|
Loricifera
Loricifera (from Latin, ''wikt:lorica, lorica'', corselet (armour) + ''ferre'', to bear) is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 43 described species and approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to . They are characterised by a protective outer case called a Lorica (biology), lorica and their habitat is in the spaces between marine gravel to which they attach themselves. The phylum was discovered in 1983 by Reinhardt Kristensen, R.M. Kristensen, near Roscoff, France. They are among the most recently discovered groups of animals. They attach themselves quite firmly to the substrate, and hence remained undiscovered for so long. The first specimen was collected in the 1970s, and described in 1983. They are found at all depths, in different sediment types, and in all latitudes. Morphology The animals have a head, mouth, and digestive system, as well as the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanaloricida
Loricifera (from Latin, '' lorica'', corselet (armour) + ''ferre'', to bear) is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 43 described species and approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to . They are characterised by a protective outer case called a lorica and their habitat is in the spaces between marine gravel to which they attach themselves. The phylum was discovered in 1983 by R.M. Kristensen, near Roscoff, France. They are among the most recently discovered groups of animals. They attach themselves quite firmly to the substrate, and hence remained undiscovered for so long. The first specimen was collected in the 1970s, and described in 1983. They are found at all depths, in different sediment types, and in all latitudes. Morphology The animals have a head, mouth, and digestive system, as well as the lorica. The head (which contains the mouth and the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhardt Kristensen
Reinhardt Møbjerg Kristensen (born 1948) is a Danish invertebrate biologist, noted for the discovery of three new phyla of microscopic animals: the Loricifera in 1983, the Cycliophora in 1995, and the Micrognathozoa in 2000. He is also considered one of the world's leading experts on tardigrades. His recent field of work revolves mostly around arctic biology. He is also known for documenting '' Dendrogramma'', an invertebrate genus that was later classified as Siphonophorae of the family Rhodaliidae. Loricifera Kristensen collected the first members of the Loricifera phylum in Roscoff, France, in 1970, but did not describe it until 1983.Heiner, I. 2005. Preliminary account of the loriciferan fauna of the Faroe Bank (NE Atlantic). Biofar Proceedings 2005: 213–219. Cycliophora Kristensen and Peter Funch described '' Symbion pandora'', on the mouth-parts of Norwegian lobsters, in 1995; other species were later found on other types of lobsters. Micrognathozoa Kristense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
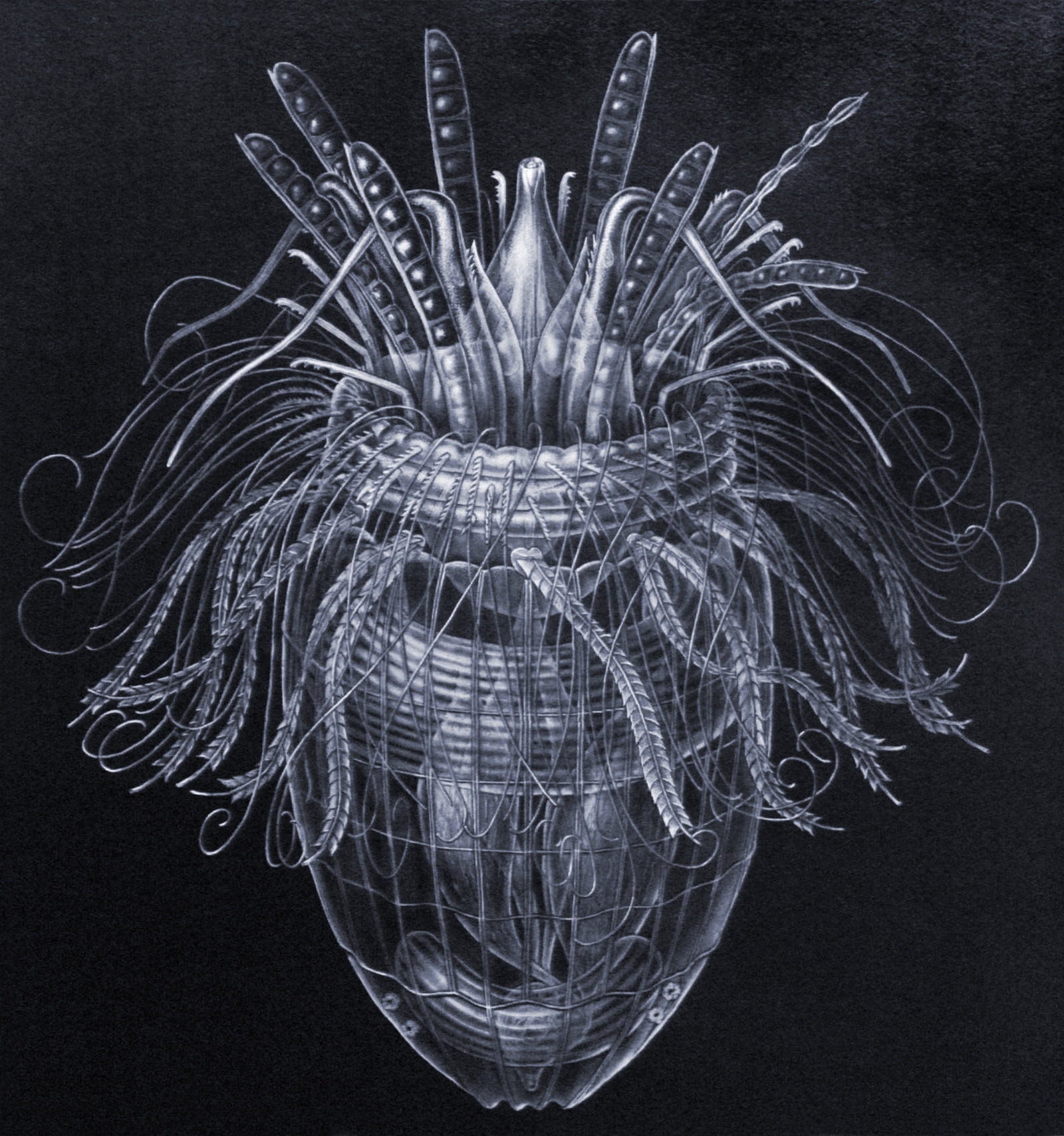
Urnaloricus
''Urnaloricus'' is a genus of loricifera Loricifera (from Latin, ''wikt:lorica, lorica'', corselet (armour) + ''ferre'', to bear) is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 43 described species and approximately 100 more that hav ...; it is distinct enough to belong to its own family, Urnaloricidae. Loricifera are phylum that are animals that live in marine area only, and very small in size. The Urnaloricus was found Southwest in the Faroe Islands, North Atlantic. It was the thirty-eighth loriciferan species found. One part of the life cycle is the Higgins larva and it is introverted with eight two-segmented clavoscalids.Neves, Kristensen, R. M., Rohal, M., Thistle, D., & Serensen, M. V. (2019). First report of Loricifera from the North East Pacific Region, with the description of two new species. Marine Biodiversity, 49(3), 1151-1168. The genus includes: References Loricifera {{Protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalidophora
Scalidophora is a group of marine pseudocoelomate ecdysozoans that was proposed on morphological grounds to unite three phyla: the Kinorhyncha, the Priapulida and the Loricifera. The three phyla have four characters in common — chitinous cuticle that is moulted, rings of scalids on the introvert, flosculi, and two rings of introvert retracts.Heiner, I., Kristensen, R.H. 2005. Two new species of the genus ''Pliciloricus'' (Loricifera, Pliciloricidae) from the Faroe Bank, North Atlantic. Zoologischer Anzeiger. 243: 121–138. The introvert and abdomen are separated by a distinct neck region in all groups, but in adult macroscopic priapulids it becomes rudimentary in ''Priapulus'' and is completely absent in ''Halicryptus''. However, the monophyly of the Scalidophora was not supported by two molecular studies, where the position of the Loricifera was uncertain or as sister to the Panarthropoda. Both studies supported a reduced Scalidophora comprising the Kinorhyncha and Priapulid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliciloricus Enigmaticus
'' Pliciloricus enigmaticus'' is a marine Loriciferan species of genus '' Pliciloricus'' first described by Higgins & Kristensen 1986. Description ''Pliciloricus enigmaticus'' is a marine species in which adults measure between 160–268 μm of length (excluding any cone mouth). The body is dual compound, located in the second row spinoscalids in position medioventral and lies fused in the middle of its length basal. It usually is very modified, strongly sclerotised, and rigid. The 15 spinoscalids have claws in the third row. Spinoscalids with 4–7 teeth that alternate with spinoscalids that are not modified. The Lorica features 7 ridges cuticular transverse and longitudinal ridges doubles, 2 plates lateroventral of the caudal region. The anus is terminal. Distribution The species name ''Pliciloricus enigmaticus'' has so far only been used for animals found in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean: Two finds off the eastern shore of North America (se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliciloricidae
Pliciloricidae are a family of marine organisms in the phylum Loricifera Loricifera (from Latin, ''wikt:lorica, lorica'', corselet (armour) + ''ferre'', to bear) is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 43 described species and approximately 100 more that hav .... It contains 23 species in 4 genera.Shinta Fujimoto, Hiroshi Yamasaki, Taeko Kimura, Susumu Ohtsuka and Reinhardt Møbjerg Kristensen. 2020. A New Genus and Species of Loricifera (Nanaloricida: Pliciloricidae) from the Deep Waters of Japan. ''Marine Biodiversity.'' 50: 103. DOI: ''10.1007/s12526-020-01130-3'' Genera * '' Pliciloricus'' * '' Rugiloricus'' * '' Titaniloricus'' * '' Wataloricus'' References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q592541 Loricifera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinctiplicata
The Vinctiplicata is a clade of Scalidophora uniting the Loricifera and the Priapulida, and representing the sister group to the Kinorhyncha. Its monophyly is supported on morphological grounds, although some molecular studies indicate that the Loricifera may be more closely related to the Nematomorpha Nematomorpha (sometimes called Gordiacea, and commonly known as horsehair worms, hairsnakes, or Gordian worms) are a phylum of parasitoid animals superficially similar to nematode worms in morphology, hence the name. Most species range in size f .... References Scalidophora Ecdysozoa unranked clades {{Protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolyn Bartlett Gast
Carolyn Bartlett Gast (April 30, 1929 – ''c.'' September 2015) was an American scientific illustrator. Early life and education Gast was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts. She studied book illustrating at Boston University and spent a year training and drafting for the Army Map Service. Career Gast worked at the Departments of Vertebrate and Invertebrate Zoology at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, Washington D.C., from 1954 to 1985. She was a scientific illustrator who used a stereoscopic microscope to make two-dimensional drawings of specimens. Her most well known and reproduced illustration is of the loriciferan phylum ''pliciloricus enigmatus,'' which was discovered in 1983 by the Danish biologist Reinhardt Møbjerg Kristensen in the microscopic ecosystem between grains of sand. She was also credited for providing illustrations in publications such as the academic journal ''Crustaceana''. Gast was founder of the Guild of Natural Science Illu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloneuralia
Cycloneuralia is a proposed clade of ecdysozoan animals including the Scalidophora ( Kinorhynchans, Loriciferans, Priapulids), the Nematoida (nematodes, Nematomorphs), and the extinct Palaeoscolecida. It may be paraphyletic, or may be a sister group to Panarthropoda. Or perhaps Panarthropoda is paraphyletic with respect to Cycloneuralia. The group has also been considered a single phylum, sometimes given the old name Nemathelminthes. The uniting character is the nervous system organization with a circumpharyngeal brain and somata–neuropil–somata pattern. The name derives from the position of the brain around the pharynx The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates .... References Ecdysozoa unranked clades {{protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about eight phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocoelomate
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it remains undifferentiated. In the past, and for practical purposes, coelom characteristics have been used to classify bilaterian animal phyla into informal groups. Etymology The term ''coelom'' derives from the Ancient Greek word () 'cavity'. Structure Development The coelom is the mesodermally lined cavity between the gut and the outer body wall. During the development of the embryo, coelom formation begins in the gastrulation stage. The developing digestive tube of an embryo forms as a blind pouch called the archenteron. In protostomes, the coelom forms by a process known as schizocoely. The archenteron initially forms, and the mesoderm splits into two layers: the first attaches to the body wall or ectoderm, forming the parieta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |