|
Kabufuda
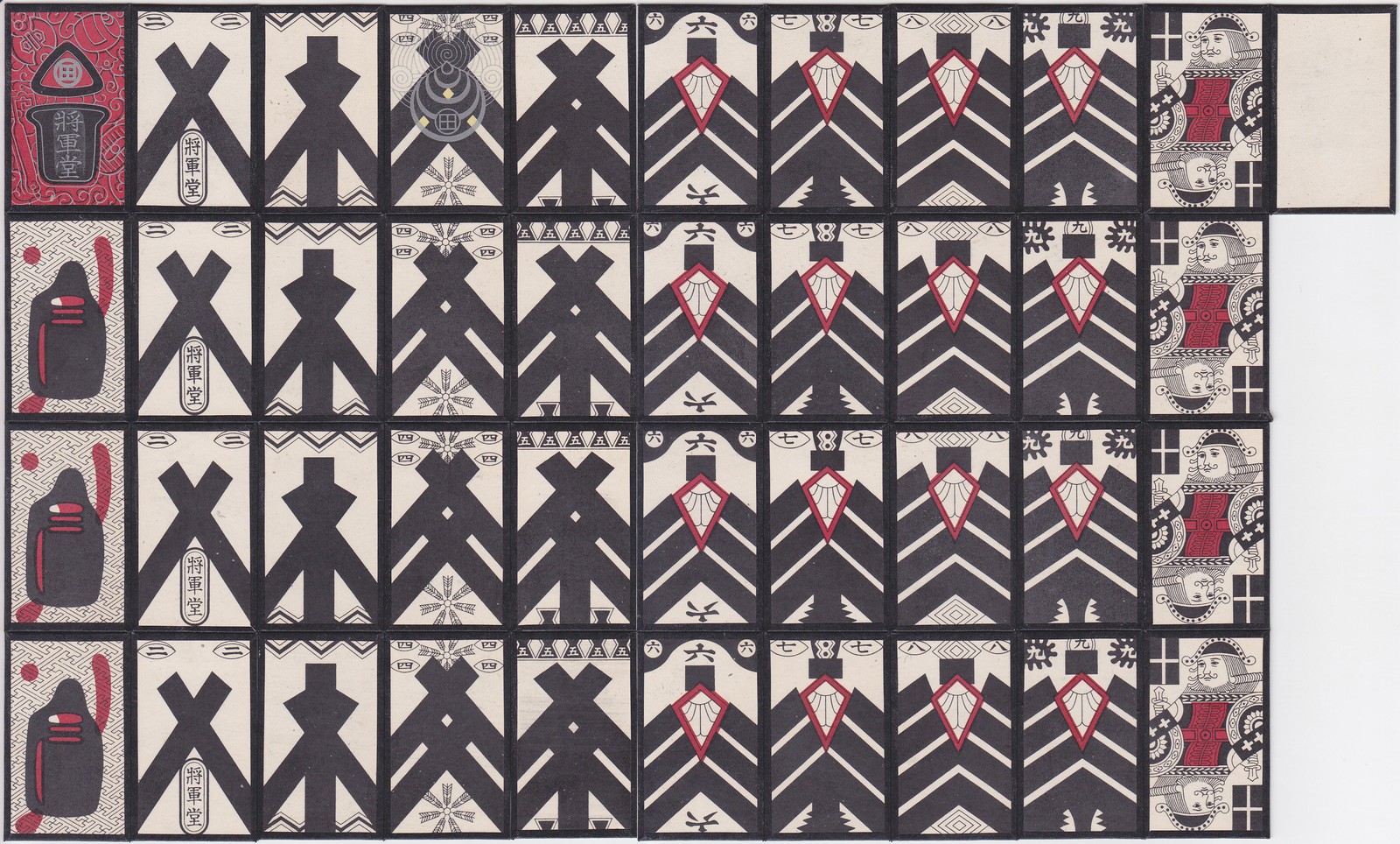
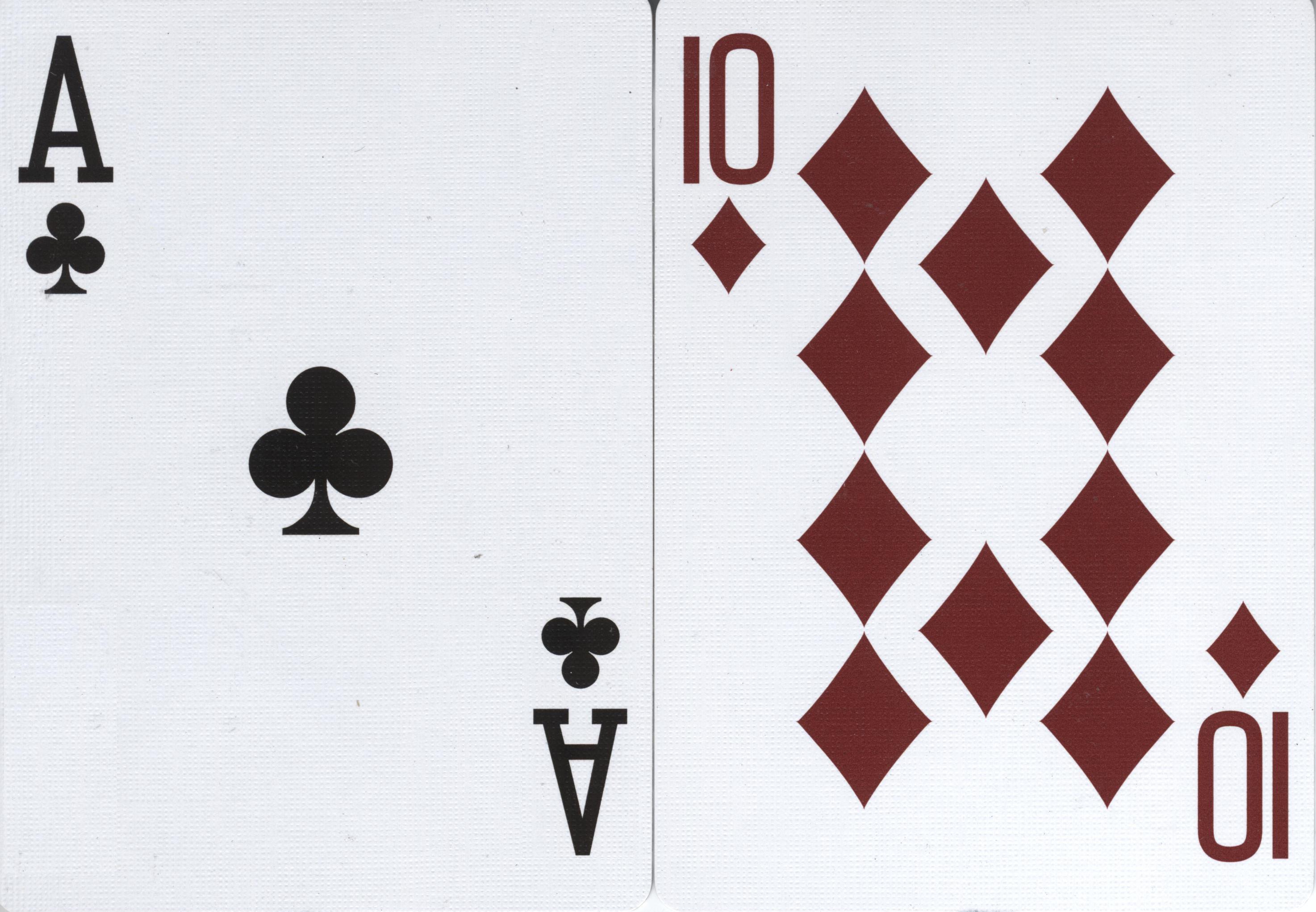
''Kabufuda'' () are Japanese playing cards used for gambling games such as '' Oicho-Kabu'' mainly used in the Kansai region. ''Kabufuda'' cards, like the related ''hanafuda'' (), are smaller and stiffer than Western playing cards. The standard Kabufuda pattern deck contains 41 cards, which includes one blank card and designs representing the numbers 1 through 10 based on the Latin club suit. There are four cards for each number. One of the 1's has a red background and is decorated gold or silver, called the Aka-pin (赤ピン 'red pin') or Aza-pin (アザピン 'Ace-pin') from Portuguese 'às pintas' ('Ace spots'). The twos often have the manufacturer or distributor's trademark. One of the 4's is also decorated gold or silver, called the Tamashi (玉四 'round four') or Kinshi (金四 'gold four'), which allows it to have a role in certain games. Like hanafuda, kabufuda is a descendant of mekuri karuta. Since suits are irrelevant in kabu games, all decks became single-suite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oicho-Kabu
is a traditional Japanese card game that is similar to baccarat. It is typically played with special ''kabufuda'' cards. A ''hanafuda'' deck can also be used, if the last two months are discarded, and French-suited playing cards, Western playing cards can be used if the face cards are removed from the deck and aces are counted as ''one''. "Oicho-Kabu" derived from Portuguese "Oito-Cabo" which in English means "Eight-End". As in baccarat, this game also has a dealer, whom the players try to beat. The goal of the game is to reach 9. As in baccarat, the last digit of any total over 10 is the hand's score: a 15 counts as 5, a 12 as 2, and a 20 as 0. The worst hands in ''oicho-kabu'' have a value of 0. One of these worst hands is an eight, a nine and a three, phonetically expressed as "ya-kyu-san". This is the origin of the Japanese word for "gangster", ''yakuza''. Gameplay Before the game starts, the players decide on the ''domae'' (胴前), which is the maximum number of points ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batons (suit)
Batons or clubs is one of the four card suit, suits of playing cards in the standard Latin playing cards, Latin deck along with the suits of Cups (card suit), cups, Coins (card suit), coins and Swords (card suit), swords. 'Batons' is the name usually given to the suit in Italian-suited cards where the symbols look like batons. 'Clubs' refers to the suit in Spanish-suited cards where the symbols look more like wooden clubs. Before 1800, French cardmaking, cardmakers, who also made Spanish card games, called them ''cartes à bâtons''. Symbol on Italian pattern cards: Symbol on Spanish pattern cards: Symbol on French Aluette (Spanish-)pattern cards: Characteristics The suit of batons is believed to have derived from Chinese playing cards#Money-suited cards, Chinese money-suited cards' String of cash coins (currency unit), String of cash coins suit being misinterpreted as polo-sticks by the Muslims when the cards came into contact with the Islamic world. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabufuda Set
''Kabufuda'' () are Japanese playing cards used for gambling games such as ''Oicho-Kabu'' mainly used in the Kansai region. ''Kabufuda'' cards, like the related ''hanafuda'' (), are smaller and stiffer than Western playing cards. The standard Kabufuda pattern deck contains 41 cards, which includes one blank card and designs representing the numbers 1 through 10 based on the Latin club suit. There are four cards for each number. One of the 1's has a red background and is decorated gold or silver, called the Aka-pin (赤ピン 'red pin') or Aza-pin (アザピン 'Ace-pin') from Portuguese 'às pintas' ('Ace spots'). The twos often have the manufacturer or distributor's trademark. One of the 4's is also decorated gold or silver, called the Tamashi (玉四 'round four') or Kinshi (金四 'gold four'), which allows it to have a role in certain games. Like hanafuda, kabufuda is a descendant of mekuri karuta. Since suits are irrelevant in kabu games, all decks became single-suited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karuta
are Culture of Japan, Japanese playing cards. Playing cards were introduced to Japan by Portuguese traders during the mid-16th century. These early decks were used for trick-taking games. The earliest indigenous ''karuta'' was invented in the town of Miike District, Miike in Chikugo Province at around the end of the 16th century. The Miike karuta Memorial Hall located in Ōmuta, Fukuoka, is the only municipal museum in Japan dedicated specifically to the history of ''karuta''. ''Karuta'' packs are classified into two groups, those that are descended from Portuguese-suited playing cards and those from ''e-awase''. ''E-awase'' originally derived from ''kai-awase'', which was played with shells but were converted to card format during the early 17th century. The basic idea of any ''e-awase karuta'' game is to be able to quickly determine which card out of an array of cards is required and then to grab the card before it is grabbed by an opponent. It is often played by children at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suit (cards)
In playing cards, a suit is one of the categories into which the cards of a deck are divided. Most often, each card bears one of several pips (symbols) showing to which suit it belongs; the suit may alternatively or additionally be indicated by the color printed on the card. The rank for each card is determined by the number of pips on it, except on face cards. Ranking indicates which cards within a suit are better, higher or more valuable than others, whereas there is no order between the suits unless defined in the rules of a specific card game. In most decks, there is exactly one card of any given rank in any given suit. A deck may include special cards that belong to no suit, often called jokers. While English-speaking countries traditionally use cards with the French suits of Clubs, Spades, Hearts and Diamonds, many other countries have their own traditional suits. Much of central Europe uses German suited cards with suits of Acorns (Clubs), Leaves (Spades), Hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanafuda
() are a type of Japanese playing cards. They are typically smaller than Western playing cards, only , but thicker and stiffer. On the face of each card is a depiction of plants, , animals, birds, or man-made objects. One single card depicts a human. The back side is usually plain, without a pattern or design of any kind, and traditionally colored either red or black. are used to play a variety of games including and . Outside Japan In Korea, are known as (, Hanja: ) and made of plastic with a textured back side. The most popular game is ''Go-Stop, Go-stop'' (), commonly played during special holidays such as Korean New Year, Lunar New Year and (). In Hawaii, is used to play Sakura (card game), Sakura. is also played in Micronesia, where it is known as and is used to play a four-person game, which is often played in partnerships. History Playing cards were introduced to Japan by the Portuguese in the mid-16th century. The Portuguese-suited playing cards, Portugues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Cards
In a deck of playing cards, the term face card (US) or court card (British and US), and sometimes royalty, is generally used to describe a card that depicts a person as opposed to the pip cards. In a standard 52-card pack of the English pattern, these cards are the King, Queen and Jack. The term picture card is also common, but that term sometimes includes the Aces. After the American innovation of corner-indices, the idea of "pictured" cards from tarot trumps was used to replace all 52 cards from the standard deck with pictures, art, or photography in some souvenir packs featuring a wide variety of subjects (animals, scenery, cartoons, pin-ups, vehicles, etc.) that may garner interest with collectors. In the standard packs of non-English speaking regions, the face or court cards may be different. For example, in Italian- and Spanish-suited packs there is a Knight or Cavalier instead of a Queen. In French-suited Tarot card packs, the Cavalier is a fourth court card. By c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tujeon
Tujeon (, literally ''fighting tablets'') are the traditional playing cards of Korea used in the latter half of the Joseon dynasty. They are also known as tupae (, literally ''fighting cards''). Composition A deck typically contains forty, sixty or eighty cards: nine numeral cards, and one General (''jang''), to each suit. In a full eight-suited deck, the suits and their generals are as follows: *Man () led by the King *Fish () led by the Dragon *Crow () led by the Phoenix *Pheasant () led by the Falcon *Roe deer () led by the Tiger *Star () led by the North Star *Rabbit () led by the Eagle *Horse () led by the Wagon Yu Deuk-gong (1749–1807) wrote in his '':ko:경도잡지, Seoul Miscellany'' () that in the suits of stars, horses, roe deer, and rabbits, the ranking of the numeral cards are in inverted order with nine being the lowest rank and one being the second highest, outranked only by the general. This ranking can also be seen in archaic games such as Ganjifa, Madiao, Trio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackjack
Blackjack (formerly black jack or ''vingt-un'') is a casino banking game. It is the most widely played casino banking game in the world. It uses decks of 52 cards and descends from a global family of casino banking games known as " twenty-one". This family of card games also includes the European games '' vingt-et-un'' and pontoon, and the Russian game . The game is a comparing card game where players compete against the dealer, rather than each other. History Blackjack's immediate precursor was the English version of '' twenty-one'' called ''vingt-un'', a game of unknown provenance. The first written reference is found in a book by the Spanish author Miguel de Cervantes. Cervantes was a gambler, and the protagonists of his " Rinconete y Cortadillo", from ''Novelas Ejemplares'', are card cheats in Seville. They are proficient at cheating at ''veintiuno'' (Spanish for "twenty-one") and state that the object of the game is to reach 21 points without going over and that the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
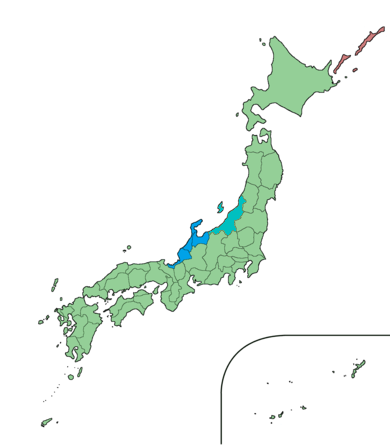
Hokuriku Region
The is located in the northwestern part of Honshu, the main island of Japan. It lies along the Sea of Japan and is part of the larger Chūbu region. It is almost equivalent to the former Koshi Province (Japan), Koshi Province and Hokurikudō area in pre-modern Japan. From the Heian period until the Edo period, the region was a core recipient of population, and grew to be proportionately much larger than it is today, despite the rural character; in modern times, its population has remained consistent, with most urban growth in the 20th century instead taking place in Kantō region, Kanto, Nagoya, Chūkyō, and Kansai region, Kansai. The Hokuriku region is also known for traditional culture that originated from elsewhere that has been long lost along the Taiheiyō Belt. The Hokuriku region includes the four prefectures of Ishikawa Prefecture, Ishikawa, Fukui Prefecture, Fukui, Niigata Prefecture, Niigata and Toyama Prefecture, Toyama, although Niigata is sometimes included as an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikoku
is the smallest of the List of islands of Japan#Main islands, four main islands of Japan. It is long and between at its widest. It has a population of 3.8 million, the least populated of Japan's four main islands. It is south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. Shikoku's ancient names include , , and , and its current name refers to the four former provinces of Japan, provinces that make up the island: Awa Province (Tokushima), Awa, Tosa Province, Tosa, Sanuki Province, Sanuki, and Iyo Province, Iyo. Geography Shikoku Island, comprising Shikoku and its surrounding islands, covers about and consists of four Prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Ehime Prefecture, Ehime, Kagawa Prefecture, Kagawa, Kōchi Prefecture, Kōchi, and Tokushima Prefecture, Tokushima. Across the Seto Inland Sea lie Wakayama Prefecture, Wakayama, Osaka Prefecture, Osaka, Hyōgo Prefecture, Hyōgo, Okayama Prefecture, Okayama, Hiroshima Prefecture, Hiroshima, and Yamaguchi Prefectures on Honshu. To th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |