|
Keldysh Formalism
In Non-equilibrium thermodynamics, non-equilibrium physics, the Keldysh formalism is a general framework for describing the quantum mechanical evolution of a system in a non-equilibrium state or systems subject to time varying external fields (electrical field, magnetic field etc.). Historically, it was foreshadowed by the work of Julian Schwinger and proposed almost simultaneously by Leonid Keldysh and, separately, Leo Kadanoff and Gordon Baym. It was further developed by later contributors such as O. V. Konstantinov and V. I. Perel. Extensions to driven-dissipative open quantum systems is given not only for bosonic systems, but also for fermionic systems. The Keldysh formalism provides a systematic way to study non-equilibrium systems, usually based on the two-point functions corresponding to excitations in the system. The main mathematical object in the Keldysh formalism is the non-equilibrium Green's function (NEGF), which is a two-point function of particle fields. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics
Non-equilibrium thermodynamics is a branch of thermodynamics that deals with physical systems that are not in thermodynamic equilibrium but can be described in terms of macroscopic quantities (non-equilibrium state variables) that represent an extrapolation of the variables used to specify the system in thermodynamic equilibrium. Non-equilibrium thermodynamics is concerned with transport processes and with the rates of chemical reactions. Almost all systems found in nature are not in thermodynamic equilibrium, for they are changing or can be triggered to change over time, and are continuously and discontinuously subject to flux of matter and energy to and from other systems and to chemical reactions. Some systems and processes are, however, in a useful sense, near enough to thermodynamic equilibrium to allow description with useful accuracy by currently known non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Nevertheless, many natural systems and processes will always remain far beyond the scope o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and in condensed matter physics to construct models of quasiparticles. QFT treats particles as excited states (also called quanta) of their underlying quantum fields, which are more fundamental than the particles. The equation of motion of the particle is determined by minimization of the Lagrangian, a functional of fields associated with the particle. Interactions between particles are described by interaction terms in the Lagrangian involving their corresponding quantum fields. Each interaction can be visually represented by Feynman diagrams according to perturbation theory in quantum mechanics. History Quantum field theory emerged from the work of generations of theoretical physicists spanning much of the 20th century. Its deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress Of Theoretical And Experimental Physics
''Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics'' (PTEP) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Physical Society of Japan. It was established as ''Progress of Theoretical Physics'' in July 1946 by Hideki Yukawa was a Japanese theoretical physicist and the first Japanese Nobel laureate for his prediction of the pi meson, or pion. Biography He was born as Hideki Ogawa in Tokyo and grew up in Kyoto with two older brothers, two older sisters, and two yo ... and obtained its current name in January 2013. ''Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics'' is part of the SCOAP3 initiative. References External links * Physics journals English-language journals Publications established in 1946 Theoretical physics Monthly journals Oxford University Press academic journals Open access journals Particle physics journals {{physics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NanoHUB
nanoHUB.org is a science and engineering gateway comprising community-contributed resources and geared toward education, professional networking, and interactive simulation tools for nanotechnology. Funded by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF), it is a product of the Network for Computational Nanotechnology (NCN). NCN supports research efforts in nanoelectronics; nanomaterials; nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS); nanofluidics; nanomedicine, nanobiology; and nanophotonics. History The Network for Computational Nanotechnology was established in 2002 to create a resource for nanoscience and nanotechnology via online services for research, education, and professional collaboration. Initially a multi-university initiative of eight member institutions including Purdue University, the University of California at Berkeley, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Molecular Foundry at Lawrence Berkeley National Laborator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kondo Effect
In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities, resulting in a characteristic change i.e. a minimum in electrical resistivity with temperature. The cause of the effect was first explained by Jun Kondo, who applied third-order perturbation theory to the problem to account for scattering of s-orbital conduction electrons off d-orbital electrons localized at impurities ( Kondo model). Kondo's calculation predicted that the scattering rate and the resulting part of the resistivity should increase logarithmically as the temperature approaches 0 K. Experiments in the 1960s by Myriam Sarachik at Bell Laboratories provided the first data that confirmed the Kondo effect. Extended to a lattice of ''magnetic impurities'', the Kondo effect likely explains the formation of ''heavy fermions'' and ''Kondo insulators'' in intermetallic compounds, especially those involving rare earth elements such as cerium, praseodymium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
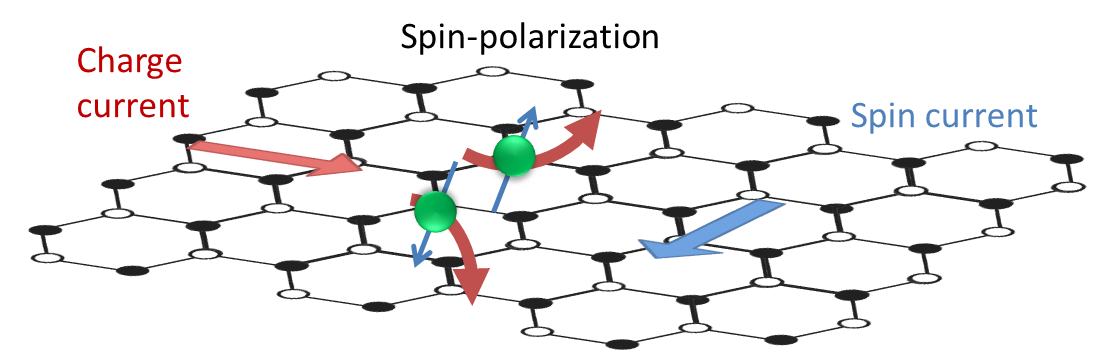
Spin Hall Effect
The spin Hall effect (SHE) is a transport phenomenon predicted by Russian physicists Mikhail I. Dyakonov and Vladimir I. Perel in 1971. It consists of the appearance of spin accumulation on the lateral surfaces of an electric current-carrying sample, the signs of the spin directions being opposite on the opposing boundaries. In a cylindrical wire, the current-induced surface spins will wind around the wire. When the current direction is reversed, the directions of spin orientation is also reversed. Definition The spin Hall effect is a transport phenomenon consisting of the appearance of spin accumulation on the lateral surfaces of a sample carrying electric current. The opposing surface boundaries will have spins of opposite sign. It is analogous to the classical Hall effect, where ''charges'' of opposite sign appear on the opposing lateral surfaces in an electric-current carrying sample in a magnetic field. In the case of the classical Hall effect the charge build up at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feynman Diagrams
In theoretical physics, a Feynman diagram is a pictorial representation of the mathematical expressions describing the behavior and interaction of subatomic particles. The scheme is named after American physicist Richard Feynman, who introduced the diagrams in 1948. The interaction of subatomic particles can be complex and difficult to understand; Feynman diagrams give a simple visualization of what would otherwise be an arcane and abstract formula. According to David Kaiser, "Since the middle of the 20th century, theoretical physicists have increasingly turned to this tool to help them undertake critical calculations. Feynman diagrams have revolutionized nearly every aspect of theoretical physics." While the diagrams are applied primarily to quantum field theory, they can also be used in other fields, such as solid-state theory. Frank Wilczek wrote that the calculations that won him the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics "would have been literally unthinkable without Feynman diagram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wick's Theorem
Wick's theorem is a method of reducing high-order derivatives to a combinatorics problem. It is named after Italian physicist Gian-Carlo Wick. It is used extensively in quantum field theory to reduce arbitrary products of creation and annihilation operators to sums of products of pairs of these operators. This allows for the use of Green's function methods, and consequently the use of Feynman diagrams in the field under study. A more general idea in probability theory is Isserlis' theorem. In perturbative quantum field theory, Wick's theorem is used to quickly rewrite each time ordered summand in the Dyson series as a sum of normal ordered terms. In the limit of asymptotically free ingoing and outgoing states, these terms correspond to Feynman diagrams. Definition of contraction For two operators \hat and \hat we define their contraction to be :\hat^\bullet\, \hat^\bullet \equiv \hat\,\hat\, - \mathopen \hat\,\hat \mathclose where \mathopen \hat \mathclose denotes the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-ordering
In theoretical physics, path-ordering is the procedure (or a meta-operator \mathcal P) that orders a product of operators according to the value of a chosen parameter: :\mathcal P \left\ \equiv O_(\sigma_) O_(\sigma_) \cdots O_(\sigma_). Here ''p'' is a permutation that orders the parameters by value: :p : \ \to \ :\sigma_ \leq \sigma_ \leq \cdots \leq \sigma_. For example: :\mathcal P \left\ = O_4(1) O_2(2) O_3(3) O_1(4) . Examples If an operator is not simply expressed as a product, but as a function of another operator, we must first perform a Taylor expansion of this function. This is the case of the Wilson loop, which is defined as a path- ordered exponential to guarantee that the Wilson loop encodes the holonomy of the gauge connection. The parameter ''σ'' that determines the ordering is a parameter describing the contour, and because the contour is closed, the Wilson loop must be defined as a trace in order to be gauge-invariant. Time ordering In qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermionic Field
In quantum field theory, a fermionic field is a quantum field whose quanta are fermions; that is, they obey Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermionic fields obey canonical anticommutation relations rather than the canonical commutation relations of bosonic fields. The most prominent example of a fermionic field is the Dirac field, which describes fermions with spin-1/2: electrons, protons, quarks, etc. The Dirac field can be described as either a 4-component spinor or as a pair of 2-component Weyl spinors. Spin-1/2 Majorana fermions, such as the hypothetical neutralino, can be described as either a dependent 4-component Majorana spinor or a single 2-component Weyl spinor. It is not known whether the neutrino is a Majorana fermion or a Dirac fermion; observing neutrinoless double-beta decay experimentally would settle this question. Basic properties Free (non-interacting) fermionic fields obey canonical anticommutation relations; i.e., involve the anticommutators = ''ab'' + ''ba'', r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosonic Field
In quantum field theory, a bosonic field is a quantum field whose quanta are bosons; that is, they obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Bosonic fields obey canonical commutation relations, as distinct from the canonical anticommutation relations obeyed by fermionic fields. Examples include scalar fields, describing spin-0 particles such as the Higgs boson, and gauge fields, describing spin-1 particles such as the photon. Basic properties Free (non-interacting) bosonic fields obey canonical commutation relations. Those relations also hold for interacting bosonic fields in the interaction picture, where the fields evolve in time as if free and the effects of the interaction are encoded in the evolution of the states. It is these commutation relations that imply Bose–Einstein statistics for the field quanta. Examples Examples of bosonic fields include scalar fields, gauge fields, and symmetric 2-tensor fields, which are characterized by their covariance under Lorentz transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |