. It can contaminate hot water tanks, hot tubs, and cooling towers of large air conditioners. It is usually spread by breathing in mist that contains the bacteria. It can also occur when contaminated water is aspirated. It typically does not spread directly between people, and most people who are exposed do not become in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia. Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, a poor ability to cough (such as following a stroke), and a weak immune system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunistic Pathogen
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune system (as can occur in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or when being treated with immunosuppressive drugs, as in cancer treatment), an altered microbiome (such as a disruption in gut microbiota), or breached integumentary barriers (as in penetrating trauma). Many of these pathogens do not necessarily cause disease in a healthy host that has a non-compromised immune system, and can, in some cases, act as commensals until the balance of the immune system is disrupted. Opportunistic infections can also be attributed to pathogens which cause mild illness in healthy individuals but lead to more serious illness when given the opportunity to take advantage of an immunocompromised host. Types of opportunistic infections A wide variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |