|
Jiajing Wokou Raids
The Jiajing wokou raids caused extensive damage to the coast of China in the 16th century, during the reign of the Jiajing Emperor (r. 1521–67) in the Ming dynasty. The term "wokou" originally referred to Japanese pirates who crossed the sea and raided Korea and China; however, by the mid-Ming, the wokou consisted of multinational crewmen that included the Japanese and the Portuguese, but a great majority of them were Chinese instead. Mid-Ming wokou activity began to pose a serious problem in the 1540s, reached its peak in 1555, and subsided by 1567, with the extent of the destruction spreading across the coastal regions of Jiangnan, Zhejiang, Fujian, and Guangdong. Historical background Maritime trade in 16th century China Up until the establishment of the Ming dynasty in 1368, China had had a great maritime trading tradition that extended the Chinese trading network by sea all the way into the Indian Ocean. In 1371, the Ming founder Hongwu Emperor implemented the "Haijin, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
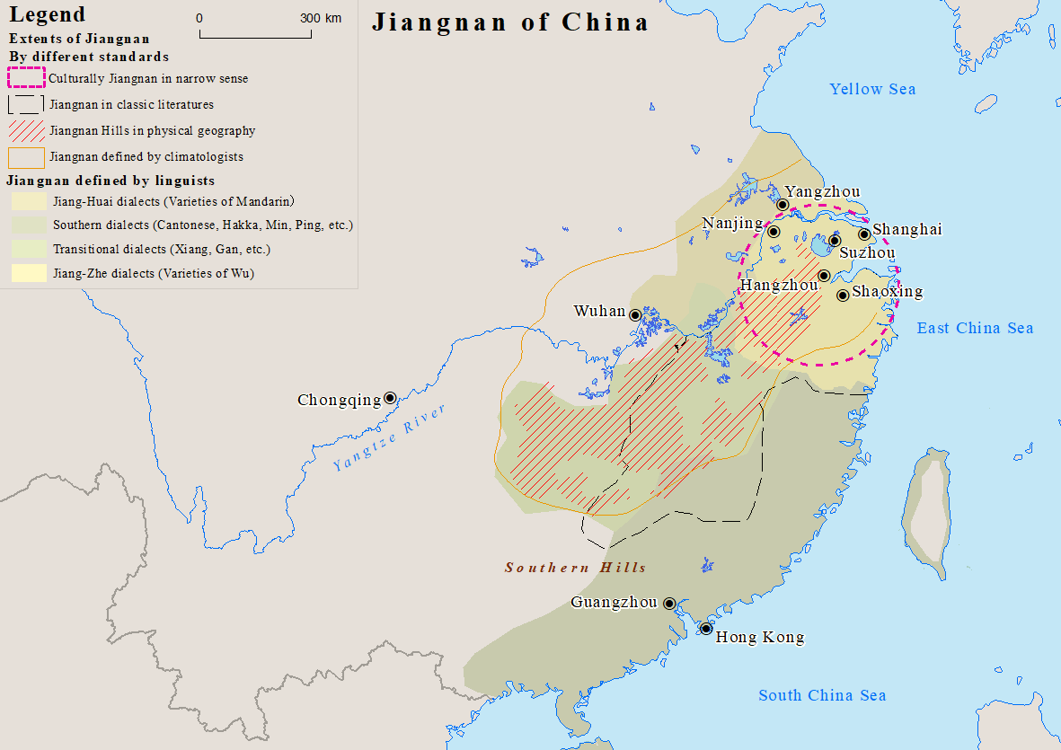
Jiangnan
Jiangnan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, Yangzhou and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The name Jiangnan is the pinyin romanization of the Standard Mandarin pronunciation of , meaning " andsSouth of the [Yangtze] River". Although ''jiang'' () is now the common Chinese word for any large river, it was historically used in Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinocentrism
Sinocentrism refers to a worldview that China is the cultural, political, or economic center of the world. Sinocentrism was a core concept in various Chinese dynasties. The Chinese considered themselves to be "all-under-Heaven", ruled by the emperor, known as Son of Heaven. Those that lived outside of the Huaxia were regarded as " barbarians". In addition, states outside of China, such as Vietnam, Japan or Korea, were considered to be vassals of China. Overview and context Depending on the historical context, Sinocentrism can refer to either the ethnocentrism of the Han society and culture, or the modern concept of ''zhonghua minzu'', popular among the Korean elites up to the final demise of the Qing dynasty. The concept came to an end in the 19th century and suffered several more blows in the 20th century, and as a result is not as widely popular among Chinese people in the present day. In pre-modern times, it often took the form of viewing China as the most advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tunmen
The Battle of Tunmen or Tamão was a naval battle in which the Ming imperial navy defeated a Portuguese fleet led by Diogo Calvo in 1521. Background Portuguese diplomat Fernão Pires de Andrade arrived at the mouth of the Pearl River in June 1517 and asked the naval commander of Nantou for permission to take his ships to Guangzhou. After a month with no definitive reply, Andrade decided to sail up the river to Guangzhou without permission from Ming authorities. When they arrived the Portuguese ships discharged cannon fire as a friendly salute, however this was not seen as a friendly gesture by the local Chinese, who were greatly alarmed by the noise. The Portuguese explained that the Chinese traders did the same thing in Malacca, but the local officials only became even more suspicious as Chinese overseas trade was forbidden under Ming law. When official reception from Guangzhou arrived, tensions relaxed, and the Portuguese were received with much pomp as well as the righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearl River (China)
The Pearl River (, or ) is an extensive river system in southern China. "Pearl River" is often also used as a catch-all for the watersheds of the Pearl tributaries within Guangdong, specifically the Xi ('west'), Bei ('north'), and Dong ('east'). These rivers all ultimately flow into the South China Sea through the Pearl River Delta. Measured from the farthest reaches of the Xi River, the Pearl– Xi– Xun– Qian– Hongshui– Nanpan Pearl River system constitutes China's third-longest, after the Yangtze River and the Yellow River, and its second largest by volume, after the Yangtze. The Pearl River Basin drains the majority of Guangdong and Guangxi provinces (collectively known as Liangguang), as well as parts of Yunnan, Guizhou, Hunan and Jiangxi; it also drains the northernmost parts of Vietnam's Northeast Cao Bằng and Lạng Sơn provinces. The Pearl River is famed as the river that flows through Guangzhou. As well as referring to the system as a whole, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World Crops
New World crops are those crops, food and otherwise, that are native to the New World (mostly the Americas) and were not found in the Old World before 1492 AD. Many of these crops are now grown around the world and have often become an integral part of the cuisine of various cultures in the Old World. Notable among them are the " Three Sisters": maize, winter squash, and climbing beans. List of crops Timeline of cultivation The new world developed agriculture by at least 8000 BC. The following table shows when each New World crop was first domesticated. Dissemination to the Old World The transfer of people, crops, precious metals, and diseases from the Old World to the New World and vice versa is called the Columbian Exchange. Food historian Lois Ellen Frank calls potatoes, tomatoes, corn, beans, squash, chili, cacao, and vanilla the "magic eight" ingredients that were found and used only in the Americas before 1492 and were taken via the Columbian Exchange The Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the New World (the Americas) in the Western Hemisphere, and the Old World (Afro-Eurasia) in the Eastern Hemisphere, from the late 15th century on. It is named after the explorer Christopher Columbus and is related to the European colonization of the Americas, European colonization and global trade following his Voyages of Christopher Columbus#First voyage, 1492 voyage. Some of the exchanges were deliberate while others were unintended. Communicable diseases of Old World origin resulted in an 80 to 95 percent reduction in the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous population of the Americas from the 15th century onwards, and their extinction in the Influx of disease in the Caribbean, Caribbean. The cultures of both hemispheres were significantly impacted by the migration of people, both free and enslaved, from the Old World to the New. Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hosokawa Clan
The is a Japanese samurai kin group or Japanese clan, clan. The clan descends from the Seiwa Genji, a branch of the Minamoto clan, and ultimately from Emperor Seiwa, through the Ashikaga clan. It produced many prominent officials in the Ashikaga shogunate's administration. In the Edo period, the clan was one of the largest landholding daimyo families in Japan. The current clan head Morihiro Hosokawa served as Prime Minister of Japan. Muromachi and Sengoku periods Ashikaga Yoshisue, son of Ashikaga Yoshizane, was the first to take the surname of Hosokawa. Hosokawa Yoriharu, a Hosokawa of the late Kamakura period, fought for the Ashikaga clan against the Kamakura shogunate. Another, Hosokawa Akiuji, helped establish the Ashikaga shogunate. The clan wielded significant power over the course of the Muromachi period, Muromachi (1336–1467), Sengoku period, Sengoku (1467–1600), and Edo periods, moving, however, from Shikoku, to Kinai, and then to Kyūshū over the centuries. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōuchi Clan
was one of the most powerful and important families in Western Japan during the reign of the Ashikaga shogunate in the 14th to 16th centuries. Their domains, ruled from the castle town of Yamaguchi in the western tip of Honshu island, comprised six provinces A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ... at their height, and the Ōuchi played a major role in supporting the Ashikaga in the Nanboku-cho Wars against the Southern Imperial Court. The Ōuchi remained powerful up until the 1550s, when they were eclipsed by their former vassals, the Mōri clan. History The genealogical record specifies that the Ōuchi clan were descended from a Prince Imseong, prince of the Rulers of Baekje, royal house of Baekje, who moved to Japan in the 7th century. The ''Ōuchi-shi Jitsrur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the Emperor of Japan, emperor and the ''kuge'' (an aristocratic class). In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku period to the daimyo of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of daimyo also varied considerably; while some daimyo clans, notably the Mōri clan, Mōri, Shimazu clan, Shimazu and Hosokawa clan, Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other daimyo were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. Daimyo often hired samurai to guard their land, and paid them in land or food, as relatively few could afford to pay them i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sengoku Period
The was the period in History of Japan, Japanese history in which civil wars and social upheavals took place almost continuously in the 15th and 16th centuries. The Kyōtoku incident (1454), Ōnin War (1467), or (1493) are generally chosen as the period's start date, but there are many competing historiographies for its end date, ranging from 1568, the date of Oda Nobunaga#Ise campaign, Omi campaign, and march to Kyoto, Oda Nobunaga's march on Kyoto, to the suppression of the Shimabara Rebellion in 1638, deep into what was traditionally considered the Edo period. Regardless of the dates chosen, the Sengoku period overlaps substantially with the Muromachi period (1336–1573). This period was characterized by the overthrow of a superior power by a subordinate one. The Ashikaga shogunate, the ''de facto'' central government, declined and the , a local power, seized wider political influence. The people rebelled against the feudal lords in revolts known as . The period saw a break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |