|
Live Coding
Live coding, sometimes referred to as on-the-fly programming,Wang G. & Cook P. (2004"On-the-fly Programming: Using Code as an Expressive Musical Instrument" In ''Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression (NIME)'' (New York: NIME, 2004). just in time programming and conversational programming, makes programming an integral part of the running program. It is most prominent as a performing arts form and a creativity technique centred upon the writing of source code and the use of interactive programming in an improvisation, improvised way. Live coding is often used to create sound and image based digital media, as well as light systems, improvised dance and poetry, though is particularly prevalent in computer music usually as improvisation, although it could be combined with algorithmic composition. Typically, the process of writing source code is made visible by projecting the computer screen in the audience space, with ways of visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Study In Keith
Study or studies may refer to: General * Education **Higher education * Clinical trial * Experiment * Field of study * Observational study * Scientific study * Research * Study skills, abilities and approaches applied to learning Other * Study (art), a drawing or series of drawings done in preparation for a finished piece * Study (film), ''Study'' (film), a 2012 film by Paolo Benetazzo * Study (Flandrin), ''Study'' (Flandrin), an 1835/36 painting by Hippolyte Flandrin * Study (room), a room in a home used as an office or library * Study (soundtrack), ''Study'' (soundtrack), a soundtrack album from the 2012 film * The Study, a private all-girls school in Westmount, Quebec, Canada * Studies (journal), ''Studies'' (journal), published by the Jesuits in Ireland * Eduard Study (1862–1930), German mathematician * Facebook Study, a market research app See also * Étude, a short musical composition * * * * Studie {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Reactive Programming
Functional reactive programming (FRP) is a programming paradigm for reactive programming (asynchronous dataflow programming) using the building blocks of functional programming (e.g., map, reduce, filter). FRP has been used for programming graphical user interfaces (GUIs), robotics, games, and music, aiming to simplify these problems by explicitly modeling time. Formulations of FRP The original formulation of functional reactive programming can be found in the ICFP 97 paper Functional Reactive Animation by Conal Elliott and Paul Hudak. FRP has taken many forms since its introduction in 1997. One axis of diversity is discrete vs. continuous semantics. Another axis is how FRP systems can be changed dynamically. Continuous The earliest formulation of FRP used continuous semantics, aiming to abstract over many operational details that are not important to the meaning of a program. The key properties of this formulation are: * Modeling values that vary over continuous time, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demoscene
The demoscene () is an international computer art subculture focused on producing demos: self-contained, sometimes extremely small, computer programs that produce audiovisual presentations. The purpose of a demo is to show off computer programming, programming, visual art, and musical skills. Demos and other demoscene productions (graphics, music, videos, games) are shared, voted on and released online at festivals known as Demoscene#Parties, demoparties. The scene started with the home computer revolution of the early 1980s, and the subsequent advent of software cracking. Crackers altered the code of computer games to remove copy protection, claiming credit by adding introduction screens of their own ("crack intro, cracktros"). They soon started competing for the best visual presentation of these additions. Through the making of intros and stand-alone demos, a new community eventually evolved, independent of the gaming and Warez scene, software sharing scenes. Demos are informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorave
An algorave (from an algorithm and rave) is an event where people dance to music generated from algorithms, often using live coding techniques. Alex McLean of Slub and Nick Collins coined the word "algorave" in 2011, and the first event under such a name was organised in London, England. It has since become a movement, with algoraves taking place around the world. Description Algoraves can include a range of styles, including a complex form of minimal techno, and the movement has been described as a meeting point of hacker philosophy, geek culture, and clubbing. Although live coding is commonplace, any algorithmic music is welcome which is "wholly or predominantly characterised by the emission of a succession of repetitive conditionals", which is a corruption of the definition of rave music (“wholly or predominantly characterised by the emission of a succession of repetitive beats”) in the UK's Criminal Justice and Public Order Act 1994. Although algorave musicians have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonic Pi
Sonic Pi is a live coding environment based on Ruby, originally designed to support both computing and music lessons in schools, developed by Sam Aaron in the University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory in collaboration with Raspberry Pi Foundation. Uses Thanks to its use of the SuperCollider synthesis engine and accurate timing model, it is also used for live coding and other forms of algorithmic music performance and production, including at algoraves. Its research and development has been supported by Nesta, via the ''Sonic PI: Live & Coding'' project. See also * Pure Data * Algorithmic composition * List of MIDI editors and sequencers * List of music software This is a list of software for creating, performing, learning, analyzing, researching, broadcasting and editing music. This article only includes software, not services. For streaming services such as iHeartRadio, Pandora (service), Pandora, Prime ... Further reading * * * * * * References External link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
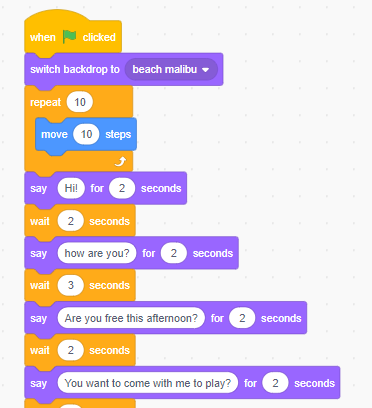
Scratch (programming Language)
Scratch is a High-level programming language, high-level, block-based visual programming language and website aimed primarily at children as an educational tool, with a target audience of ages 8 to 16. Users on the site can create projects on the website using a block-like interface. Scratch was conceived and designed through collaborative National Science Foundation grants awarded to Mitchel Resnick and Yasmin Kafai. Scratch is developed by the MIT Media Lab and has been translated into 70+ languages, being used in most parts of the world. Scratch is taught and used in after-school centers, schools, and colleges, as well as other public knowledge institutions. As of 15 February 2023, community statistics on the language's official website show more than 123 million projects shared by over 103 million users, and more than 95 million monthly website visits. Overall, more than 1.15 billion projects have been created in total, with the site reaching its one billionth project on A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Data
Pure Data (Pd) is a visual programming language developed by Miller Puckette in the 1990s for creating interactive computer music and multimedia works. While Puckette is the main author of the program, Pd is an open-source software, open-source project with a large developer base working on new extensions. It is released under BSD licenses, BSD-3-Clause. It runs on Linux, MacOS, iOS, Android (operating system), Android and Windows. Ports exist for FreeBSD and IRIX. Pd is very similar in scope and design to Puckette's original Max (software), Max program, developed while he was at IRCAM, and is to some degree interoperable with Max/MSP, the commercial predecessor to the Max language. They may be collectively discussed as members of the Patcher family of languages. With the addition of the Graphics Environment for Multimedia (GEM) external, and externals designed to work with it (like Pure Data Packet / PiDiP for Linux, ), framestein for Windows, GridFlow (as n-dimensional matri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharo
Pharo is a Cross-platform software, cross-platform implementation of the classic Smalltalk-80 programming language and runtime system. It is based on the OpenSmalltalk virtual machine (VM) named Cog, which evaluates a dynamic, Reflective programming, reflective, and Object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language with a Syntax (programming languages), syntax closely resembling Smalltalk#Syntax, Smalltalk-80. It is free and open-source software, released under a mix of MIT License, MIT, and Apache License, Apache 2 licenses. Pharo is shipped with source code compiled into a ''system image'' that contains all software needed to run Pharo. Like the original Smalltalk-80, Pharo provides several live programming features such as immediate object manipulation, Reflective programming, live updates, and just-in-time compilation (JIT). The system image includes an integrated development environment (IDE) to modify its components. Pharo was forked from Squeak v3.9 in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max (software)
Max, also known as Max/MSP/Jitter, is a visual programming language for music and multimedia developed and maintained by San Francisco-based software company Cycling '74. Over its more than thirty-year history, it has been used by composers, performers, software designers, researchers, and artists to create recordings, performances, and installations. The Max program is modular, with most routines existing as shared library, shared libraries. An application programming interface (API) allows third-party development of new routines (named ''external objects''). Thus, Max has a large user base of programmers unaffiliated with Cycling '74 who enhance the software with commercial and non-commercial Software extension, extensions to the program. Because of this Extensibility, extensible design, which simultaneously represents both the Computer program, program's structure and its graphical user interface (GUI), Max has been described as the lingua franca for developing interactive mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixi Lang
Ixi lang is a programming language for live coding musical expression. It is taught at diverse levels of musical education and used in Algorave performances. Like many other live coding languages, such TidalCycles, ixi lang is a domain-specific language that embraces simplicity and constraints in design. In 2015, ixi lang was presented at the Loop summit, organised by the music software manufacturer Ableton, where it gained critical acclaim as an alternative way of making music in the studio as well as in live performance. Mark Smith, of techno-duo Garland writes about the language: "By entering the name of a sound, drawing your own bars and typing notes with numbers, you can make simple beats and melodies almost immediately. If you memorise a few different command lines a broad range of modulations and structural changes becomes possible. Whatever simple information you entered beforehand becomes hugely pliable – and you can do all this to your own uploaded bank of samples. Gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extempore (software)
Extempore is a live coding environment focused on real-time audiovisual software development. It is designed to accommodate the demands of cyber-physical computing.Sorensen, Andrew, and Henry Gardner. 2010. "Programming with Time: Cyber-Physical Programming with Impromptu." In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Object Oriented Programming Systems Languages and Applications, 822–34. New York: ACM. Extempore consists of two integrated languages, Scheme (with extensions) and ''Extempore Language''. It uses the LLVM cross-language compiler to achieve performant digital signal processing and related low-level features, on-the-fly. Relationship to Impromptu Extempore shares the use of Scheme syntax, real-time audiovisual emphasis and lead developer Andrew Sorensen with the older and related project Impromptu. It runs under both Linux and Mac OS X. The bindings to Apple An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |