|
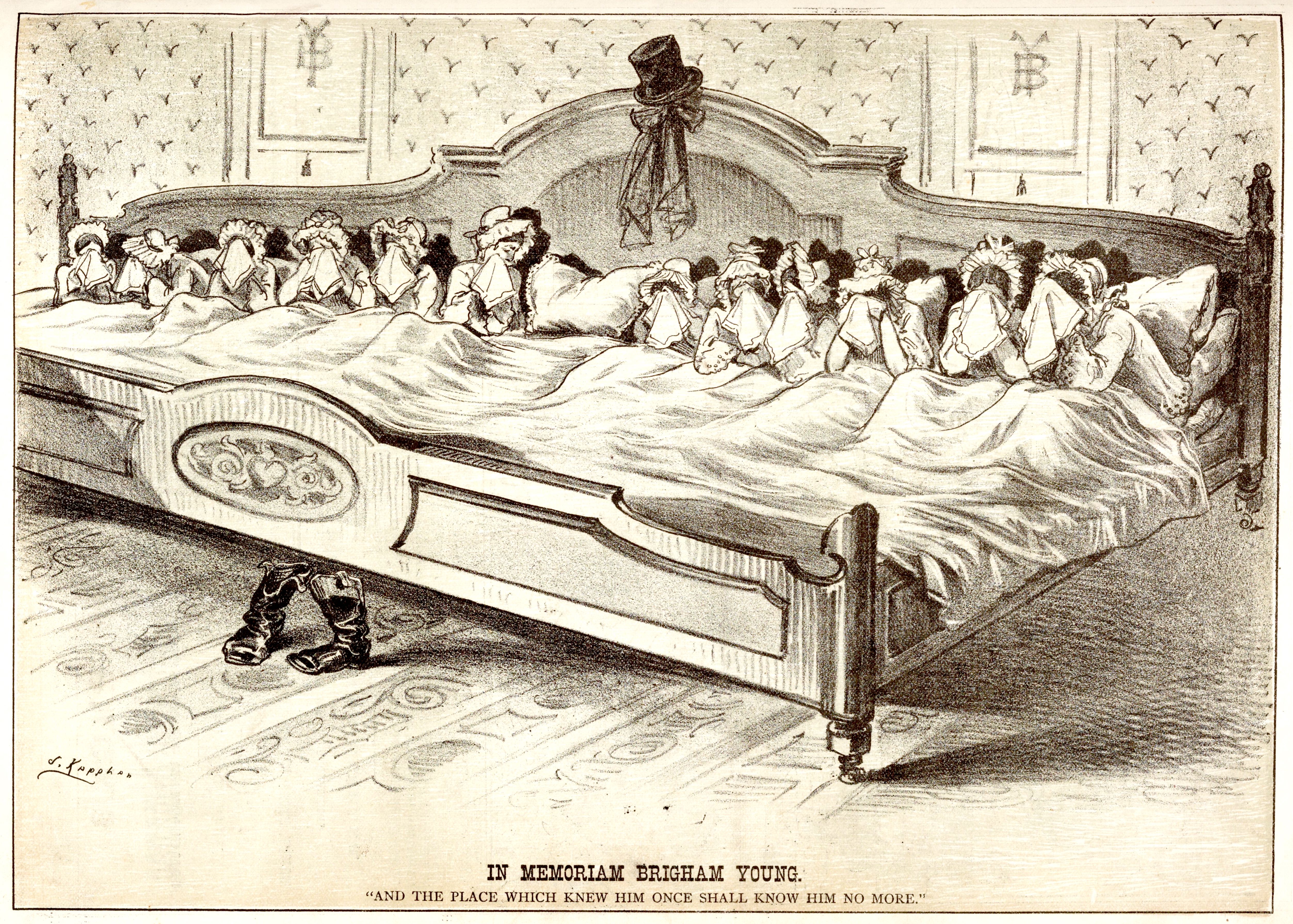
Latter Day Saint Polygamy In The Late-19th Century
Possibly as early as the 1830s, followers of the Latter Day Saint movement (also known as Mormonism), were practicing the doctrine of polygamy or "plural marriage". After the death of church founder Joseph Smith, the doctrine was officially announced in Utah Territory in 1852 by Mormon leader Brigham Young. The practice was attributed posthumously to Smith and it began among Mormons at large, principally in Utah where the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) had relocated after the Illinois Mormon War. In the years after members of the LDS Church began practicing polygamy, it drew intense scrutiny and criticism from the United States government. This criticism led to the Utah Mormon War, and eventually the abandonment of the practice pursuant to the 1890 Manifesto issued by Wilford Woodruff. Official sanction by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints The Mormon doctrine of plural wives was officially announced by one of the Twelve Apostles, Orson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latter Day Saint Movement
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian Restorationist movement founded by Joseph Smith in the late 1820s. Collectively, these churches have over 17 million nominal members, including over 17 million belonging to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), 250,000 in Community of Christ, and several other denominations with memberships generally ranging in the thousands of members. The predominant theology of the churches in the movement is Mormonism, which sees itself as restoring again on Earth the Early Christianity, early Christian church; their members are most commonly known as Mormons. An additional doctrine of the church allows for prophets to receive and publish modern-day Revelation (Latter Day Saints), revelations. A minority of Latter Day Saint adherents, such as members of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage, Illinois
Carthage is a city in and the county seat of Hancock County, Illinois, United States. Its population was 2,490 as of the 2020 census. Carthage is best known for being the site of the 1844 murder of Joseph Smith, who founded the Latter Day Saint movement. History The first European-American settlers arrived in Carthage and in Hancock County in the first few decades of the 19th century. By 1833, they had erected simple buildings in Carthage. That year, a log cabin was built to serve as the county courthouse, and the county seat was moved from Montebello to Carthage. The town was platted in 1838. The only person legally hanged in Hancock County, Efram Fraim, had been defended in his trial by roaming circuit attorney Abraham Lincoln. Fraim was found guilty of murder. Lincoln filed an appeal with the judge in the trial, which was as far as most appeals in those days went. Because Carthage then had no jail, Fraim was kept at the courthouse, which was next to the school. Fraim convers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Dollar
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish dollar, Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100 cent (currency), cents, and authorized the Mint (facility), minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color. The U.S. dollar was originally defined under a bimetallism, bimetallic standard of (0.7734375 troy ounces) fine silver or, from Coinage Act of 1834, 1834, fine gold, or $20.67 per troy ounce. The Gold Standard Act of 1900 linked the dollar solely to gold. From 1934, its equivalence to gold was revised to $35 per troy ounce. In 1971 all links to gold were repealed. The U.S. dollar became an important intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plural Marriage
Polygamy (called plural marriage by Latter-day Saints in the 19th century or the Principle by modern fundamentalist practitioners of polygamy) was practiced by leaders of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) for more than half of the 19th century, and practiced publicly from 1852 to 1890 by between 20 and 30 percent of Latter-day Saint families. Polygamy among Latter-day Saints has been controversial, both in Western society and within the LDS Church itself. Many U.S. politicians were strongly opposed to the practice; the Republican platform even referred to polygamy and slavery as "the twin relics of barbarism." Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter-day Saint movement, first introduced polygamy privately in the 1830s. Later, in 1852, Orson Pratt, a member of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles, publicly announced and defended the practice at the request of then-church president Brigham Young. Throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, the LDS C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War, defeating the Confederate States of America and playing a major role in the End of slavery in the United States, abolition of slavery. Lincoln was born into poverty in Kentucky and raised on the American frontier, frontier. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Illinois state Illinois House of Representatives, legislator, and U.S. representative. Angered by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854, which opened the territories to slavery, he became a leader of the new History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. He reached a national audience in the Lincoln–Douglas debates, 1858 Senate campaign debates against Stephen A. Douglas. Lincoln won the 1860 United States presidential election, 1860 presidential election, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morrill Anti-Bigamy Act
The Morrill Anti-Bigamy Act ( 37th United States Congress, Sess. 2., ch. 126, ) was a federal enactment of the United States Congress that was signed into law on July 1, 1862, by President Abraham Lincoln. Sponsored by Justin Smith Morrill of Vermont, the act banned bigamy in federal territories such as Utah and limited church and non-profit ownership in any territory of the United States to $50,000. The act targeted the Mormon practice of plural marriage and the property dominance of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) in the Utah Territory. The measure had no funds allocated for enforcement, and Lincoln chose not to enforce this law; instead Lincoln gave Brigham Young tacit permission to ignore the Morrill Act in exchange for not becoming involved with the Civil War. General Patrick Edward Connor, commanding officer of the federal forces garrisoned at Fort Douglas, Utah beginning in 1862, was explicitly instructed not to confront the Mormons over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormon Reformation
The Mormon Reformation was a period of renewed emphasis on spirituality within the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), and a centrally-directed movement, which called for a spiritual reawakening among church members. It took place during 1856 and 1857 and was under the direction of church president Brigham Young. During the Reformation, Young sent his counselor, Jedediah M. Grant, and other church leaders to preach to the people throughout Utah Territory and surrounding Latter-day Saint communities with the goal of inspiring them to reject sin and turn towards spiritual things. During this time, some of the most conservative or reactionary elements of LDS Church doctrine came to dominate public discussion. As part of the Reformation, almost all "active" or involved LDS Church members were rebaptized as a symbol of their commitment. The Reformation is considered in three phases: a structural reform phase, a phase of intense demand for a demonstration of spirit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
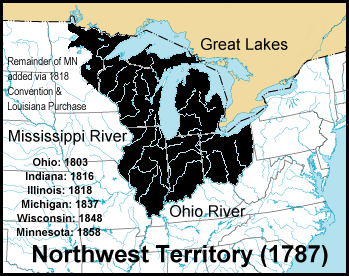
Organic Act
In United States law, an organic act is an act of the United States Congress that establishes an administrative agency or local government, for example, the laws that established territory of the United States and specified how they are to be governed, or established agency to manage certain federal lands. In the absence of organic law, the body of laws that define and establish a government, a territory is classified as unorganized. The first such act was the Northwest Ordinance, passed in 1787 by the U.S. Congress of the Confederation (under the Articles of Confederation, predecessor of the United States Constitution). The Northwest Ordinance created the Northwest Territory in the land west of Pennsylvania and northwest of the Ohio River and set the pattern of development that was followed for all subsequent territories. The Northwest Territory covered more than 260,000 square miles and included all of the modern states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentile
''Gentile'' () is a word that today usually means someone who is not Jewish. Other groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, have historically used the term ''gentile'' to describe outsiders. More rarely, the term is used as a synonym for ''heathen'', '' pagan''. As a term used to describe non-members of a religious/ethnic group, ''gentile'' is sometimes compared to other words used to describe the "outgroup" in other cultures See for example a discussion of the similarity to the Japanese term '' gaijin'' in (see List of terms for ethnic out-groups). In some translations of the Quran, ''gentile'' is used to translate an Arabic word that refers to non-Jews and/or people not versed in or not able to read scripture. The English word ''gentile'' derives from the Latin word , meaning "of or belonging to the same people or nation" (). Archaic and specialist uses of the word ''gentile'' in English (particularly in linguistics) still carry this meaning of "relating to a pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John A
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (10 or 11January 18156June 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 until his death in 1891. He was the Fathers of Confederation, dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, and had a political career that spanned almost half a century. Macdonald was born in Scotland; when he was a boy his family immigrated to Kingston, Ontario, Kingston in the Province of Upper Canada (today in eastern Ontario). As a lawyer, he was involved in several high-profile cases and quickly became prominent in Kingston, which elected him in 1844 to the legislature of the Province of Canada. By 1857, he had become List of Joint Premiers of the Province of Canada, premier under the colony's unstable political system. In 1864, when no party proved capable of governing for long, he agreed to a proposal from his political rival, George Brown (Canadian politician), George Brown, that the parties unite in a Great Coalition to seek fede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Party Platform
A political party platform (American English), party program, or party manifesto (preferential term in British and often Commonwealth English) is a formal set of principal goals which are supported by a political party or individual candidate, to appeal to the general public, for the ultimate purpose of garnering the general public's support and votes about complicated topics or issues. A component of a political platform is often called a plank – the opinions and viewpoints about an individual topic, as held by a party, person, or organization. The word "plank" depicts a component of an overall political platform, as a metaphorical reference to a basic stage made of boards or planks of wood. The metaphor can return to its literal origin when public speaking or debates are actually held upon a physical platform. In the United Kingdom and certain other countries, the party platform is referred to as the party's "manifesto" or political programme. The manifesto contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |