|
Leech Embryogenesis
Leech embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo of the leech forms and develops. The embryonic development of the larva occurs as a series of stages. During stage 1, the first cleavage occurs, which gives rise to an AB and a CD blastomere, and is in the interphase of this cell division when a yolk-free cytoplasm called teloplasm is formed. The teloplasm is known to be a determinant for the specification of the D cell fate. In stage 3, during the second cleavage, an unequal division occurs in the CD blastomere. As a consequence, it creates a large D cell on the left and a smaller C cell to the right. This unequal division process is dependent on actomyosin, and by the end of stage 3 the AB cell divides. On stage 4 of development, the micromeres and teloblast stem cells are formed and subsequently, the D quadrant divides to form the DM and the DNOPQ teloblast precursor cells. By the end stage 6, the zygote contains a set of 25 micromeres, 3 macromeres (A, B and C) and 10 telobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodites and have a clitellum, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid; the coelom, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels. The majority of leeches live in freshwater habitats, while some species can be found in terrestrial or marine environments. The best-known species, such as the medicinal leech, ''Hirudo medicinalis'', are hematophagous, attaching themselves to a host with a sucker and feeding on blood, having first secreted the pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Neurobiology
''Developmental Neurobiology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of neural development. It was established in 1969 as ''Journal of Neurobiology'', covering all of neuroscience, but when the scope become more specialized, it obtained its current name in 2007. The journal is published by Wiley-Blackwell. The editor-in-chief is Bin Chen (University of California, Santa Cruz) and the associate editors are Song-Hai Shi ( Tsinghua University, Beijing, China) and Andreas Prokop (University of Manchester). Abstracting and indexing The journals is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.935. References External links * {{Off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Bulletin
''The Biological Bulletin'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of biology. The journal was established in 1897 as the ''Zoological Bulletin'' by Charles Otis Whitman and William Morton Wheeler. In 1899 the title was changed to ''The Biological Bulletin'', and production was transferred to the Marine Biological Laboratory at Woods Hole, Massachusetts. The current editor-in-chief is Kenneth M. Halanych. ''The Biological Bulletin'' is indexed by several bibliographic services, including Index Medicus, MEDLINE, Chemical Abstracts, Current Contents, BIOBASE, and Geo Abstracts. Six issues are published per year and all content is made freely available one year after publication. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports ''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publication by Clarivate. It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science Core Collection. It provides information about academic journals in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of the transcription facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Development (journal)
''Development'' is a bi-weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of developmental biology that covers cellular and molecular mechanisms of animal and plant development. It is published by The Company of Biologists. ''Development'' is partnered with Publons, is part of the Review Commons initiative and has two-way integration with bioRxiv. In 2009, the BioMedical & Life Sciences Division of the Special Libraries Association included ''Development'' in their list of top 100 journals in Biology and Medicine over the last 100 years. Brief history Originally called ''Journal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology'' () and established in 1953, the journal provided a periodical that would be primarily devoted to morphogenesis. In 1987, the journal was renamed ''Development''. The journal's full archive from 1953 is available online. ''Development'' is now a hybrid journal and publishes 24 issues a year. Content over 6 months old is free to read. Scope and content ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubifex
''Tubifex'' is a cosmopolitan genus of tubificid annelids that inhabits the sediments of lakes, rivers and occasionally sewer lines. At least 13 species of ''Tubifex'' have been identified, with the exact number not certain, as the species are not easily distinguishable from each other. Reproduction ''Tubifex'' worms are hermaphroditic: each individual has both male (testes) and female (ovaries) organs in the same animal. These minute reproductive organs are attached to the ventral side of the body wall in the celomic cavity. In mature specimens, the reproductive organs are clearly found on the ventral side of the body. Copulation and cocoon formation Although the ''Tubifex'' worms are hermaphrodites, the male and female organs become mature at different times; thus self-fertilization is avoided, and cross-fertilization is encouraged. Two mature ''Tubifex'' worms undergo copulation by joining ventral and anterior surfaces together with their anterior ends pointing opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer ( stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the sole of the foot with most being roughly 90μm. Thickness does not vary between the sexes but becomes thinner with age. The human epidermis is an example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek language, Greek ''ektos'' meaning "outside", and ''derma'' meaning "skin".Gilbert, Scott F. Developmental Biology. 9th ed. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, 2010: 333-370. Print. Generally speaking, the ectoderm differentiates to form epithelial tissue, epithelial and nervous system, neural tissues (spinal cord, nerves and brain). This includes the Epidermis (skin), skin, linings of the mouth, anus, nostrils, sweat glands, hair and nails, and tooth enamel. Other types of epithelium are derived from the endoderm. In vertebrate embryos, the ectoderm can be divided into two parts: the dorsal surface ectoderm also known as the external ectoderm, and the neural plate, which inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Morphology
The ''Journal of Morphology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of anatomy and morphology featuring primary research articles, review articles, and meeting abstracts. The journal was established in 1887 by zoologists and morphologists Edward Phelps Allis and C. O. Whitman. The journal appeared regularly from 1887 onwards and made a financial loss. Allis provided the support necessary for the journal to continue appearing until, after a short gap, the journal underwent reorganization in 1907 when it was taken over by Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, as a more permanent solution to its financial problems. As of 2022, it is edited by J. Matthias Starck.''Am. Zool. (1979) 19 (4): 1251-1253.'' According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermatozoon). Once fertilized, the ovum becomes a single diploid cell known as a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitosis, mitotic cell division, divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage (embryo), cleavage) and cellular differentiation, leading to development of a multicellular embryo after passing through an organizational checkpoint during mid-embryogenesis. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to the early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages. The main stages of animal embryonic development are as follows: * The zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions (called cleavage) to form a structure called a morula. * The morula develops into a structure called a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teloblast
A teloblast is a large cell in the embryos of clitellate annelids which asymmetrically divide to form many smaller cells known as blast cells. These blast cells further proliferate and differentiate to form the segmentation (biology), segmental tissues of the annelid. Teloblasts are well studied in leeches, though they are also present in the other major class of clitellates: the oligochaetes. Developmental role and morphology All teloblasts are specified from the D quadrant macromere after the second round of divisions post-fertilization. They are larger than the other cells that result from cleavage of macromere D'. There are five pairs of teloblasts, one on each side of the embryo. Four of the teloblasts (N, O, P, and Q) give rise to ectodermal tissue and one pair (M) gives rise to mesodermal tissue. The column of blast cells arising out of each teloblast is known as a bandlet. All five bandlets coalesce into one germinal band on each side of the embryo, extending out f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
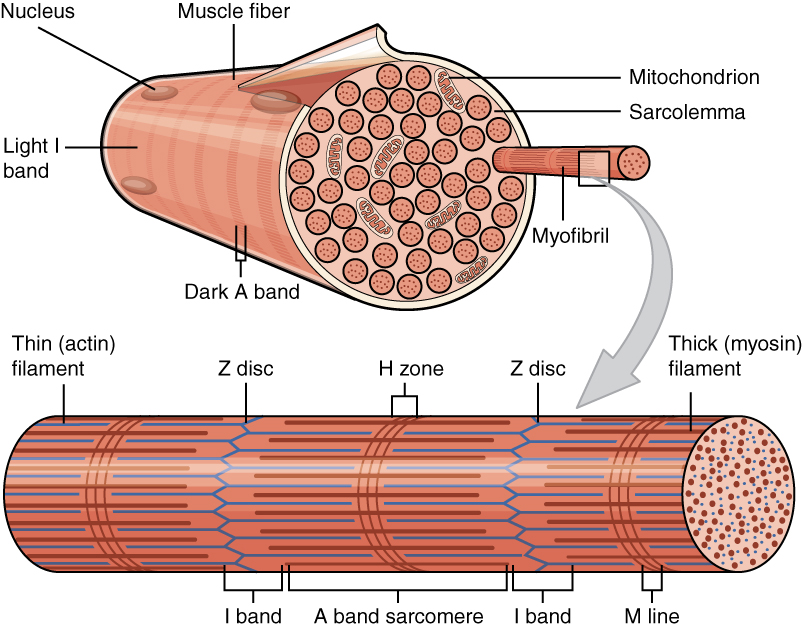
Actomyosin
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one of mostly actin, and a very thin one of mostly titin. Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates), and non-striated smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered. Smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments. Structure There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thick filaments consist primarily of a type of myosin, a motor protein – myosin II. Each thick filament is ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |