|
Kusunda Language
Kusunda or Kusanda (endonym ) is a language isolate spoken by a few among the Kusunda people in western and central Nepal. As of 2023, it only has a single fluent speaker, Kamala Sen-Khatri, although there are efforts underway to keep the language alive. There are 23 native speakers according to the 2021 Nepal census. Rediscovery For decades the Kusunda language was thought to be on the verge of extinction, with little hope of ever knowing it well. The little material that could be gleaned from the memories of former speakers suggested that the language was an isolate, but, without much evidence, it was often classified along with its neighbors as Tibeto-Burman. However in 2004 three Kusundas, Gyani Maya Sen, Prem Bahadur Shahi and Kamala Singh, were brought to Kathmandu for help with citizenship papers. There, members of Tribhuvan University discovered that one of them, a native of Sakhi VDC in southern Rolpa District, was a fluent speaker of the language. Several of her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundanese Language
Sundanese ( ; , Sundanese script: , ) is an Austronesian language spoken in Java, primarily by the Sundanese. It has approximately 32 million native speakers in the western third of Java; they represent about 15% of Indonesia's total population. Classification According to American linguist Robert Blust, Sundanese is closely related to the Malayic languages, as well as to language groups spoken in Borneo such as the Land Dayak languages or the Kayan–Murik languages, based on high lexical similarities between these languages. History and distribution Sundanese is mainly spoken on the west side of the island of Java, in an area known as Tatar Sunda ( Pasundan). However, Sundanese is also spoken in the western part of Central Java, especially in Brebes and Cilacap Regency, because these areas were previously under the control of the Galuh Kingdom. Many place names in Cilacap are still Sundanese names such as Dayeuhluhur, Cimanggu, Cipari, even as far as Banyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman Languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed paral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burushaski
Burushaski (; , ) is a language isolate, spoken by the Burusho people, who predominantly reside in northern Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. There are also a few hundred speakers of this language in northern Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir, India. In Pakistan, Burushaski is spoken by the people of the Hunza District, the Nagar District, the northern Gilgit District, the Yasin Valley, Yasin Valley in the Gupis-Yasin District, and the Ishkoman Valley, Ishkoman Valley of the northern Ghizer District (2019–), Ghizer District. Their native region is northern Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit–Baltistan. It also borders the Pamir corridor to the north. In India, Burushaski is spoken in Botraj Mohalla of the Hari Parbat region in Srinagar. It is generally believed that the language was spoken in a much wider area in the past. It is also known as ''Werchikwar'' and ''Miśa:ski''. Classification Attempts have been made to establish links between Burushaski and several diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
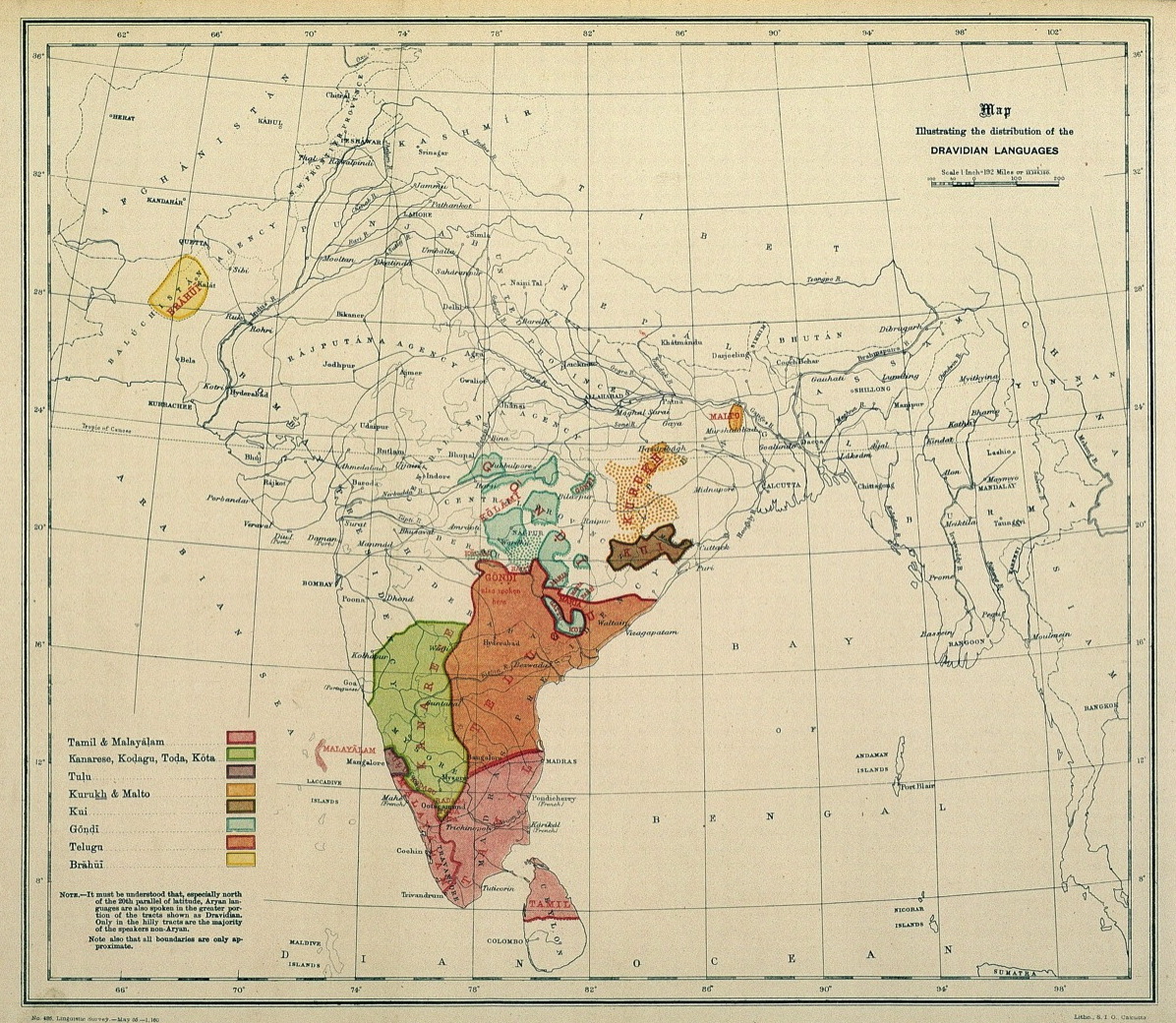
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munda Languages
The Munda languages are a group of closely related languages spoken by about eleven million people in India, Bangladesh and Nepal. Historically, they have been called the Kolarian languages. They constitute a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which means they are more distantly related to languages such as the Mon and Khmer languages, to Vietnamese, as well as to minority languages in Thailand and Laos and the minority Mangic languages of South China. Bhumij, Ho, Mundari, and Santali are notable Munda languages. The family is generally divided into two branches: North Munda, spoken in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Odisha and West Bengal, as well as in parts of Bangladesh and Nepal, and South Munda, spoken in central Odisha and along the border between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. North Munda, of which Santali is the most widely spoken and recognised as an official language in India, has twice as many speakers as South Munda. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranian Languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also known as Indo-Iranic languages or collectively the Aryan languages) constitute the largest branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.7 billion speakers worldwide, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia. Indo-Iranian languages are divided into three major branches: Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and Nuristani languages. The Badeshi language remains unclassified within the Indo-Iranian branch. The largest Indo-Iranian language is the Hindustani language (Hindi-Urdu)."Hindi" L1: 322 million (2011 Indian census), including perhaps 150 million speakers of other languages that reported their language as "Hindi" on the census. L2: 274 million (2016, source unknown). Urdu L1: 67 million (2011 & 2017 censuses), L2: 102 million (1999 Pakistan, source unknown, and 2001 Indian census): ''Ethnologue'' 21. . . The areas with Indo-Iranian languages stretch from Europe ( Romani) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stance
Stance may refer to: Sports *Stance (American football), the position an American football player adopts when a play begins *Stance (martial arts), the distribution, foot orientation and body positions adopted when attacking, defending, advancing or retreating ** Stances (tae kwon do), several stances used for different activities **Horse stance, a posture in Asian martial arts **Karate stances, body positions used to create power, flexibility and movement **Wushu stances, a fundamental part of all Chinese martial arts * Stance (yoga), also known as a posture or asana, a body position Music * ''Stance'' (EP), a 1978 record by R. Stevie Moore * Stance Punks, a Japanese punk rock band, formed in 1999 Other uses * Stance (brand), an American sock and underwear brand * Stance (vehicle), a characteristic of a motor vehicle * Stance (Vranje), a village in the municipality of Vranje, Serbia * Stance (linguistics), linguistic expression of judgement or philosophical position * Emanue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watters2005
Watters may refer to: * Watters (surname), a list of notable people with the name *Watters, Pennsylvania Watters is an unincorporated community located in Forward Township, Butler County, Pennsylvania Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, ..., an unincorporated community in Butler County, Pennsylvania, United States * Watters Gallery, a former art gallery in Sydney, Australia * Watters Smith Memorial State Park, a historical park in West Virginia See also * Watterstown, Wisconsin, a town in Grant County, Wisconsin, United States * Waters (name) * Watter (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David E
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uday Raj Aaley
Uday Raj Aaley is a language researcher, lexicographer, writer and activist from Nepal. He is known for documenting and revitalising the moribund Kusunda language and teaching it to young children along with Kusunda elders Gyani Maiya Sen-Kusunda and Kamala Sen-Khatri. In 2019, he and Timotheus Adrianus Bodt raised funds to document audio and video materials in Kusunda and create a list of 250 concepts in Kusunda. Aaley has indicated the lack of prescriptive grammar in Kusunda to generalise and formalise Kusunda in his research findings. Early life Uday Raj Aaley was born in western Nepal and is a native Magar language speaker. Career Aaley began documenting the Kusunda language in 2010s and published the trilingual (English-Nepali-Kusunda) dictionary ''Kusunda Jatira Shabdakosh'' in 2017. He began an education programme together with Gyani Maiya Sen-Kusunda and Kamala Sen-Khatri in January 2019 for teaching 20 children Kusunda with support from Nepal's Language Commis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyani Maiya Sen-Kusunda
Gyani Maiya Sen-Kusunda (1937 – 25 January 2020) was a Kusunda community elder from Nepal. She was presumed to be the last known speaker of Kusunda, a language isolate listed as the critically endangered language in the ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger''. Sen-Kusunda could not converse with others in her community in Kusunda despite being fluent as the language fell out of use over time after the nomadic Kusunda community started to settle in villages and married outside the community. She was interviewed widely by linguists and other scholars in an effort to document the Kusunda language. She died on 25 January 2020. Early life Sen-Kusunda was born in 1937 in the Dang district of Nepal to a family of hunter-gatherers and settled in the Kulmor village in Dang. Her mother's name is Puni Thakuri and sister's name is Kamala Sen-Khatri. She and her mother and sister spoke Kusunda until Thakuri's death in 1985, after which Khatri moved to India for work. Then, Sen-Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moribund Language
An endangered language or moribund language is a language that is at risk of disappearing as its speakers die out or shift to speaking other languages. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers and becomes a " dead language". If no one can speak the language at all, it becomes an "extinct language". A dead language may still be studied through recordings or writings, but it is still dead or extinct unless there are fluent speakers left. Although languages have always become extinct throughout human history, endangered languages are currently dying at an accelerated rate because of globalization, mass migration, cultural replacement, imperialism, neocolonialism and linguicide (language killing). Language shift most commonly occurs when speakers switch to a language associated with social or economic power or one spoken more widely, leading to the gradual decline and eventual death of the endangered language. The process of language shift is often influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |