|
Kaguru Language
Kaguru (Kagulu) is a Bantu language of the Morogoro and Dodoma regions of Tanzania. It is closely related to Gogo and Zaramo The Zaramo people, also referred to as Dzalamo or Saramo (''Wazaramo'', in Swahili language, Swahili), are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group native to the central eastern coast of Tanzania, particularly the Dar es Salaam Region and Pwani Regio ..., but is not intelligible with other languages. References Further reading * Accessed 12 Jan. 2023. * * Accessed 12 Jan. 2023. External links''Grammar of the Kagúru language'' By J T. Last (1886) Languages of Tanzania Northeast Coast Bantu languages {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. According to a 2024 estimate, Tanzania has a population of around 67.5 million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania. In the Stone and Bronze Age, prehistoric migrations into Tanzania included South Cushitic languages, Southern Cushitic speakers similar to modern day Iraqw people who moved south from present-day Ethiopia; Eastern Cushitic people who moved into Tanzania from north of Lake Turkana about 2,000 and 4,000 years ago; and the Southern Nilotic languages, Southern Nilotes, including the Datooga people, Datoog, who originated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic–Congo Languages
The Atlantic–Congo languages make up the largest demonstrated family of languages in Africa. They have characteristic noun class systems and form the core of the Niger–Congo family hypothesis. They comprise all of Niger–Congo apart from Mande, Dogon, Ijoid, Siamou, Kru, the Katla and Rashad languages (previously classified as Kordofanian), and perhaps some or all of the Ubangian languages. Hans Gunther Mukanovsky's "Western Nigritic" corresponded roughly to modern Atlantic–Congo. In the infobox, the languages which appear to be the most divergent are placed at the top. The Atlantic branch is defined in the narrow sense (as Senegambian), while the former Atlantic branches Mel and the isolates Sua, Gola and Limba are split out as primary branches; they are mentioned next to each other because there is no published evidence to move them; Volta–Congo is intact apart from Senufo and Kru. ''Glottolog'', based primarily on Güldemann (2018), has a more limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
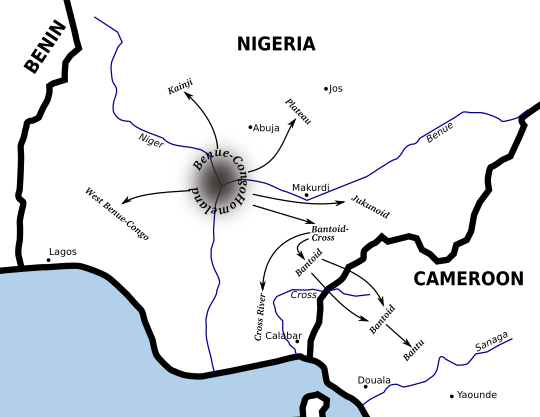
Benue–Congo Languages
Benue–Congo (sometimes called East Benue–Congo) is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Subdivisions Central Nigerian (or Platoid) contains the Plateau languages, Plateau, Jukunoid languages, Jukunoid and Kainji languages, Kainji families, and Bantoid–Cross combines the Bantoid languages, Bantoid and Cross River languages, Cross River groups. Bantoid is only a collective term for every subfamily of Bantoid–Cross except Cross River, and this is no longer seen as forming a valid branch, however one of the subfamilies, Southern Bantoid, is still considered valid. It is Southern Bantoid which contains the Bantu languages, which are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa. This makes Benue–Congo one of the largest subdivisions of the Niger–Congo language family, both in number of languages, of which ''Ethnologue'' counts 976 (2017), and in speakers, numbering perhaps 350 million. Benue–Congo also includes a few minor Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantoid Languages
Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and after which Bantoid is named. History The term "Bantoid" was first used by Krause in 1895 for languages that showed resemblances in vocabulary to Bantu. Joseph Greenberg, in his 1963 ''The Languages of Africa'', defined Bantoid as the group to which Bantu belongs together with its closest relatives; this is the sense in which the term is still used today. However, according to Roger Blench, the Bantoid languages probably do not actually form a coherent group. Internal classification A proposal that divided Bantoid into Northern Bantoid languages, North Bantoid and Southern Bantoid languages, South Bantoid was introduced by Williamson. In this proposal, the Mambiloid and Dakoid languages (and later Tikar language, Tikar) are grouped together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Bantu
The Northeast Bantu languages are a group of Bantu languages spoken in East Africa. In Guthrie's geographic classification, they fall within Bantu zones E50 plus E46 (Sonjo), E60 plus E74a (Taita), F21–22, J, G60, plus Northeast Coast Bantu (of zones E & G).Derek Nurse, 2003, ''The Bantu Languages'' Some of these languages (F21, most of E50, and some of J) share a phonological innovation called Dahl's law that is unlikely to be borrowed as a productive process, though individual words reflecting Dahl's law have been borrowed into neighboring languages. The languages, or clusters, are: *Northeast Bantu languages **Kikuyu–Kamba Thagiicu (primarily E50): *** Sonjo (E40) *** Cuka *** Meru (incl. Tharaka, Mwimbi-Muthambi) ***South ****Kamba, Daisu **** Gikuyu, Embu **Chaga–Taita *** Taita (Dawida; E70) – Sagalla *** Chaga languages (E60) ** Northeast Coast Bantu (G10-G40): Swahili (E70), ''etc.'' ** Takama: Sukuma– Nyamwezi (+ Konongo–Ruwila), Kimbu (F20), Iram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Coast Bantu
The Northeast Coast Bantu languages are the Bantu languages spoken along the coast of Tanzania and Kenya, and including inland Tanzania as far as Dodoma.Derek Nurse & Thomas Spear, 1985, ''The Swahili'' In Guthrie's geographic classification, they fall within Bantu zones G and E. The languages, or clusters, are: *Pare-Taveta (G20+E70): **Pareic *** Pare, Mbugu ** Taveta * Sabaki (G40+E70): Swahili, Nyika, Comorian ''etc.'' *Seuta (G20+G30): Shambala, Bondei, Zigula ( Mushungulu), Ngulu *Ruvu (G30+G10): Gogo, Sagara, Vidunda, Kaguru, Luguru, Kutu, Kami, Zaramo The Zaramo people, also referred to as Dzalamo or Saramo (''Wazaramo'', in Swahili language, Swahili), are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group native to the central eastern coast of Tanzania, particularly the Dar es Salaam Region and Pwani Regio ..., Kwere, Doe The Ruvu languages are 60–70% similar lexically. Mbugu (Ma'a) is a mixed language based largely on Pare. Notes Languages of Kenya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Language
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morogoro Region
Morogoro Region (''Mkoa wa Morogoro'' in Swahili language, Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative Regions of Tanzania, regions. It covers an area of . and is comparable in size to the combined land area of the nation state of Ireland. Morogoro Region is bordered to the north by the Manyara Region and Tanga Region, to the east by the Pwani Region, Pwani and Lindi Region, Lindi Regions, to the south by the Ruvuma Region and to the west by the Iringa Region, Iringa Njombe Region, Njombe and Dodoma Region, Dodoma Regions. The regional capital is the municipality of Morogoro. According to the 2022 national census, the region had a population of 3,197,104. Geography The area is found in the Mid-Eastern portion of mainland Tanzania and is situated between latitudes 5° 58' and 10' south of the equator and between longitudes 35° 25' and 38° 30' east Greenwich. 4,623,005 acres, or 4.9% of the area of Tanzania's Mainland, is the size of the Morogoro region (94,278,400 ha). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodoma Region
Dodoma Region (''Mkoa wa Dodoma'' in Swahili language, Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative Regions of Tanzania, regions. The regional capital is the city of Dodoma, which is also the capital of Tanzania. Dodoma region is located in central Tanzania, bordered by Singida Region, Singida region to the west, Manyara Region, Manyara region to the north, Iringa Region, Iringa region to the south, and Morogoro Region, Morogoro region to the east. Dodoma hosts the National Assembly of Tanzania or Bunge. Dodoma region also hosts one of the largest universities in Tanzania, the University of Dodoma. The region is the home of the Tanzanian wine industry, which is the second largest wine industry on the continent after South Africa. According to the 2022 national census, the region had a population of 3,085,625; in the 2012 national census, the population was 2,083,588. History Dodoma's name derives from the Gogo people, Gogo word ''Idodomya'', the place where an elephant sunk i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gogo Language
Gogo is a Bantu language spoken by the Gogo people of Dodoma Region in Tanzania. The language is spoken throughout Dodoma Region and into the neighbouring district of Manyoni. The language is considered to have three dialects: Nyambwa (Cinyambwa or West Gogo), spoken to the west of Dodoma and in Manyoni; Nyaugogo (Cinyaugogo or Central Gogo), spoken in the environs of Dodoma; and Tumba (Citumba or East Gogo), spoken to the east. The Gogo group is grouped with Kagulu, which has a 56% lexical similarity with Gogo proper. Gogo has about 50% lexical similarity with Hehe and Sangu (both Bena–Kinga languages (G.60), 48% with Kimbu and 45% with Nilamba. These last two are both in Guthrie's Zone F. Gogo is spoken by both Christians and Muslim Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaramo Language
Zaramo is a Niger-Congo language, formerly primary language of the Zaramo people of eastern Tanzania Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t .... Zaramo is also known as Zalamo, Kizaramo, Dzalamo, Zaramu, Saramo and, Myagatwa. The language is critically endangered. The ethnic population of the Zaramo people reaches about 200,000, yet there are only a few elderly speakers remaining. These speakers are mostly located in the villages surrounding the city of Dar es Salaam. Zaramo is thought to be passed down matrilineally to the children in these villages, while it remains critically endangered in the city. There are very few translations of the language in existence except for a few native speakers' documented translations, and the publication of the New Testament from 1975 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |