|
Kinematic Synthesis
In mechanical engineering, kinematic synthesis (also known as mechanism synthesis) determines the size and configuration of mechanisms that shape the flow of power through a mechanical system, or machine, to achieve a desired performance. The word ''synthesis'' refers to combining parts to form a whole. Hartenberg and Denavit describe kinematic synthesis asHartenberg, R.S. and J. Denavit (1964Kinematic synthesis of linkages New York: McGraw-Hill — Online link from Cornell University. ...it is design, the creation of something new. Kinematically, it is the conversion of a motion idea into hardware. The earliest machines were designed to amplify human and animal effort, later gear trains and linkage systems captured wind and flowing water to rotate millstones and pumps. Now machines use chemical and electric power to manufacture, transport, and process items of all types. And kinematic synthesis is the collection of techniques for designing those elements of these mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
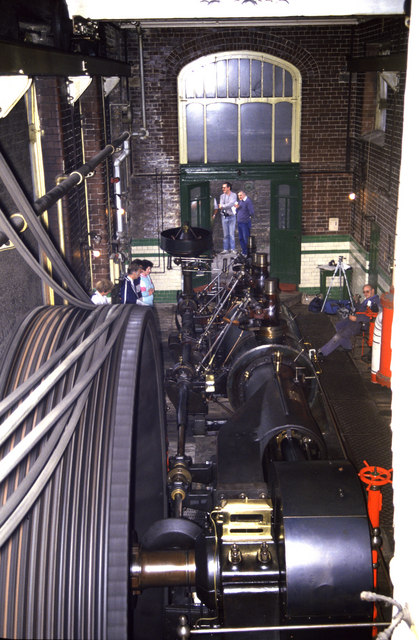
Rope Drive
A rope drive is a form of belt drive, used for mechanical power transmission. Rope drives use a number of circular section ropes, rather than a single flat or vee belt. Multiple rope drive The first multiple rope drive was a 9-rope drive of 200 bhp produced by Combe Barbour for their Falls Foundry, Belfast, in 1863. James Combe experimented first with circular ropes laid from leather strips, then from manila hemp. The idea of using rope drives had arisen from his earlier, 1856, experiments in using a rope drive together with an expanding vee pulley, as part of a Van Doorne or Variomatic transmission. Combe Barbour were makers of textile machinery and differential speed gearing was often needed as part of the spinning process, where one shaft could be smoothly adjusted to run slightly faster or slower than another. Usage Rope drives were most widely used for power-transmission in mills and factories, where a single mill engine would have a large rope drive to eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
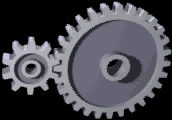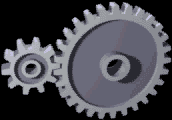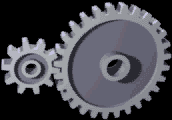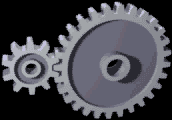
Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Came Disque Types Suiveurs
A came is a divider bar used between small pieces of glass to make a larger glazing panel. There are two kinds of came: the H-shaped sections that hold two pieces together and the U-shaped sections that are used for the borders. Cames are mostly made of lead, zinc, copper, brass or brass-capped lead.Stevenson, Christine. (2004). ''Creative Stained Glass: Modern Designs & Simple Techniques.'' Lark Books. p. 12. . Of the metal strips, lead is softer and more flexible, making it easier to cut and bend. The harder metals are used to work with slightly curved lines and pieces that require greater structural support. They can also be used as border came, once again for stability and support.Shannon, George and Pat Torlen. (2002). ''The new stained glass: techniques, projects, patterns, designs.'' Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. p. 51. . Purpose Came serves three purposes:Berry, Leigh Ann. (2003). ''Basic Stained Glass Making: All the Skills and Tools You Need to Get Started.'' Stack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
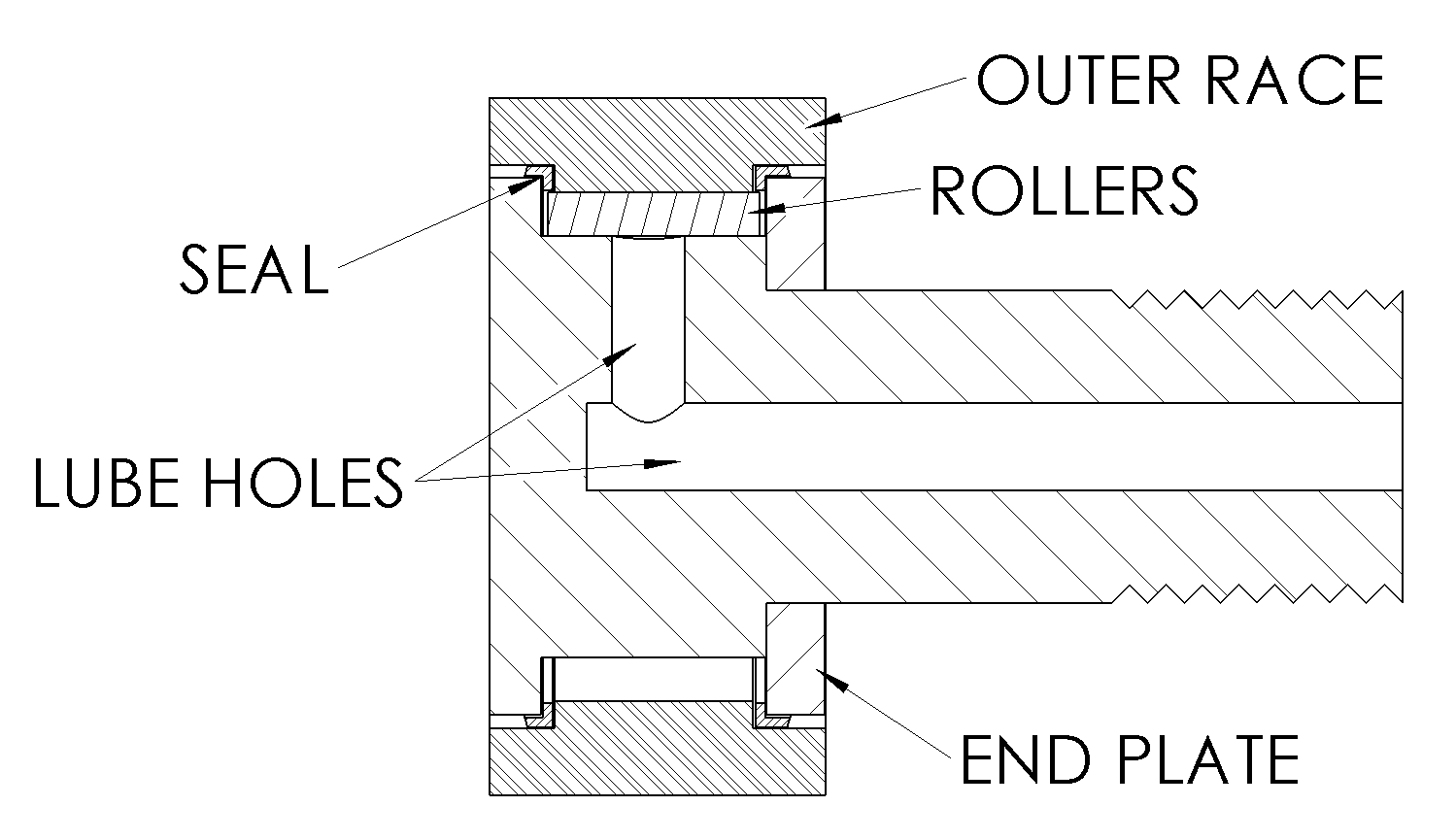
Cam Follower
In mechanical engineering, a cam follower, also known as a track follower, is a specialized type of roller or needle bearing designed to follow cam lobe profiles. Cam followers come in a vast array of different configurations, however the most defining characteristic is how the cam follower mounts to its mating part; ''stud'' style cam followers use a stud while the ''yoke'' style has a hole through the middle. Construction The modern stud type follower was invented and patented in 1937 by Thomas L. Robinson of the McGill Manufacturing Company. It replaced using a standard bearing and bolt. The new cam followers were easier to use because the stud was already included and they could also handle higher loads. While roller cam followers are similar to roller bearings, there are quite a few differences. Standard ball and roller bearings are designed to be pressed into a rigid housing, which provides circumferential support. This keeps the outer race from deforming, so the race cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmester Theory
In kinematics, Burmester theory comprises geometric techniques for synthesis of linkages. It was introduced in the late 19th century by Ludwig Burmester (1840–1927). His approach was to compute the geometric constraints of the linkage directly from the inventor's desired movement for a floating link. From this point of view a four-bar linkage is a floating link that has two points constrained to lie on two circles. Burmester began with a set of locations, often called ''poses'', for the floating link, which are viewed as snapshots of the constrained movement of this floating link in the device that is to be designed. The design of a crank for the linkage now becomes finding a point in the moving floating link that when viewed in each of these specified positions has a trajectory that lies on a circle. The dimension of the crank is the distance from the point in the floating link, called the circling point, to the center of the circle it travels on, called the center point. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Burmester
Ludwig Ernst Hans Burmester (5 May 1840 – 20 April 1927) was a German kinematician and geometer. His doctoral thesis (from German: ''About the elements of a theory of isophotes'') concerned lines on a surface defined by light direction. After a period as a teacher in Łódź he became professor of synthetic geometry at Dresden where his growing interest in kinematics culminated in his (''Textbook of Kinematics, First Volume, Planar Motion'') of 1888, developing the approach to the theory of linkages introduced by Franz Reuleaux, whereby a planar mechanism was understood as a collection of Euclidean planes in relative motion with one degree of freedom. Burmester considered both the theory of planar kinematics and practically all actual mechanisms known in his time. In doing so, Burmester developed Burmester theory which applies projective geometry to the loci of points on planes moving in straight lines and in circles, where any motion may be understood in relation to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crank (mechanism)
A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod). The term often refers to a human-powered crank which is used to manually turn an axle, as in a bicycle crankset or a brace and bit drill. In this case a person's arm or leg serves as the connecting rod, applying reciprocating force to the crank. There is usually a bar perpendicular to the other end of the arm, often with a freely rotatable handle or pedal attached. Examples Familiar examples include: Hand-powered cranks * Spinning Wheel * Mechanical pencil sharpener * Fishing reel and other reels for cables, wires, ropes, etc. *Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinematics Equations
Kinematics equations are the constraint equations of a mechanical system such as a robot manipulator that define how input movement at one or more joints specifies the configuration of the device, in order to achieve a task position or end-effector location. Kinematics equations are used to analyze and design articulated systems ranging from four-bar linkages to serial and parallel robots. Kinematics equations are constraint equations that characterize the geometric configuration of an articulated mechanical system. Therefore, these equations assume the links are rigid and the joints provide pure rotation or translation. Constraint equations of this type are known as holonomic constraints in the study of the dynamics of multi-body systems. Loop equations The kinematics equations for a mechanical system are formed as a sequence of rigid transformations along links and around joints in a mechanical system. The principle that the sequence of transformations around a loop must r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Component Assembly
Circuit Component may refer to: •Are devices that perform functions when they are connected in a circuit. In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems *System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assembly or software module, within a system considered at a particular level of analysis *Lumped element model, a model of spatially distributed systems Electrical *Component video, a type of analog video information that is transmitted or stored as two or more separate signals *Electronic components, the constituents of electronic circuits *Symmetrical components, in electrical engineering, analysis of unbalanced three-phase power systems Mathematics *Color model, a way of describing how colors can be represented, typically as multiple values or color components *Component (group theory), a quasi-simple subnormal sub-group *Connected component (graph theory), a maximal connected subgraph *Connected component (topology), a maximal connected su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinematic Coupling
Kinematic coupling describes fixtures designed to exactly constrain the part in question, providing precision and certainty of location. A canonical example of a kinematic coupling consists of three radial v-grooves in one part that mate with three hemispheres in another part. Each hemisphere has two contact points for a total of six contact points, enough to constrain all six of the part's degrees of freedom. An alternative design consists of three hemispheres on one part that fit respectively into a tetrahedral dent, a v-groove, and a flat. Background Kinematic couplings arose from the need of precision coupling between structural interfaces that were meant to be routinely taken apart and put back together. Kelvin Coupling The Kelvin coupling is named after William Thompson (Lord Kelvin) who published the design in 1868–71. It consists of three spherical surfaces that rest on a concave tetrahedron, a V-groove pointing towards the tetrahedron and a flat plate. The tetrah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |