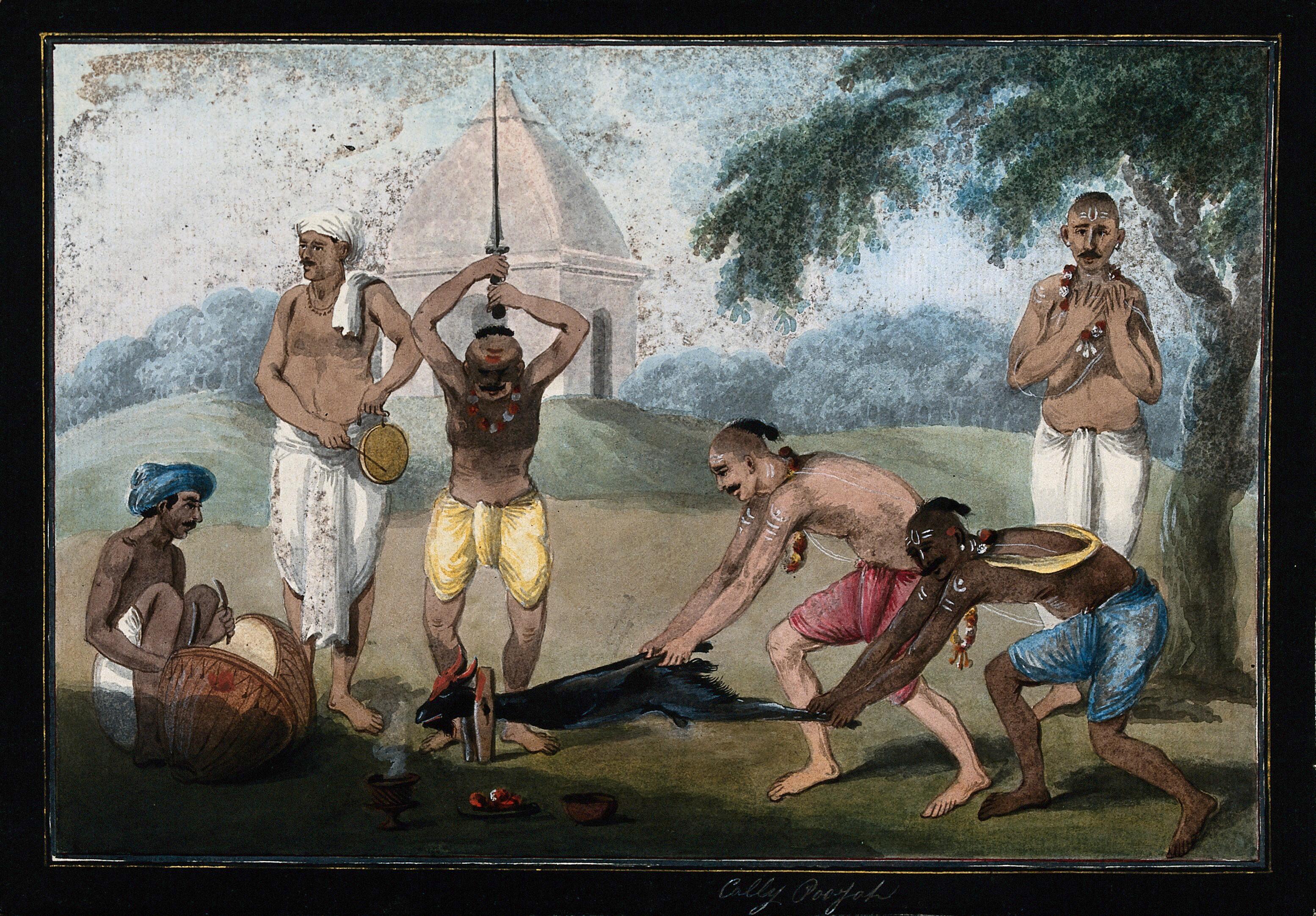|
Left-Hand Path
In Western esotericism, left-hand path and right-hand path are two opposing approaches to magic. Various groups engaged with the occult and ceremonial magic use the terminology to establish a dichotomy, broadly simplified as (malicious) black magic on the left and (benevolent) white magic on the right. Others approach the left/right paths as different kinds of workings, without connotations of good or bad magical actions. Still others treat the paths as fundamental schemes, connected with external divinities on the right, contrasted with self-deification on the left. The terms have their origins in tantra: the right-hand path (RHP, or ''dakṣiṇācāra'') applied to magical groups that follow specific ethical codes and adopt social convention, while the left-hand path (LHP, or '' vāmācāra'') adopts the opposite attitude, breaking taboos and abandoning set morality. Contemporary occultists such as Peter J. Carroll have stressed that both paths can be followed by a magi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baphomet By Éliphas Lévi
Baphomet is a figure incorporated across various occult and Western esotericism, Western esoteric traditions. During Trials of the Knights Templar, trials starting in 1307, the Knights Templar were accused of heresy for worshipping Baphomet as a Demon, demonic Cult image, idol. Baphomet subsequently resurfaced during 19th century speculation and debate regarding the suppression of the Templars, with various occult and mystical traditions claiming Baphomet as a symbol of balance and synthesis, originating in teachings of the Gnostics, while others maintained Baphomet as a profane deity. Since 1856 the figure of Baphomet has been associated with the Sabbatic Goat illustration by Éliphas Lévi, composed of binary elements representing the "symbolization of the equilibrium of opposites": both Human–animal hybrid, human and animal, both Androgyny, masculine and feminine, combined in Unity of opposites, metaphysical unity. Lévi's intention was to symbolize his concept of balance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, organ systems. The external human body consists of a human head, head, hair, neck, torso (which includes the thorax and abdomen), Sex organ, genitals, arms, Hand, hands, human leg, legs, and Foot, feet. The internal human body includes organs, Human tooth, teeth, bones, muscle, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels and blood, lymphatic vessels and lymph. The study of the human body includes anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body Anatomical variation, varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar, iron, and oxygen in the blood. The body is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakshinachara
''Dakṣiṇācāra'' is a tantric term meaning 'right-hand path'. It is used to describe tantric sects that do not engage in heterodox practices. In contrast, '' vamachara'' ('left-hand path') is used to describe particular tantric practices that are considered heterodox. Etymology N. N. Bhattacharyya explains the Sanskrit technical term '' '' as follows: The means of spiritual attainment which varies from person to person according to competence.... ''Ācāras'' are generally of seven kinds – Veda, Vaiṣṇava, Śaiva, Dakṣiṇa, Vāma, Siddhāṇta, and Kaula, falling into two broad categories – Dakṣiṇa and Vāma. Interpretations vary regarding the nature and grouping of the ''ācāras''. '' '' means 'right'. For this reason, the term ''dakṣiṇāra'' is often translated "right-hand path". Practices The ''Brahma Yamala'', a tantric text, says there are three currents of tradition (''dakshina'', ''vama'', and ''madhyama'') characterized respectively by the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vāmācāra
''Vāmācāra'' (, ) is a tantric term meaning 'left-hand path' and is synonymous with the Sanskrit term ''vāmamārga''. It is used to describe a particular mode of worship or '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) that uses heterodox things to sublimate for spiritual growth. These practices are often generally considered to be tantric in orientation. The converse term is ''dakṣiṇācāra'' "right-hand path", which is used to refer not only to orthodox sects but to modes of spirituality that engage in spiritual practices that accord with Vedic injunction and are generally agreeable to the status quo. Left-handed and right-handed modes of practice may be evident in both orthodox and heterodox practices of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and Buddhism and are a matter of taste, culture, proclivity, initiation, ''sadhana'' and lineage ('' parampara''). Nomenclature and etymology N. N. Bhattacharyya explains the Sanskrit technical term '' '' as follows: e mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sexuality
Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, psychological, physical, erotic, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Someone's sexual orientation is their pattern of sexual interest in the opposite and/or same sex. Physical and emotional aspects of sexuality include bonds between individuals that are expressed through profound feelings or physical manifestations of love, trust, and care. Social aspects deal with the effects of human society on one's sexuality, while spirituality concerns an individual's spiritual connection with others. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, moral, ethical, and religi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state with Stateless society, stateless societies and voluntary Free association (communism and anarchism), free associations. A historically left-wing movement, anarchism is usually described as the libertarian wing of the socialist movement (libertarian socialism). Although traces of anarchist ideas are found all throughout history, modern anarchism emerged from the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment. During the latter half of the 19th and the first decades of the 20th century, the anarchist movement flourished in most parts of the world and had a significant role in Labour movement, workers' struggles for emancipation. #Schools of thought, Various anarchist schools of thought formed during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogma
Dogma, in its broadest sense, is any belief held definitively and without the possibility of reform. It may be in the form of an official system of principles or doctrines of a religion, such as Judaism, Roman Catholicism, Protestantism, or Islam, the positions of a philosopher or philosophical school, such as Stoicism, and political belief systems such as fascism, socialism, progressivism, liberalism, and conservatism. In the pejorative sense, dogma refers to enforced decisions, such as those of aggressive political interests or authorities. More generally, it is applied to some strong belief that its adherents are not willing to discuss rationally. This attitude is named as a dogmatic one, or dogmatism, and is often used to refer to matters related to religion, though this pejorative sense strays far from the formal sense in which it is applied to religious belief. The pejorative sense is not limited to theistic attitudes alone and is often used with respect to political or ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satanism
Satanism refers to a group of religious, ideological, or philosophical beliefs based on Satan—particularly his worship or veneration. Because of the ties to the historical Abrahamic religious figure, Satanism—as well as other religious, ideological, or philosophical beliefs that align with Satanism—is considered a countercultural Abrahamic religion. Satan is associated with the Devil in Christianity, a fallen angel regarded as chief of the demons who tempt humans into sin. Satan is also associated with the Devil in Islam, a jinn who has rebelled against God, the leader of the devils (''shayāṭīn''), made of fire who was cast out of Heaven because he refused to bow before the newly created Adam and incites humans to sin. The phenomenon of Satanism shares "historical connections and family resemblances" with the Left Hand Path milieu of other occult figures such as Asmodeus, Beelzebub, Mephistopheles, Samael, Lilith, Lucifer, Hecate, and Set. Self-identifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Magic
Sex magic (sometimes spelled sex magick) is any type of sexual activity used in magical, ritualistic or otherwise religious and spiritual pursuits. One practice of sex magic is using sexual arousal or orgasm with visualization of a desired result. A premise posited by sex magicians is the concept that sexual energy is a potent force that can be harnessed to transcend one's normally perceived reality. Paschal Beverly Randolph The earliest known practical teachings of sex magic in the Western world come from 19th-century American occultist Paschal Beverly Randolph (1825–1875). Son of a wealthy Virginian father and a slave mother, he was a well-known spiritualist who was greatly influenced by the work of English Rosicrucian and scholar of phallicism, Hargrave Jennings. Randolph developed one of the most influential systems of sex magic. As per him, the moment when one reaches orgasm is the most intense and the most powerful experience a human can have in life, for in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Status Quo
is a Latin phrase meaning the existing state of affairs, particularly with regard to social, economic, legal, environmental, political, religious, scientific or military issues. In the sociological sense, the ''status quo'' refers to the current state of social structure or values. With regard to policy debate, it means how conditions are contrasted with a possible change. For example: "The countries are now trying to maintain the ''status quo'' with regard to their nuclear arsenals." To maintain the ''status quo'' is to keep things the way they presently are. The related phrase '' status quo ante'', literally 'the status before', refers to the state of affairs that existed previously. Political usage The status quo may be changed via social movements. These seek to alleviate or prevent a particular issue and often to shape social feeling and cultural expression of a society or nation. Advocating to improve the status quo is a persuasive rhetorical device. This is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrahamic Religions
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them with Indian religions, Iranian religions, and East Asian religions. The term has been introduced in the 20th century and superseded the term Judeo-Christianity, Judeo-Christian tradition for the inclusion of Islam. However, the categorization has been criticized by some for oversimplification of different cultural and doctrinal nuances. For example, Islam shares cultural and doctrinal exchange from Asian religions, which Abrahamic religions are usually contrasted with. Usage The term ''Abrahamic religions'' (and its variations) is a collective religious descriptor for elements shared by Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. It features prominently in interfaith dialogue and political discourse but also has entered Academic discourse socializati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |