|
Kindling Model Of Epilepsy
Kindling is a commonly used model for the development of seizures and epilepsy in which the duration and behavioral involvement of induced seizures increases after seizures are induced repeatedly. Kindling is also referred as an animal visual model of epilepsy that can be produced by focal electrical stimulation in the brain. This is mainly used in visualising epilepsy in humans. The kindling model was first proposed in the late 1960s by Graham V. Goddard and colleagues. Although kindling is a widely used model, its applicability to human epilepsy is controversial. Method The word ''kindling'' is a metaphor: the increase in response to small stimuli is similar to the way small burning twigs can produce a large fire. It is used by scientists to study the effects of repeated seizures on the brain. A seizure may increase the likelihood that more seizures will occur; an old saying in epilepsy research is "seizures beget seizures". Repeated stimulation "lowers the threshold" for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Modelling
Scientific modelling is an activity that produces models representing empirical objects, phenomena, and physical processes, to make a particular part or feature of the world easier to understand, define, quantify, visualize, or simulate. It requires selecting and identifying relevant aspects of a situation in the real world and then developing a model to replicate a system with those features. Different types of models may be used for different purposes, such as conceptual models to better understand, operational models to operationalize, mathematical models to quantify, computational models to simulate, and graphical models to visualize the subject. Modelling is an essential and inseparable part of many scientific disciplines, each of which has its own ideas about specific types of modelling. The following was said by John von Neumann. There is also an increasing attention to scientific modelling in fields such as science education, philosophy of science, systems theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, or consciousness. Symptoms vary widely. Some seizures involve subtle changes, such as brief lapses in attention or awareness (as seen in absence seizures), while others cause generalized convulsions with loss of consciousness ( tonic–clonic seizures). Most seizures last less than two minutes and are followed by a postictal period of confusion, fatigue, or other symptoms. A seizure lasting longer than five minutes is a medical emergency known as status epilepticus. Seizures are classified as provoked, when triggered by a known cause such as fever, head trauma, or metabolic imbalance, or unprovoked, when no immediate trigger is identified. Recurrent unprovoked seizures define the neurological condition epilepsy. Clinical features Seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from brief lapses of awareness or muscle jerks to prolonged convulsions. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly, such as broken bones, or through causing accidents. The diagnosis of epilepsy typically requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart. In some cases, however, it may be diagnosed after a single unprovoked seizure if clinical evidence suggests a high risk of recurrence. Isolated seizures that occur without recurrence risk or are provoked by identifiable causes are not considered indicative of epilepsy. The underlying cause is often unknown, but epilepsy can result from brain injury, stroke, infections, Brain tumor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Temkin
Nancy R. Temkin is an American statistician who works on the biostatistics of traumatic brain injury. She is a professor of neurological surgery and biostatistics at the University of Washington, and serves on the National Research Council Committee on Sports-Related Concussions in Youth. Temkin earned bachelor's and master's degrees in mathematics and statistics, respectively, from the University of Connecticut in 1970 and 1971. She completed her PhD in 1976 from the University at Buffalo. She is a fellow of the American Statistical Association and a recipient of the Distinguished Service Award of the American Epilepsy Society The American Epilepsy Society (AES) is a nationwide 501(c)(3) non-profit organization for medical professionals and scientific investigators dedicated to finding the prevention, treatment, and cure of epilepsy Epilepsy is a group of Non-co .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Temkin, Nancy American women statisticians American biostatisticians Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Experimentation
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, animal research, and ''in vivo'' testing, is the use of animals, as model organisms, in experiments that seek answers to scientific and medical questions. This approach can be contrasted with field studies in which animals are observed in their natural environments or habitats. Experimental research with animals is usually conducted in universities, medical schools, pharmaceutical companies, defense establishments, and commercial facilities that provide animal-testing services to the industry. The focus of animal testing varies on a continuum from pure research, focusing on developing fundamental knowledge of an organism, to applied research, which may focus on answering some questions of great practical importance, such as finding a cure for a disease. Examples of applied research include testing disease treatments, breeding, defense research, and toxicology, including cosmetics testing. In education, animal testing is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
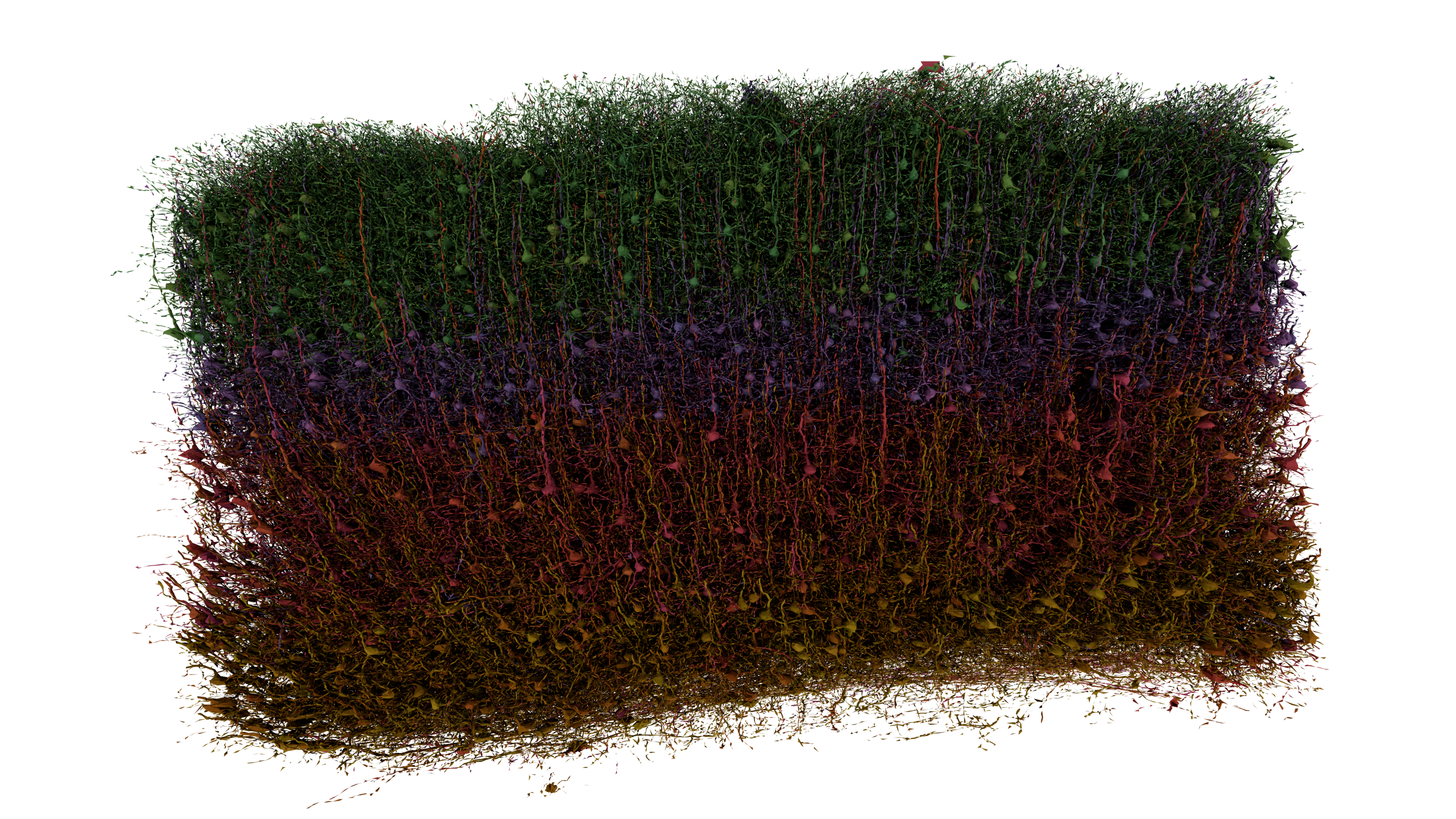
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are components of the hippocampal formation located in the limbic system. The hippocampus plays important roles in the Memory consolidation, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables Navigation#Navigation in spatial cognition, navigation. In humans, and other primates the hippocampus is located in the archicortex, one of the three regions of allocortex, in each cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere with direct neural projections to, and reciprocal indirect projections from the neocortex. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisation and number of layers, of the cerebral tissues. The neocortex cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindling (sedative–hypnotic Withdrawal)
Kindling due to substance withdrawal is the neurological condition which results from repeated withdrawal episodes from sedative–hypnotic drugs such as alcohol and benzodiazepines. Each withdrawal leads to more severe withdrawal symptoms than in previous episodes. Individuals who have had more withdrawal episodes are at an increased risk of very severe withdrawal symptoms, up to and including seizures and death. Long-term activation of the GABA receptor by sedative–hypnotic drugs causes chronic GABA receptor downregulation as well as glutamate overactivity, which can lead to drug and neurotransmitter sensitization, central nervous system hyperexcitability, and excitotoxicity. Symptoms Binge drinking is believed to increase impulsivity due to altered functioning of prefrontal–subcortical and orbitofrontal circuits. Binge drinking in alcoholics who have undergone repeated detoxification is associated with an inability to interpret facial expressions properly; this is believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epileptogenesis
Epileptogenesis refers to the gradual process through which a previously non-epileptic brain undergoes pathological changes that ultimately lead to the development of epilepsy. Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition characterized by an enduring predisposition to generate epileptic seizures, which are episodes of abnormal, hypersynchronous neuronal firing. It encompasses the transformation of neuronal networks following an initial insult, such as trauma, infection, or prolonged seizures, resulting in a brain capable of generating spontaneous recurrent seizures. This process is distinct from ictogenesis, which describes the immediate mechanisms underlying the initiation of individual seizure events. While ictogenesis accounts for seizure generation, epileptogenesis involves the long-term alterations that predispose the brain to recurrent seizures. Initiating events Epileptogenesis is typically triggered by an initial brain insult that disrupts normal neuronal networks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These Disorder of consciousness, disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique diagnosis, treatment, and patient care challenges. At their core, they represent disruptions to the intricate communication systems within the nervous system, stemming from genetic predispositions, environmental factors, infections, structural abnormalities, or degenerative processes. The impact of neurological disorders is profound and far-reaching. Conditions like epilepsy create recurring seizures through abnormal electrical brain activity, while multiple sclerosis damages the protective myelin covering of nerve fibers, interrupting communication between the brain and body. Parkinson's disease progressively affects movement through the loss of dopamine-producing nerve cells, and strokes can cause immediate and potentially permanent neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |