|
Lamport's Bakery Algorithm
Lamport's bakery algorithm is a computer algorithm devised by computer scientist Leslie Lamport, as part of his long study of the formal correctness of concurrent systems, which is intended to improve the safety in the usage of shared resources among multiple threads by means of mutual exclusion. In computer science, it is common for multiple threads to simultaneously access the same resources. Data corruption can occur if two or more threads try to write into the same memory location, or if one thread reads a memory location before another has finished writing into it. Lamport's bakery algorithm is one of many mutual exclusion algorithms designed to prevent concurrent threads entering critical sections of code concurrently to eliminate the risk of data corruption. Algorithm Analogy Lamport envisioned a bakery with a numbering machine at its entrance so each customer is given a unique number. Numbers increase by one as customers enter the store. A global counter display ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compare-and-swap
In computer science, compare-and-swap (CAS) is an atomic instruction used in multithreading to achieve synchronization. It compares the contents of a memory location with a given value and, only if they are the same, modifies the contents of that memory location to a new given value. This is done as a single atomic operation. The atomicity guarantees that the new value is calculated based on up-to-date information; if the value had been updated by another thread in the meantime, the write would fail. The result of the operation must indicate whether it performed the substitution; this can be done either with a simple boolean response (this variant is often called compare-and-set), or by returning the value read from the memory location (''not'' the value written to it). Overview A compare-and-swap operation is an atomic version of the following pseudocode, where denotes access through a pointer: function cas(p: pointer to int, old: int, new: int) is if *p ≠ old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semaphore (programming)
In computer science, a semaphore is a variable or abstract data type used to control access to a common resource by multiple threads and avoid critical section problems in a concurrent system such as a multitasking operating system. Semaphores are a type of synchronization primitive. A trivial semaphore is a plain variable that is changed (for example, incremented or decremented, or toggled) depending on programmer-defined conditions. A useful way to think of a semaphore as used in a real-world system is as a record of how many units of a particular resource are available, coupled with operations to adjust that record ''safely'' (i.e., to avoid race conditions) as units are acquired or become free, and, if necessary, wait until a unit of the resource becomes available. Semaphores are a useful tool in the prevention of race conditions; however, their use is not a guarantee that a program is free from these problems. Semaphores which allow an arbitrary resource count are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
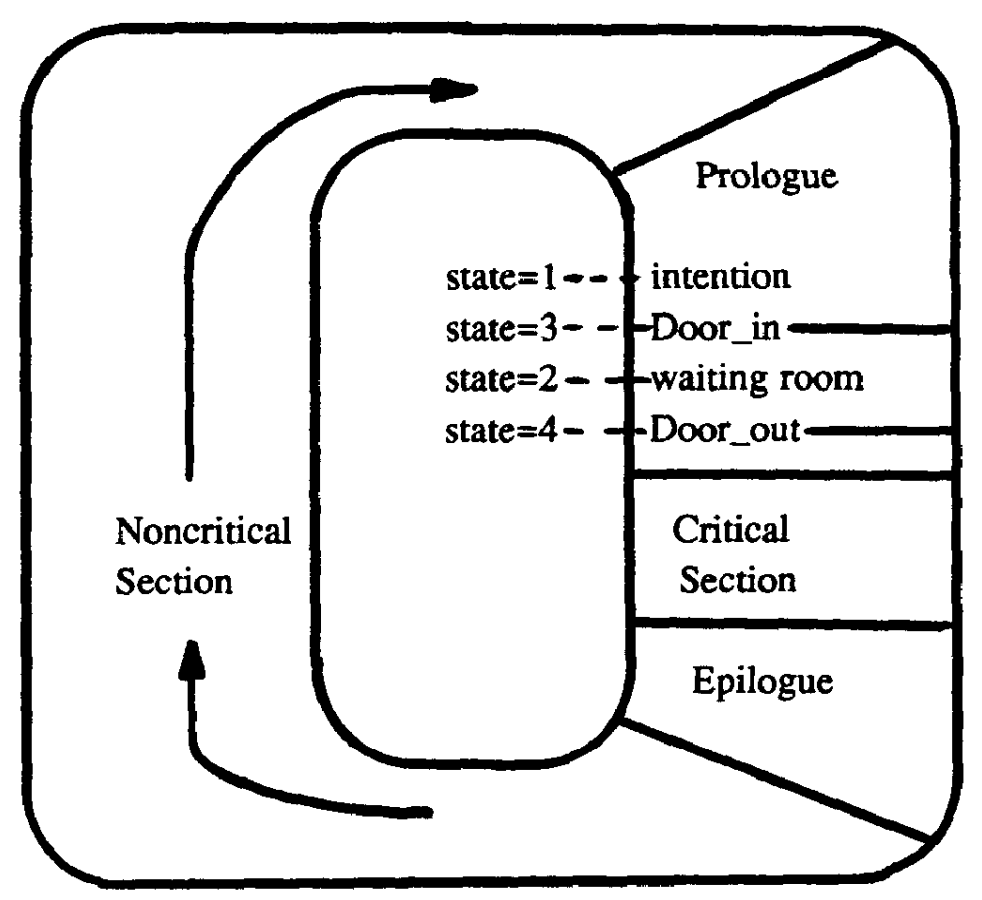
Szymański's Algorithm
Szymański's Mutual Exclusion Algorithm is a mutual exclusion algorithm devised by computer scientist Dr. Bolesław Szymański, which has many favorable properties including linear wait, and which extension solved the open problem posted by Leslie Lamport whether there is an algorithm with a constant number of communication bits per process that satisfies every reasonable fairness and failure-tolerance requirement that Lamport conceived of (Lamport's solution used n factorial communication variables vs. Szymański's 5). The algorithm The algorithm is modeled on a waiting room with an entry and exit doorway. Initially the entry door is open and the exit door is closed. All processes which request entry into the critical section at roughly the same time enter the waiting room; the last of them closes the entry door and opens the exit door. The processes then enter the critical section one by one (or in larger groups if the critical section permits this). The last process to leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterson's Algorithm
Peterson's algorithm (or Peterson's solution) is a concurrent programming algorithm for mutual exclusion that allows two or more processes to share a single-use resource without conflict, using only shared memory for communication. It was formulated by Gary L. Peterson in 1981.G. L. Peterson: "Myths About the Mutual Exclusion Problem", ''Information Processing Letters'' 12(3) 1981, 115–116 While Peterson's original formulation worked with only two processes, the algorithm can be generalized for more than two.As discussed in ''Operating Systems Review'', January 1990 ("Proof of a Mutual Exclusion Algorithm", M Hofri). The algorithm The algorithm uses two variables: flag and turn. A flag /code> value of true indicates that the process n wants to enter the critical section. Entrance to the critical section is granted for process P0 if P1 does not want to enter its critical section and if P1 has given priority to P0 by setting turn to 0. The algorithm satisfies the three essenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisenberg & McGuire Algorithm
The Eisenberg & McGuire algorithm is an algorithm for solving the critical sections problem, a general version of the dining philosophers problem. It was described in 1972 by Murray A. Eisenberg and Michael R. McGuire. Algorithm All the ''n''-processes share the following variables: enum pstate = ; pstate flags int turn; The variable turn is set arbitrarily to a number between 0 and ''n''−1 at the start of the algorithm. The flags variable for each process is set to WAITING whenever it intends to enter the critical section. flags takes either IDLE or WAITING or ACTIVE. Initially the flags variable for each process is initialized to IDLE. repeat until ((index >= n) && ((turn = i) , , (flagsurn= IDLE))); /* Start of CRITICAL SECTION */ /* claim the turn and proceed */ turn := i; /* Critical Section Code of the Process */ /* End of CRITICAL SECTION */ /* find a process which is not IDLE */ /* (if there are no others, we will find ourselves) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dekker's Algorithm
Dekker's algorithm is the first known correct solution to the mutual exclusion problem in concurrent programming where processes only communicate via shared memory. The solution is attributed to Dutch mathematician Th. J. Dekker by Edsger W. Dijkstra in an unpublished paper on sequential process descriptions and his manuscript on cooperating sequential processes. It allows two threads to share a single-use resource without conflict, using only shared memory for communication. It avoids the strict alternation of a naïve turn-taking algorithm, and was one of the first mutual exclusion algorithms to be invented. Overview If two processes attempt to enter a critical section at the same time, the algorithm will allow only one process in, based on whose it is. If one process is already in the critical section, the other process will busy wait for the first process to exit. This is done by the use of two flags, and , which indicate an intention to enter the critical section on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicographical Order
In mathematics, the lexicographic or lexicographical order (also known as lexical order, or dictionary order) is a generalization of the alphabetical order of the dictionaries to sequences of ordered symbols or, more generally, of elements of a totally ordered set. There are several variants and generalizations of the lexicographical ordering. One variant applies to sequences of different lengths by comparing the lengths of the sequences before considering their elements. Another variant, widely used in combinatorics, orders subsets of a given finite set by assigning a total order to the finite set, and converting subsets into increasing sequences, to which the lexicographical order is applied. A generalization defines an order on a Cartesian product of partially ordered sets; this order is a total order if and only if all factors of the Cartesian product are totally ordered. Motivation and definition The words in a lexicon (the set of words used in some language) have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PlusCal
PlusCal (formerly called +CAL) is a formal specification language created by Leslie Lamport, which transpiles to TLA+. In contrast to TLA+'s action-oriented focus on distributed systems, PlusCal most resembles an imperative programming language and is better-suited when specifying sequential algorithm In computer science, a sequential algorithm or serial algorithm is an algorithm that is executed sequentially – once through, from start to finish, without other processing executing – as opposed to concurrently or in parallel. The term is prim ...s. PlusCal was designed to replace pseudocode, retaining its simplicity while providing a formally-defined and verifiable language. A one-bit clock is written in PlusCal as follows: -- fair algorithm OneBitClock See also * TLA+ * Pseudocode References External links * PlusCal tools and documentation are found on thPlusCal Algorithm Language page Formal methods Formal specification languages Algorithm descripti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Multitasking
Cooperative multitasking, also known as non-preemptive multitasking, is a style of computer multitasking in which the operating system never initiates a context switch from a running process to another process. Instead, in order to run multiple applications concurrently, processes voluntarily yield control periodically or when idle or logically blocked. This type of multitasking is called ''cooperative'' because all programs must cooperate for the scheduling scheme to work. In this scheme, the process scheduler of an operating system is known as a cooperative scheduler whose role is limited to starting the processes and letting them return control back to it voluntarily. Usage Although it is rarely used as the primary scheduling mechanism in modern operating systems, it is widely used in memory-constrained embedded systems and also, in specific applications such as CICS or the JES2 subsystem. Cooperative multitasking was the primary scheduling scheme for 16-bit application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocode
In computer science, pseudocode is a plain language description of the steps in an algorithm or another system. Pseudocode often uses structural conventions of a normal programming language, but is intended for human reading rather than machine reading. It typically omits details that are essential for machine understanding of the algorithm, such as variable declarations and language-specific code. The programming language is augmented with natural language description details, where convenient, or with compact mathematical notation. The purpose of using pseudocode is that it is easier for people to understand than conventional programming language code, and that it is an efficient and environment-independent description of the key principles of an algorithm. It is commonly used in textbooks and scientific publications to document algorithms and in planning of software and other algorithms. No broad standard for pseudocode syntax exists, as a program in pseudocode is not an execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |