|
Korea Deposit Insurance Corporation
The Korea Deposit Insurance Corporation (KDIC) is a South Korean deposit insurance corporation, established in 1996 to protect depositors and maintain the stability of the financial system. The main functions of KDIC are insurance management, risk surveillance, resolution, recovery, and investigation. Historical highlights The Depositor Protection Act was enacted on December 29, 1995, and the KDIC established on June 1, 1996. The KDIC began its operations as a deposit insurer on January 1, 1997, collecting The first deposit insurance premiums on April 30 that year. The first Deposit Insurance Fund Bond was issued on January 3, 1998, and on April 1 deposit insurance funds were consolidated under the management of the KDIC. The Resolution Finance Corporation (RFC) was established on December 27, 1999. 2001 * Jan. 01 Limited Coverage System was reinstated. * Dec. 24 The Special Investigation Mission began its operations. 2002 * May. 06 The KDIC Joined the International Associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheonggyecheon
Cheonggyecheon (, ) is a stream and public space in downtown Seoul, South Korea. A natural stream sourced from the Suseongdong Valley in Inwangsan, it was historically maintained as part of Seoul's early sewerage until the mid-20th century, when post-Korean War rapid economic development and deteriorating conditions prompted the filling of the stream with concrete and the construction of an elevated freeway, the Cheonggye Expressway, in its place. In 2003, the city government began an urban renewal project to remove the expressway and restore the stream, which was completed in 2005 at a cost of over (approximately US$281 million). The Cheonggyecheon restoration project initially attracted significant public criticism, but since its opening in 2005 it has become popular among residents and tourists. Geography Cheonggyecheon is an stream flowing west to east through downtown Seoul, and then meeting Jungnangcheon, which connects to the Han River and empties into the Yellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant Bank
A merchant bank is historically a bank dealing in commercial loans and investment. In modern British usage, it is the same as an investment bank. Merchant banks were the first modern banks and evolved from medieval merchants who traded in commodities, particularly cloth merchants. Historically, merchant banks' purpose was to facilitate or finance the production and trade of commodities, hence the name ''merchant''. Few banks today restrict their activities to such a narrow scope. In modern usage in the United States, the term additionally has taken on a more narrow meaning, and refers to a financial institution providing capital to companies in form of share ownership instead of loans. A merchant bank also provides advice on corporate matters to the firms in which they invest. History Merchant banks were the first modern banks. They emerged in the Middle Ages from the Italian grain and cloth merchants community and started to develop in the 11th century during the large E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deposit Insurance
Deposit insurance, deposit protection or deposit guarantee is a measure implemented in many countries to protect bank depositors, in full or in part, from losses caused by a bank's inability to pay its debts when due. Deposit insurance or deposit guarantee systems are one component of a financial system safety net that promotes financial stability. Process Banks are allowed (and usually encouraged) to lend or invest most of the money deposited with them instead of safe-keeping the full amounts (see fractional-reserve banking). If many of a bank's borrowers fail to repay their loans when due, the bank's creditors, including its depositors, risk loss. Because they rely on customer deposits that can be withdrawn on little or no notice, banks in financial trouble are prone to bank runs, where depositors seek to withdraw funds quickly ahead of a possible bank insolvency. Because banking institution failures have the potential to trigger a broad spectrum of harmful events, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insurance Companies Of South Korea
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to protect against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss. An entity which provides insurance is known as an insurer, insurance company, insurance carrier, or underwriter. A person or entity who buys insurance is known as a policyholder, while a person or entity covered under the policy is called an insured. The insurance transaction involves the policyholder assuming a guaranteed, known, and relatively small loss in the form of a payment to the insurer (a premium) in exchange for the insurer's promise to compensate the insured in the event of a covered loss. The loss may or may not be financial, but it must be reducible to financial terms. Furthermore, it usually involves something in which the insured has an insurable interest established by o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government-owned Companies Of South Korea
State ownership, also called public ownership or government ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, property, or enterprise by the national government of a country or state, or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownership specifically refers to industries selling goods and services to consumers and differs from public goods and government services financed out of a government's general budget. Public ownership can take place at the national, regional, local, or municipal levels of government; or can refer to non-governmental public ownership vested in autonomous public enterprises. Public ownership is one of the three major forms of property ownership, differentiated from private, collective/cooperative, and common ownership. In market-based economies, state-owned assets are often managed and operated as joint-stock corporations with a government owning all or a controlling stake of the company's shares. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korean Companies Established In 1996
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', ), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). South is sometimes abbreviated as S. Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Financial Regulatory Authorities By Jurisdiction
In this list of financial regulatory and supervisory authorities, central banks are only listed where they act as direct supervisors of individual financial firms, and competition authorities and takeover panels are not listed unless they are set up exclusively for financial services. Financial intelligence units and policy banks are not listed, unless they also have a financial supervisory mandate. List of current authorities Authorities by sovereign states Others authorities by sovereign states and dependencies Extinct financial regulatory authorities Only those former authorities with a dedicated Wikipedia article are listed here. * Belgian Banking Commission (1935–2011) * (SBIF, 1925–2019), (SAFP, 1980–2008) and (SVS, 1980–2018) * China Banking Regulatory Commission (2003–2018), China Insurance Regulatory Commission (2003–2018), China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (2018–2023), and Financial Stability and Development Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restructuring
Restructuring or Reframing is the corporate management term for the act of reorganizing the legal, ownership, operational, or other structures of a company for the purpose of making it more profitable, or better organized for its present needs. Other reasons for restructuring include a change of ownership or ownership structure, demerger, or a response to a crisis or major change in the business such as bankruptcy, repositioning, or buyout. Restructuring may also be described as corporate restructuring, debt restructuring and financial restructuring. Executives involved in restructuring often hire financial and legal advisors to assist in the transaction's details and negotiations. It may also be done by a newly-hired CEO specifically to make the difficult and controversial decisions, required to save or reposition the company. It generally involves financing debt, selling portions of the company to investors, and reorganizing or reducing operations. The basic nature of restr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Layoff
A layoff or downsizing is the temporary suspension or permanent termination of employment of an employee or, more commonly, a group of employees (collective layoff) for business reasons, such as personnel management or downsizing an organization. Originally, ''layoff'' referred exclusively to a temporary interruption in work, or employment but this has evolved to a permanent elimination of a position in both British and US English, requiring the addition of "temporary" to specify the original meaning of the word. A layoff is not to be confused with Wrongful dismissal, wrongful termination. ''Laid off workers'' or ''displaced workers'' are workers who have lost or left their jobs because their employer has closed or moved, there was insufficient work for them to do, or their position or Shift work, shift was abolished (Borbely, 2011). Downsizing in a company is defined to involve the reduction of employees in a workforce. Downsizing in companies became a popular practice in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1997 Asian Financial Crisis
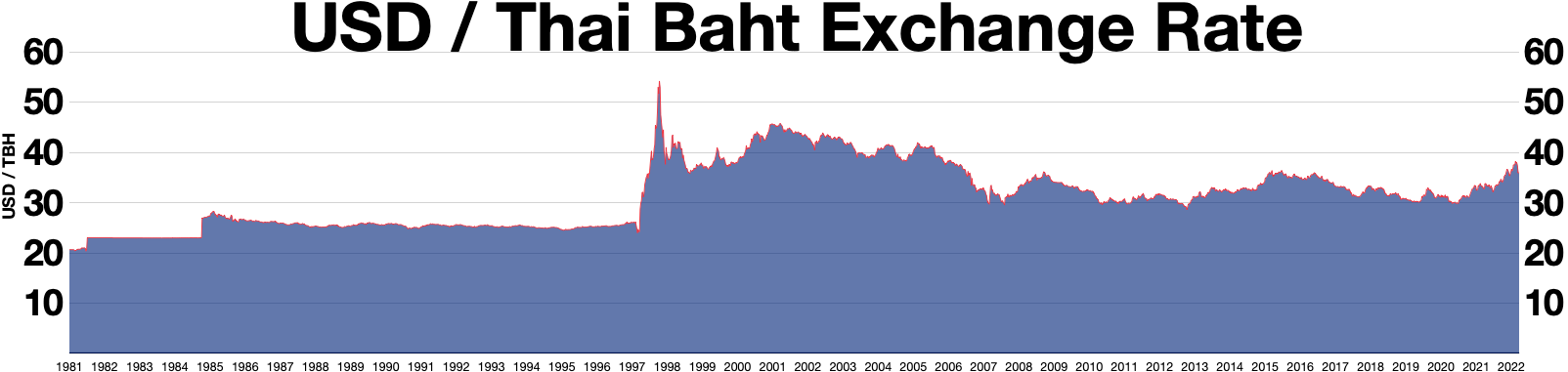
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided. Originating in Thailand, where it was known as the ''Tom yum, Tom Yum Kung crisis'' () on 2 July, it followed the financial collapse of the Thai baht after the Thai government was forced to floating currency, float the baht due to lack of list of circulating currencies, foreign currency to support its currency fixed exchange rate, peg to the U.S. dollar. Capital flight ensued almost immediately, beginning an international chain reaction. At the time, Thailand had acquired a burden of foreign debt. As the crisis spread, other Southeast Asian countries and later Japan and South Korea saw slumping currencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Credit Insurance
Trade credit insurance, business credit insurance, export credit insurance, or credit insurance is a type of insurance policy and a risk management product offered by private insurance companies and governmental export credit agencies to business entities wishing to protect their accounts receivable from loss due to credit risks such as protracted default, insolvency or bankruptcy. This insurance product is a type of property and casualty insurance, and should not be confused with such products as credit life or credit disability insurance, which individuals obtain to protect against the risk of loss of income needed to pay debts. Trade credit insurance can include a component of political risk insurance which is offered by the same insurers to insure the risk of non-payment by foreign buyers due to currency issues, political unrest, expropriation etc. This points to the major role trade credit insurance plays in facilitating international trade. Trade credit is offered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |