|
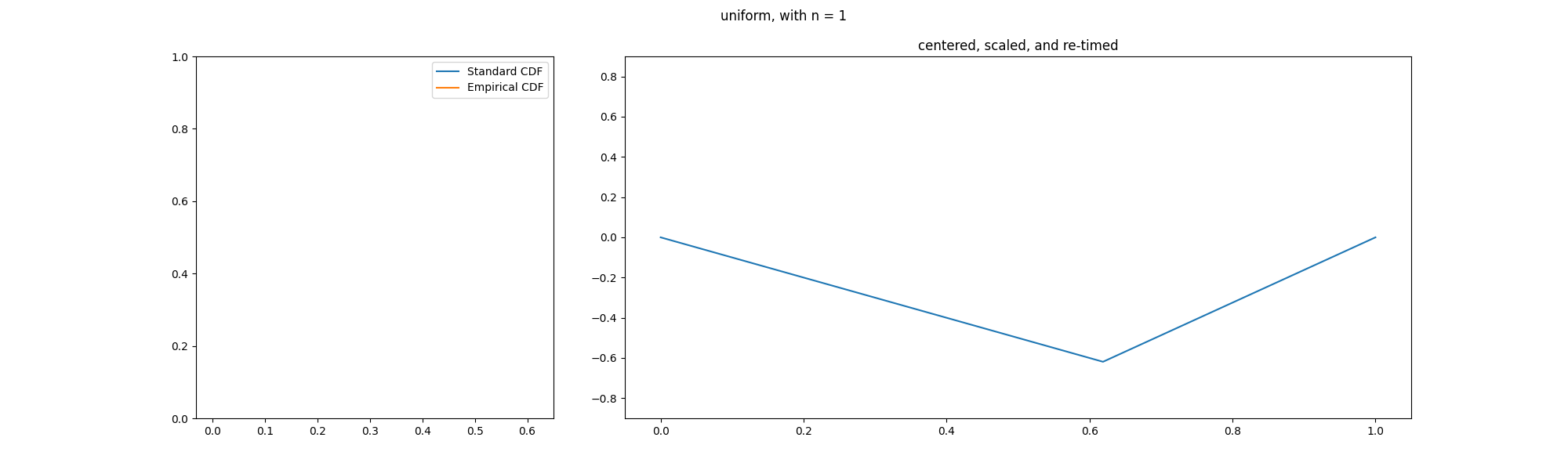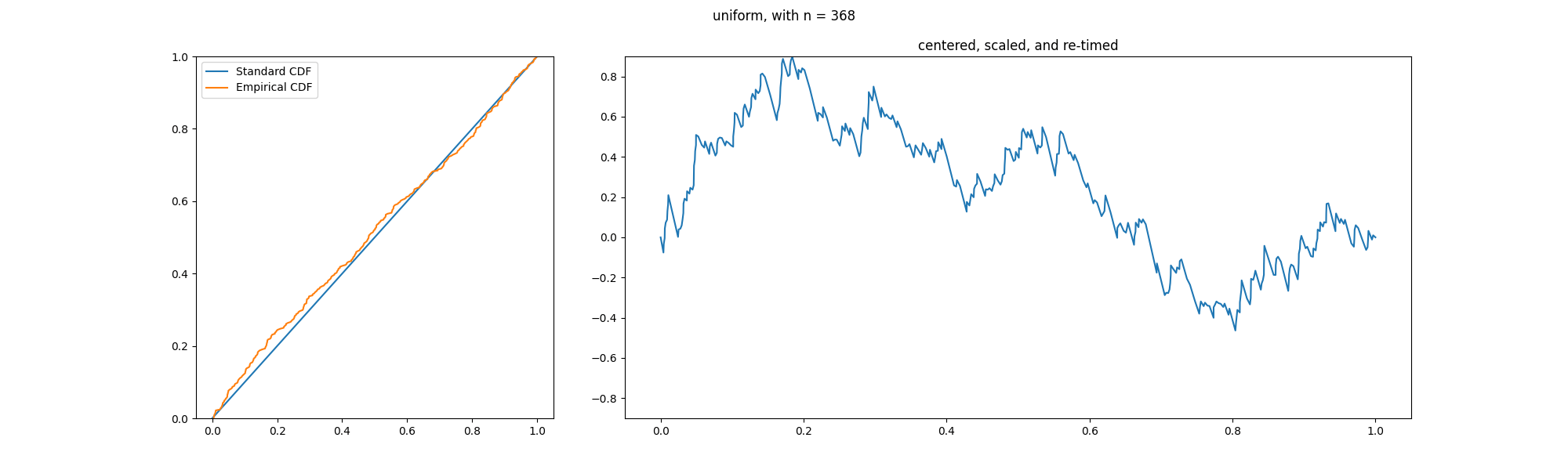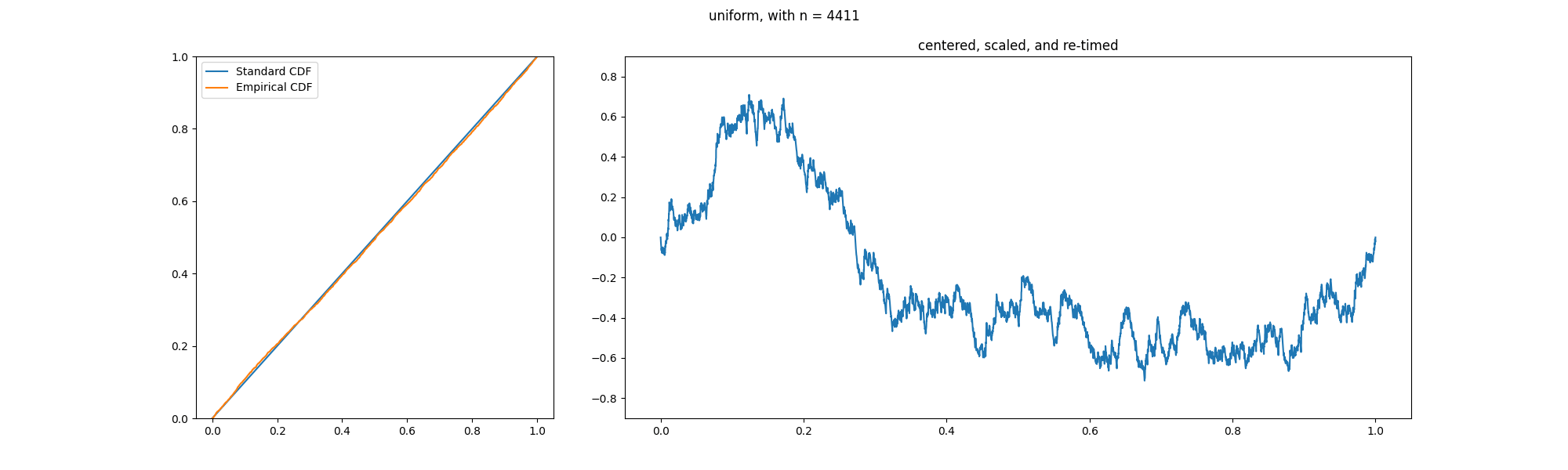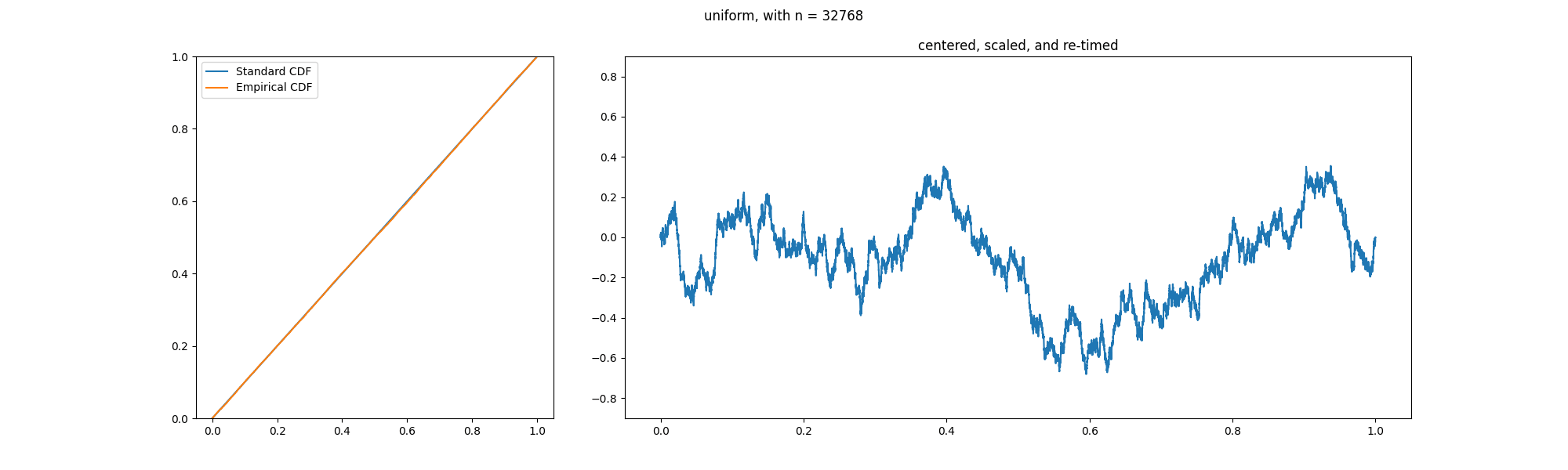
Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test
In statistics, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (also K–S test or KS test) is a nonparametric statistics, nonparametric test of the equality of continuous (or discontinuous, see #Discrete and mixed null distribution, Section 2.2), one-dimensional probability distributions. It can be used to test whether a random sample, sample came from a given reference probability distribution (one-sample K–S test), or to test whether two samples came from the same distribution (two-sample K–S test). Intuitively, it provides a method to qualitatively answer the question "How likely is it that we would see a collection of samples like this if they were drawn from that probability distribution?" or, in the second case, "How likely is it that we would see two sets of samples like this if they were drawn from the same (but unknown) probability distribution?". It is named after Andrey Kolmogorov and Nikolai Smirnov (mathematician), Nikolai Smirnov. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistic quantifies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KS Example
KS and variants may refer to: Businesses and organizations * , a German postwar commando frogman force * , a Norwegian type of company * Norwegian Association of Local and Regional Authorities * Keenspot, a webcomics/webtoons portal founded in March 2000 by cartoonist Chris Crosby * KS, IATA code of :de:AirConnect, a Romanian airline * KS, then-IATA code of PenAir, Peninsula Airways, a defunct airline based in Anchorage, Alaska, US Language * Kashmiri language, a Dardic language of Kashmir (ISO 639 alpha-2 language code "ks") * Kernowek Standard, an orthography for Revived Cornish * Kiasu, Hokkien (a Chinese spoken variant) word for 'extreme fear of losing' (怕输) * Sound of the Latin letter X in many languages Places * Kansas (US postal abbreviation KS) * South Kalimantan, Indonesia (ISO 3166-2 province code) * Krems an der Donau, Austria (vehicle plate code) * Kassel, Germany (vehicle plate code) * Khatumo State, an unrecognised proto-state in northern Somalia * Northampto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is f(x) = \frac e^\,. The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma^2 is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a Mathematics, mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on randomness, random events. The term 'random variable' in its mathematical definition refers to neither randomness nor variability but instead is a mathematical function (mathematics), function in which * the Domain of a function, domain is the set of possible Outcome (probability), outcomes in a sample space (e.g. the set \ which are the possible upper sides of a flipped coin heads H or tails T as the result from tossing a coin); and * the Range of a function, range is a measurable space (e.g. corresponding to the domain above, the range might be the set \ if say heads H mapped to -1 and T mapped to 1). Typically, the range of a random variable is a subset of the Real number, real numbers. Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donsker's Theorem
In probability theory, Donsker's theorem (also known as Donsker's invariance principle, or the functional central limit theorem), named after Monroe D. Donsker, is a functional extension of the central limit theorem for empirical distribution functions. Specifically, the theorem states that an appropriately centered and scaled version of the empirical distribution function converges to a Gaussian process. Let X_1, X_2, X_3, \ldots be a sequence of independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables with mean 0 and variance 1. Let S_n:=\sum_^n X_i. The stochastic process S:=(S_n)_ is known as a random walk. Define the diffusively rescaled random walk (partial-sum process) by : W^(t) := \frac, \qquad t\in ,1 The central limit theorem asserts that W^(1) converges in distribution to a standard Gaussian random variable W(1) as n\to\infty. Donsker's invariance principle extends this convergence to the whole function W^:=(W^(t))_. More precisely, in its modern form, Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almost Surely
In probability theory, an event is said to happen almost surely (sometimes abbreviated as a.s.) if it happens with probability 1 (with respect to the probability measure). In other words, the set of outcomes on which the event does not occur has probability 0, even though the set might not be empty. The concept is analogous to the concept of "almost everywhere" in measure theory. In probability experiments on a finite sample space with a non-zero probability for each outcome, there is no difference between ''almost surely'' and ''surely'' (since having a probability of 1 entails including all the sample points); however, this distinction becomes important when the sample space is an infinite set, because an infinite set can have non-empty subsets of probability 0. Some examples of the use of this concept include the strong and uniform versions of the law of large numbers, the continuity of the paths of Brownian motion, and the infinite monkey theorem. The terms almost certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glivenko–Cantelli Theorem
In the theory of probability, the Glivenko–Cantelli theorem (sometimes referred to as the fundamental theorem of statistics), named after Valery Ivanovich Glivenko and Francesco Paolo Cantelli, describes the asymptotic behaviour of the empirical distribution function as the number of Independent and identically distributed random variables, independent and identically distributed observations grows. Specifically, the empirical distribution function Uniform convergence, converges uniformly to the true distribution function almost surely. The uniform convergence of more general empirical measures becomes an important property of the Glivenko–Cantelli classes of functions or sets. The Glivenko–Cantelli classes arise in Vapnik–Chervonenkis theory, with applications to machine learning. Applications can be found in econometrics making use of M-estimators. Statement Assume that X_1,X_2,\dots are independent and identically distributed random variables in \mathbb with commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supremum
In mathematics, the infimum (abbreviated inf; : infima) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the greatest element in P that is less than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. If the infimum of S exists, it is unique, and if ''b'' is a lower bound of S, then ''b'' is less than or equal to the infimum of S. Consequently, the term ''greatest lower bound'' (abbreviated as ) is also commonly used. The supremum (abbreviated sup; : suprema) of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the least element in P that is greater than or equal to each element of S, if such an element exists. If the supremum of S exists, it is unique, and if ''b'' is an upper bound of S, then the supremum of S is less than or equal to ''b''. Consequently, the supremum is also referred to as the ''least upper bound'' (or ). The infimum is, in a precise sense, dual to the concept of a supremum. Infima and suprema of real numbers are common special cases that are important in analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistic
A statistic (singular) or sample statistic is any quantity computed from values in a sample which is considered for a statistical purpose. Statistical purposes include estimating a population parameter, describing a sample, or evaluating a hypothesis. The average (or mean) of sample values is a statistic. The term statistic is used both for the function (e.g., a calculation method of the average) and for the value of the function on a given sample (e.g., the result of the average calculation). When a statistic is being used for a specific purpose, it may be referred to by a name indicating its purpose. When a statistic is used for estimating a population parameter, the statistic is called an '' estimator''. A population parameter is any characteristic of a population under study, but when it is not feasible to directly measure the value of a population parameter, statistical methods are used to infer the likely value of the parameter on the basis of a statistic computed from a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicator Function
In mathematics, an indicator function or a characteristic function of a subset of a set is a function that maps elements of the subset to one, and all other elements to zero. That is, if is a subset of some set , then the indicator function of is the function \mathbf_A defined by \mathbf_\!(x) = 1 if x \in A, and \mathbf_\!(x) = 0 otherwise. Other common notations are and \chi_A. The indicator function of is the Iverson bracket of the property of belonging to ; that is, \mathbf_(x) = \left x\in A\ \right For example, the Dirichlet function is the indicator function of the rational numbers as a subset of the real numbers. Definition Given an arbitrary set , the indicator function of a subset of is the function \mathbf_A \colon X \mapsto \ defined by \operatorname\mathbf_A\!( x ) = \begin 1 & \text x \in A \\ 0 & \text x \notin A \,. \end The Iverson bracket provides the equivalent notation \left x\in A\ \right/math> or that can be used instead of \mathbf_\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent And Identically Distributed Random Variables
Independent or Independents may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups * Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in Pennsylvania, United States * Independentes (English: Independents), a Portuguese artist group Music Groups, labels, and genres * Independent music, a number of genres associated with independent labels * Independent record label, a record label not associated with a major label * Independent Albums, American albums chart Albums * ''Independent'' (Ai album), 2012 * ''Independent'' (Faze album), 2006 * ''Independent'' (Sacred Reich album), 1993 Songs * "Independent" (song), a 2007 song by Webbie * "Independent", a 2002 song by Ayumi Hamasaki from '' H'' News media organizations * Independent Media Center (also known as Indymedia or IMC), an open publishing network of journalist collectives that report on political and social issues, e.g., in ''The Indypendent'' newspaper of NYC * ITV (TV network) (Independent Televi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson–Darling Test
The Anderson–Darling test is a statistical test of whether a given sample of data is drawn from a given probability distribution. In its basic form, the test assumes that there are no parameters to be estimated in the distribution being tested, in which case the test and its set of critical values is distribution-free. However, the test is most often used in contexts where a family of distributions is being tested, in which case the parameters of that family need to be estimated and account must be taken of this in adjusting either the test-statistic or its critical values. When applied to testing whether a normal distribution adequately describes a set of data, it is one of the most powerful statistical tools for detecting most departures from normality. ''K''-sample Anderson–Darling tests are available for testing whether several collections of observations can be modelled as coming from a single population, where the distribution function does not have to be specified. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |