|
Lechitic Tribes
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and the Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians. History According to Polish legend, Mieszko I inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder ( Polans, Masovians, Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians) into a single country of Poland. His son, Bolesław I the Brave, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław, Kołobrzeg, and Kraków, and an archbishopric at Gniezno. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemia, Moravia, Kievan Rus' and Lusatia, and forced the western Pomeranians to pay Poland a tribute. Shortly before his deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadeusz Lehr-Spławiński
Tadeusz Lehr-Spławiński (September 20, 1891 – February 17, 1965) was a Polish linguist, scholar, and professor of Slavonic studies. He was twice elected rector of the Jagiellonian University in Kraków before and after the Nazi German occupation of Poland. Biography Lehr-Spławiński was born in Kraków, the son of Edward Lehr, an engineer, and Maria '' née'' Spławińska. He went to Jan III Sobieski high school and, in the years 1909–1915 studied linguistics, history of Polish literature as well as classical philology, at the Jagiellonian University in Kraków. He continued his studies in Vienna, and began his teaching career in Zakopane. In 1918 (following Poland's return to independence), Lehr-Spławiński became professor at Poznań University and, from 1922, the University of Lwów, at both of which he led the Department of Slavonic Philology. From 1929 until his retirement in 1962, he was professor of linguistics at Jagiellonian University, elected as its Rector for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugii
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his '' Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some centuries later, they were considered one of the "Gothic" or "Scythian" peoples who were located in the Middle Danube region. Like several other Gothic peoples there, they possibly arrived in the area as allies of Attila until his death in 453. They settled in what is now Lower Austria after the defeat of the Huns at Nedao in 454. The Baltic Rugii mentioned by Tacitus are possibly related to the people known as the ''Rutikleioi'', and the place known as Rougion, both mentioned in the second century by Ptolemy. Both these names are associated with the coastal island known today as Rügen. They have also been associated with the ''Ulmerugi'' mentioned in the sixth century by Jordanes, as people who had lived on the Baltic coast near th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław Chrobry
Boleslav or Bolesław may refer to: In people: * Boleslaw (given name) In geography: * Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland * Bolesław, Olkusz County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland * Bolesław, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland *Brandýs nad Labem-Stará Boleslav, Czech Republic *Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic See also * Pulß * Václav (other) * Wenceslaus (other) Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar names) are Latinized forms of the Czech name Václav. The other language versions of the name are german: Wenzel, pl, Wacław, Więcesław, Wieńczysław, es, Wenceslao, russian: ... {{disambig, geo de:Bolesław ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesians
Silesians ( szl, Ślōnzŏki or Ślůnzoki; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; german: Schlesier; pl, Ślązacy; cz, Slezané) is a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Europe divided by the current national boundaries of Poland, Germany and the Czech Republic. Historically, the region of Silesia (Lower and Upper) has been inhabited by Germans (German speakers), Czechs, Poles and Slavic Upper Silesians. Therefore, the term Silesian can refer to anyone of these ethnic groups. However, in 1945, great demographic changes occurred in the region as a result of the Potsdam Agreement leaving most of the region ethnically Polish and/or Slavic Upper Silesian. There have been some debates on whether or not the Silesians (historically, Upper Silesians) constitute a distinct nation. In modern history, they have often been pressured to declare themselves to be German, Polish or Czech, and use the language of the nation wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vistulans
The Vistulans, or Vistulanians ( pl, Wiślanie), were an early medieval Lechitic tribe inhabiting the western part of modern Lesser Poland."The main tribe inhabiting the reaches of the Upper Vistula and its tributaries was the Vislane (Wislanie) who, by the mid-ninth century were considered by the neighbouring Moravians as "very powerful" The expansionist policy of the Christian Moravian state led to eventual conflict with the pogan Vislane. ending in the defeat of the latter and their annexation to the Great Moravian Empire between Ad 875-879" . n:''Trade and urban development in Poland: an economic geography of Cracow''. Francis W. Carter. P. 46. 1994 op. cit. L. Hajdukiewicz and M. Karaś. ''The Jagiellonian University: Traditions, The Present, The Future''. Cracow. 1978, p. 17. Etymology Their name derives from the hydronym of the river Vistula, meaning "inhabitants of Vistula"; the region is mentioned as ''Uuislane'' by the Bavarian Geographer, ''v Vislè'' and ''v Vislèh'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masovians
Masovians, also spelled as Mazovians, and historically known as Masurians, is an ethnographic group of Polish people that originate from the region of Masovia, located mostly within borders of the Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. They speak the Masovian dialect dialect of Polish.G. Odoj, A. Peć: ''Dziedzictwo kulturowe – edukacja regionalna''. Dzierżoniów: Wydawnictwo Alex, 2000, p. 74, ISBN 83-85589-35-X, OCLC 749376082. The group originate from the Lechitic tribe of Masovians, first referenced in the historical records by Nestor the Chronicler in the 11th century. Name The name Masovian, in Polish, ''Mazowszanin'', comes from the name of the region of Masovia, in Polish known as ''Mazowsze''. The name of the region, comes from its Old Polish names ''Mazow'', and ''Mazosze'', and most likely came from word ''maz'' (ancestory word of modern ''maź'' and ''mazać''), which was used to either describe a "''muddy region''" or a "''person covered in mud''". Historically, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polans (western)
The Western Polans (also known as Polanes, Polanians; , derived from Old Slavic ''pole'', "field" or "plain", from Proto-Indo-European ''*pleh₂-'' "flatland") were a West Slavic and Lechitic tribe, inhabiting the Warta River basin of the contemporary Greater Poland region starting in the 6th century. They were one of the main tribes in Central Europe and were closely related to the Vistulans, Masovians, Czechs and Slovaks. History In the 9th century, the Polans united several West Slavic (Lechitic) groups to the north of Great Moravia. The union led by the Piast dynasty developed into the Duchy of Poland, whose name derives from that of the Polans. The earliest Polan rulers mentioned by name are the legendary figures of Piast the Wheelwright and Popiel (8th–9th centuries). The first historical ruler was Mieszko I (960–992), who enlarged the territory later named Poland by incorporating Masovia and conquering Silesia Silesia (, also , ) is a historical regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany as part of the Oder–Neisse line. The river ultimately flows into the Szczecin Lagoon north of Szczecin and then into three branches (the Dziwna, Świna and Peene) that empty into the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. Names The Oder is known by several names in different languages, but the modern ones are very similar: English and ; Czech, Polish, and , ; (); Medieval Latin: ''Od(d)era''; Renaissance Latin: ''Viadrus'' (invented in 1534). Ptolemy knew the modern Oder as the Συήβος (''Suebos''; Latin ''Suevus''), a name apparently derived from the Suebi, a Germanic people. While he also refers to an outlet in the area as the Οὐιαδούα ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and a grandson of Lestek. He was the father of Bolesław I the Brave (the first crowned king of Poland) and of Gunhild of Wenden. Most sources identify Mieszko I as the father of Sigrid the Haughty, a Scandinavian queen (though one source identifies her father as Skoglar Toste), the grandfather of Canute the Great (Gundhild's son) and the great-grandfather of Gunhilda of Denmark, Canute the Great's daughter and wife of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor. He was the first Christian ruler of Poland, but he continued the policies of both his father and grandfather, who initiated the process of creation of the Polish state. Through both alliances and military force, Mieszko extended ongoing Polish conquests and early in his reign subjugated Kuya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes
Limes may refer to: * the plural form of lime (other) Lime commonly refers to: * Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit * Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide * Lime (color), a color between yellow and green Lime may also refer to: Botany ... * the Latin word for ''limit'' which refers to: ** Limes (Roman Empire), a border marking and defense system of the ancient Roman Empire ** ''Limes'' (magazine), an Italian geopolitical magazine See also * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
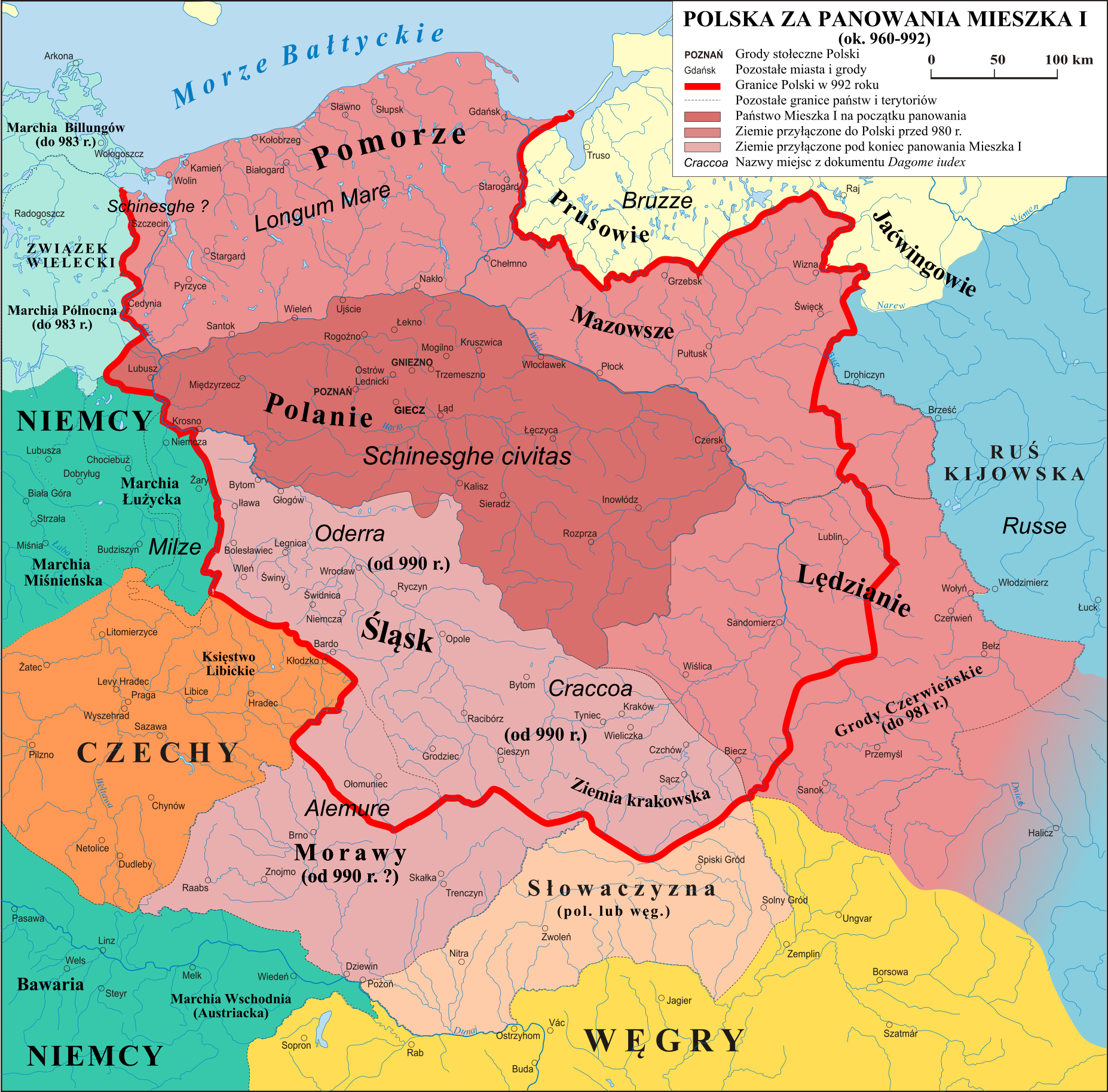
Polska 960 - 992
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Długosz
Jan Długosz (; 1 December 1415 – 19 May 1480), also known in Latin as Johannes Longinus, was a Polish priest, chronicler, diplomat, soldier, and secretary to Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki of Kraków. He is considered Poland's first historian.Isayevych, Ya. Jan Długosz (ДЛУГОШ ЯН)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. 2004 Life Jan Długosz is best known for his (''Annales seu cronici incliti regni Poloniae'') in 12 volumes and originally written in Latin, covering events in southeastern Europe, but also in Western Europe, from 965 to 1480, the year he died. Długosz combined features of Medieval chronicles with elements of humanistic historiography. For writing the history of the Kingdom of Poland, Długosz also used Ruthenian (Russian) chronicles including those that did not survive to our times (among which there could have been used the Kyiv collection of chronicles of the 11th century in the Przemysl's edition around 1100 and the Przemysl episcopal collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



