|
Language Module
The language module or language faculty is a hypothetical structure in the human brain which is thought to contain innate capacities for language, originally posited by Noam Chomsky. There is ongoing research into brain modularity in the fields of cognitive science and neuroscience, although the current idea is much weaker than what was proposed by Chomsky and Jerry Fodor in the 1980s. In today's terminology, 'modularity' refers to specialisation: language processing is specialised in the brain to the extent that it occurs partially in different areas than other types of information processing such as visual input. The current view is, then, that language is neither compartmentalised nor based on general principles of processing (as proposed by George Lakoff). It is modular to the extent that it constitutes a specific cognitive skill or area in cognition. Meaning of a module The notion of a dedicated language module in the human brain originated with Noam Chomsky's theory of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activities of the human body, body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sensory nervous system. The brain integrates sensory information and coordinates instructions sent to the rest of the body. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six Cerebral cortex#Layers of neocortex, neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes of the brain, lobes – the frontal lobe, frontal, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative research studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is highly multidisciplinary involving neuroscience, computer science, psychology and statistics, and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging is sometimes confused with neuroradiology. Neuroradiology is a medical specialty that uses non-statistical brain imaging in a clinical setting, practiced by radiologists who are medical practitioners. Neuroradiology primarily focuses on recognizing brain lesions, such as vascular diseases, strokes, tumors, and inflammatory diseases. In contrast to neuroimaging, neuroradiology is qualitative (based on subjective impressions and extensive clinical training) but sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cognitive Architecture
A cognitive architecture is both a theory about the structure of the human mind and to a computational instantiation of such a theory used in the fields of artificial intelligence (AI) and computational cognitive science. These formalized models can be used to further refine comprehensive theories of cognition and serve as the frameworks for useful artificial intelligence programs. Successful cognitive architectures include ACT-R (Adaptive Control of Thought – Rational) and SOAR. The research on cognitive architectures as software instantiation of cognitive theories was initiated by Allen Newell in 1990. A theory for a cognitive architecture is an "''hypothesis about the fixed structures that provide a mind, whether in natural or artificial systems, and how they work together — in conjunction with knowledge and skills embodied within the architecture — to yield intelligent behavior in a diversity of complex environments." History Herbert A. Simon, one of the founders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Neurolinguistics
Neurolinguistics is the study of Nervous system, neural mechanisms in the human brain that control the comprehension, production, and acquisition of language. As an interdisciplinary field, neurolinguistics draws methods and theories from fields such as neuroscience, linguistics, cognitive science, communication disorders and neuropsychology. Researchers are drawn to the field from a variety of backgrounds, bringing along a variety of experimental techniques as well as widely varying theoretical perspectives. Much work in neurolinguistics is informed by models in psycholinguistics and theoretical linguistics, and is focused on investigating how the brain can implement the processes that theoretical and psycholinguistics propose are necessary in producing and comprehending language. Neurolinguists study the physiological mechanisms by which the brain processes information related to language, and evaluate linguistic and psycholinguistic theories, using aphasiology, brain imagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics or psychology of language is the study of the interrelation between linguistic factors and psychological aspects. The discipline is mainly concerned with the mechanisms by which language is processed and represented in the mind and brain; that is, the psychology, psychological and neurobiology, neurobiological factors that enable humans to acquire, use, comprehend, and produce language. Psycholinguistics is concerned with the cognitive faculties and processes that are necessary to produce the grammatical constructions of language. It is also concerned with the perception of these constructions by a listener. Initial forays into psycholinguistics were in the philosophical and educational fields, mainly due to their location in departments other than applied sciences (e.g., cohesive data on how the human brain functioned). Modern research makes use of biology, neuroscience, cognitive science, linguistics, and information science to study how the mind-brain process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
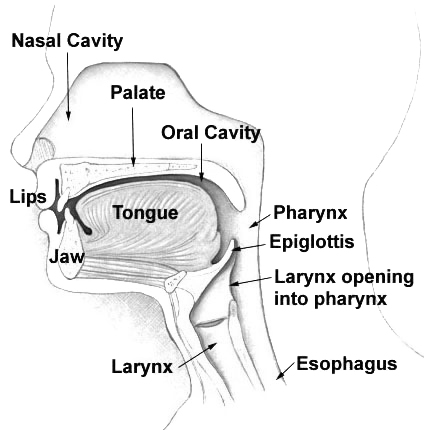 |
Motor Theory Of Speech Perception
The motor theory of speech perception is the hypothesis that people perceive spoken words by identifying the vocal tract gestures with which they are pronounced rather than by identifying the sound patterns that speech generates. It originally claimed that speech perception is done through a specialized module that is innate and human-specific. Though the idea of a module has been qualified in more recent versions of the theory, the idea remains that the role of the speech motor system is not only to produce speech articulations but also to detect them. The hypothesis has gained more interest outside the field of speech perception than inside. This has increased particularly since the discovery of mirror neurons that link the production and perception of motor movements, including those made by the vocal tract. The theory was initially proposed in the Haskins Laboratories in the 1950s by Alvin Liberman and Franklin S. Cooper, and developed further by Donald Shankweiler, Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Language Center
In neuroscience and psychology, the term language center refers collectively to the areas of the brain which serve a particular function for speech processing and production. Language is a core system that gives humans the capacity to solve difficult problems and provides them with a unique type of social interaction. Language allows individuals to attribute symbols (e.g. words or signs) to specific concepts, and utilize them through sentences and phrases that follow proper grammatical rules. Finally, speech is the mechanism by which language is orally expressed. Information is exchanged in a larger system, including language-related regions. These regions are connected by white matter fiber tracts that make possible the transmission of information between regions. The white matter fiber bunches were recognized to be important for language production after suggesting that it is possible to make a connection between multiple language centers. The three classical language areas t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
PsycNET
PsycINFO is a database of abstracts of literature in the field of psychology. It is produced by the American Psychological Association and distributed on the association's APA PsycNET and through third-party vendors. It is the electronic version of the now-ceased ''Psychological Abstracts''. In 2000, it absorbed PsycLIT which had been published on CD-ROM. PsycINFO contains citations and summaries from the 19th century to the present of journal articles, book chapters, books, and dissertations. Overview The database, which is updated weekly, contained over 3.5 million records as of October 2013. Approximately 175,000 records were added to the database in 2012. Coverage More than 2,540 peer-reviewed journal titles are included in the database, and they make up 78% of the overall content. Journals are included if they are archival, scholarly, peer-reviewed, and regularly published with titles, abstracts, and keywords in English. As of October 2013, over 1,700 journal titles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
McGurk Effect
The McGurk effect is a perceptual phenomenon that demonstrates an interaction between hearing and vision in speech perception. The illusion occurs when the auditory component of one sound is paired with the visual component of another sound, leading to the perception of a third sound. The visual information a person gets from seeing a person speak changes the way they hear the sound. If a person is getting poor-quality auditory information but good-quality visual information, they may be more likely to experience the McGurk effect. Integration abilities for audio and visual information may also influence whether a person will experience the effect. People who are better at sensory integration have been shown to be more susceptible to the effect. Many people are affected differently by the McGurk effect based on many factors, including brain damage and other disorders. Background It was first described in 1976 in a paper by Harry McGurk and John MacDonald, titled "Hearing Lip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
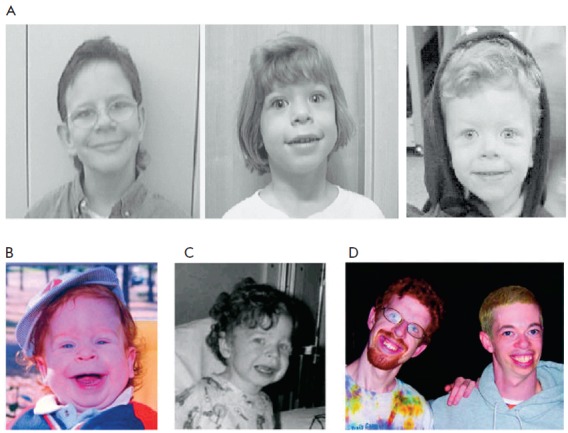 |
Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS), also Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed, particularly challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing. Verbal skills are relatively unaffected. Many people have an outgoing personality, a happy disposition, an openness to engaging with other people, increased empathy and decreased aggression. Medical issues with teeth, heart problems (especially supravalvular aortic stenosis), and periods of hypercalcemia, high blood calcium are common. Williams syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality, specifically a Deletion (genetics), deletion of about 27 genes from the long arm of one of the two chromosome 7s. Typically, this occurs as a random event during the formation of the egg or sperm from which a person develops. In a small number of cases, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Specific Language Impairment
Specific language impairment (SLI) is diagnosed when a child's language does not develop normally and the difficulties cannot be accounted for by generally slow development, physical abnormality of the speech apparatus, autism spectrum disorder, apraxia, acquired brain damage or hearing loss. Twin studies have shown that it is under genetic influence. Although language impairment can result from a single-gene mutation, this is unusual. More commonly SLI results from the combined influence of multiple genetic variants, each of which is found in the general population, as well as environmental influences. Classification Specific language impairment (SLI) is diagnosed when a child has delayed or disordered language development for no apparent reason. Usually the first indication of SLI is that the child is later than usual in starting to speak and subsequently is delayed in putting words together to form sentences. Spoken language may be immature. In many children with SLI, understan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Steven Pinker
Steven Arthur Pinker (born September 18, 1954) is a Canadian-American cognitive psychology, cognitive psychologist, psycholinguistics, psycholinguist, popular science author, and public intellectual. He is an advocate of evolutionary psychology and the computational theory of mind. Pinker is the Johnstone Family Professor of Psychology at Harvard University. He specializes in visual cognition and developmental linguistics, and his experimental topics include mental imagery, shape recognition, visual attention, regularity and irregularity in language, the neural basis of words and grammar, and childhood language development. Other experimental topics he works on are the psychology of cooperation and of communication, including emotional expression, euphemism, innuendo, and how people use "common knowledge", a term of art meaning the shared understanding in which two or more people know something, know that the other one knows, know the other one knows that they know, and so on. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |