|
Khor Al
Khor (also ''Hurru'', ''Kharu'') is the second, later name used by ancient Egyptians after using Retjenu in designating the wider Syrian region, where speakers of Canaanite languages lived. It was long an outpost of ancient Egypt and is explicitly mentioned in the Great Hymn to the Aten as a geographic region, along with the kingdoms of Kush and Egypt. Based on the Amarna letters, it is plausible that Khor is a Middle Egyptian reference to Canaan. This word spelled as ''Hurru'' or ''Kharru'' is also used on the Merneptah Stele. In this inscription, Taharqa, Tarqo of Kush and pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, claimed to conquer this territory as attested by the "list of conquered Asiatic principalities" from the Mut temple at Karnak, as well as in Sanam temple inscriptions. Taharqa disputed this region with Sennacherib of Assyria. The Egyption Story of Wenamun refers to a location named ''Kharu''. According to Alessandra Nibbi Alessandra Nibbi (30 June 1923& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taharqa
Taharqa, also spelled Taharka or Taharqo, Akkadian: ''Tar-qu-ú'', , Manetho's ''Tarakos'', Strabo's ''Tearco''), was a pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt and qore (king) of the Kingdom of Kush (present day Sudan) from 690 to 664 BC. He was one of the "Black Pharaohs" - or, more consensually, Nubian or Kushite Pharaohs - who ruled over Egypt for nearly a century. Early life Taharqa may have been the son of Piye, the Nubian king of Napata who had first conquered Egypt, though the relationships in this family are not completely clear (see Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt family tree). Taharqa was also the cousin and successor of Shebitku. The successful campaigns of Piye and Shabaka paved the way for a prosperous reign by Taharqa. Ruling period Taharqa's reign can be dated from 690 BC to 664 BC. Evidence for the dates of his reign is derived from the Serapeum stele, catalog number 192. This stela records that an Apis bull born and installed (fourth month o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth dynasties. Through radiocarbon dating, the establishment of the New Kingdom has been placed between 1570 and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt, Third Intermediate Period. It was the most prosperous time for the Egyptians#History, Egyptian people and marked the peak of Egypt's power. In 1845, the concept of a "New Kingdom" as Periodization of ancient Egypt, one of three "golden ages" was coined by German scholar Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen; the original definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alessandra Nibbi
Alessandra Nibbi (30 June 1923 – 15 January 2007) was an Italian-born Australian archaeologist. Biography Born on 30 June 1923 in Porto San Giorgio, Italy, in 1928 she migrated with her family to Australia because of the political situation in Italy; Nibbi grew up in Melbourne with an English education.Claude Vandersleyen, Alessandra Nibbi' - Obituary from the Griffith Institute website In 1947, after the war and the fall of fascism, Nibbi and her family temporarily returned to Italy, and here she got married. In 1963 she came again to Italy and during the journey she joined an excursion in Egypt, where she became fascinated by ancient Egyptian civilization at the point that once in Italy she started to study archaeology at the University of Perugia and later graduated at the University of Florence. Shortly after, Nibbi left Italy for Oxford, England. In 1969 she published the Etruscans-themed ''The Tyrrhenians'', but a certain notoriety only came in 1972 with the self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Story Of Wenamun
The Story of Wenamun (alternately known as the Report of Wenamun, The Misadventures of Wenamun, Voyage of Unamūn, or nformallyas just Wenamun) is a literary text written in hieratic in the Late Egyptian language. It is only known from one incomplete copy discovered in 1890 at al-Hibah, Egypt, and subsequently purchased in 1891 in Cairo by the Russian Egyptologist Vladimir Golenishchev. It was found in a jar together with the Onomasticon of Amenope and the Tale of Woe. The story features a mixture of literary tropes along with an administrative writing style, which has led to a longstanding uncertainty about whether it is a fictitious account or a genuine historical document. Despite this, what scholars can agree on is its importance in showing the political and religious state of Egypt during the transition between the New Kingdom and the Third Intermediate Period. The papyrus is now in the collection of the Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, and officially designated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, North Africa and East Mediterranean throughout much of the 9th to 7th centuries BC, becoming the List of largest empires, largest empire in history up to that point. Because of its geopolitical dominance and ideology based in world domination, the Neo-Assyrian Empire has been described as the first world empire in history. It influenced other empires of the ancient world culturally, administratively, and militarily, including the Neo-Babylonian Empire, Neo-Babylonians, the Achaemenid dynasty, Achaemenids, and the Seleucid Empire, Seleucids. At its height, the empire was the strongest military power in the world and ruled over all of Mesopotamia, the Levant and Egypt, as well as parts of Anatolia, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and modern-day Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( or , meaning "Sin (mythology), Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 705BC until his assassination in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynasty, Sennacherib is one of the most famous Assyrian kings for the role he plays in the Hebrew Bible, which describes his Sennacherib's campaign in the Levant, campaign in the Levant. Other events of his reign include his destruction of the city of Babylon in 689BC and his renovation and expansion of the last great Assyrian capital, Nineveh. Although Sennacherib was one of the most powerful and wide-ranging Assyrian kings, he faced considerable difficulty in controlling Babylonia, which formed the southern portion of his empire. Many of Sennacherib's Babylonian troubles stemmed from the Chaldean tribal chief Marduk-apla-iddina II, who had been List of kings of Babylon, Babylon's king until Sennacherib's father defeated him. Shortly after Sennacherib inherited the throne in 705BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
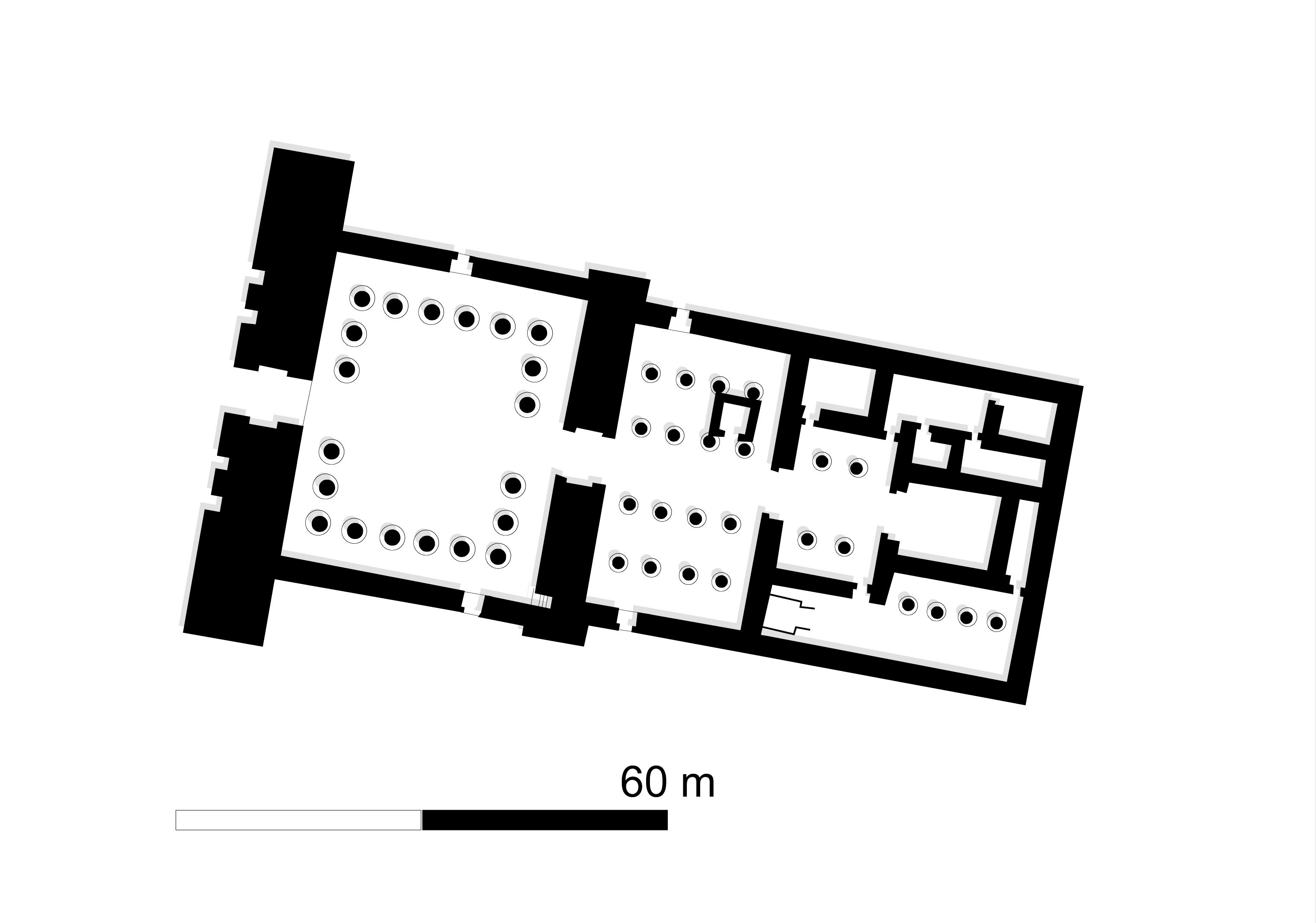
Sanam, Sudan
Sanam is a modern village in Sudan. It is located at the bank of the Nile river next to Merowe. Here were found the remains of an ancient town which flourished mainly in the Napatan Period. These are perhaps the remains of Napata, the capital of the Kushite empire from about 800 to 300 BC. Parts of the town were excavated in 1912 to 1913 by Francis Llewellyn Griffith. The excavation was focused on numerous distinct structures He found the remains of a badly preserved temple and of a building he called ''treasury''. The temple was built under king Taharqo with additions by king Aspelta Aspelta was a ruler of the kingdom of Kush (c. 600 – c. 580 BCE). More is known about him and his reign than most of the rulers of Kush. He left several stelae carved with accounts of his reign. Family Aspelta was the son of Senkamanisken and Q .... Most importantly, he excavated a big cemetery belonging to the inhabitants of the town. This is one of the few so far excavated cemeteries of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
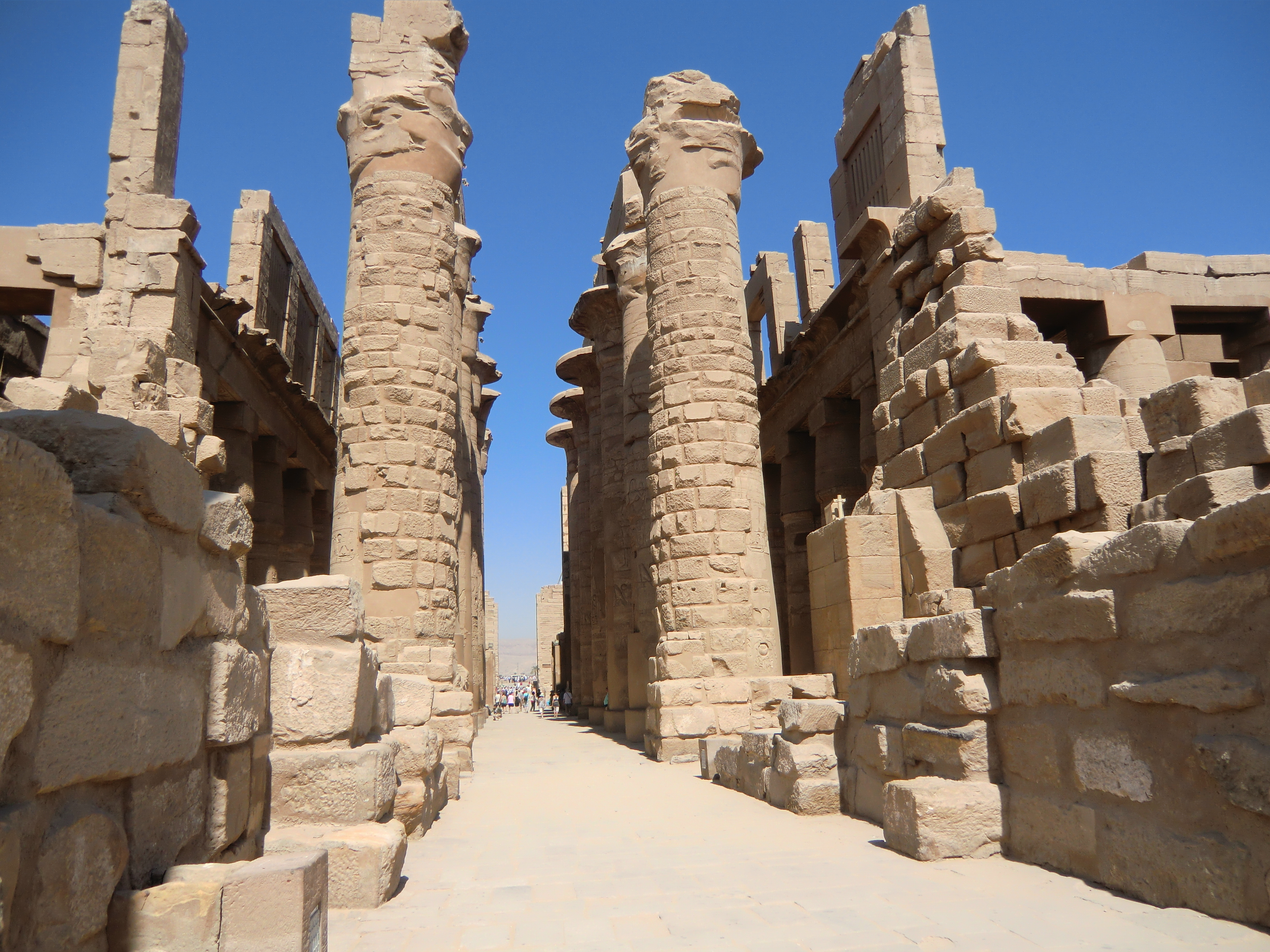
Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (), comprises a vast mix of temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I (reigned 1971–1926 BC) in the Middle Kingdom () and continued into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (305–30 BC), although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian ''Ipet-isut'' ("The Most Selected of Places") and the main place of worship of the 18th Dynastic Theban Triad, with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes, and in 1979 it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List along with the rest of the city. Karnak gets its name from the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, north of Luxor. Name The original name of the temple was ''Ipet-isut'', meaning "The Most Select of Places". The complex's modern name "Karnak" comes from the nearby village of el-Karnak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precinct Of Mut
The Precinct of Mut is an Ancient Egyptian temple compound located in the present city of Luxor (ancient Thebes), on the east bank of the Nile in South Karnak. The compound is one of the four key ancient temples that creates the Karnak Temple Complex. It is approximately 325 meters (1,066 feet) south of the precinct of the god Amun. The precinct itself encompasses approximately 90,000 square meters (968,751 square feet) of the entire area. The Mut Precinct contains at least six temples: the Mut Temple, the Contra Temple, and Temples A, B, C, and D. Surrounding the Mut Temple proper, on three sides, is a sacred lake called the Isheru. To the south of the sacred lake is a vast amount of land currently being excavated by Betsy Bryan and her team from the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. Today, most of the compound is still destroyed, but it is currently being renovated. Surrounding the Mut Temple, the Contra Temple, and Temples A, B, C, and D, is an enclosure wall ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-fifth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXV, alternatively 25th Dynasty or Dynasty 25), also known as the Nubian Dynasty, the Kushite Empire, the Black Pharaohs, or the Napatans, after their capital Napata, was the last dynasty of the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt that occurred after the Kushite invasion. The 25th dynasty was a line of pharaohs who originated in the Kingdom of Kush, located in present-day northern Sudan and Upper Egypt. Most of this dynasty's kings saw Napata as their spiritual homeland. They reigned in part or all of Ancient Egypt for nearly a century, from 744 to 656 BC. The 25th dynasty was highly Egyptianized, using the Egyptian language and writing system as their medium of record and exhibiting an unusual devotion to Egypt's religious, artistic, and literary traditions. Earlier scholars have ascribed the origins of the dynasty to immigrants from Egypt, particularly the Egyptian Amun priests. The third intermediate-period Egyptian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |