|
Jelly Roll (options)
A jelly roll, or simply a roll, is an options trading strategy that captures the cost of carry of the underlying asset while remaining otherwise neutral. It is often used to take a position on dividends or interest rates, or to profit from mispriced calendar spreads. A jelly roll consists of a long call and a short put with one expiry date, and a long put and a short call with a different expiry date, all at the same strike price. In other words, a trader combines a synthetic long position at one expiry date with a synthetic short position at another expiry date. Equivalently, the trade can be seen as a combination of a long time spread and a short time spread, one with puts and one with calls, at the same strike price. The value of a call time spread (composed of a long call option and a short call option at the same strike price but with different expiry dates) and the corresponding put time spread should be related by put-call parity, with the difference in price explai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Option Strategy
Option strategies are the simultaneous, and often mixed, buying or selling of one or more options that differ in one or more of the options' variables. Call options, simply known as Calls, give the buyer a right to buy a particular stock at that option's strike price. Opposite to that are Put options, simply known as Puts, which give the buyer the right to sell a particular stock at the option's strike price. This is often done to gain exposure to a specific type of opportunity or risk while eliminating other risks as part of a trading strategy. A very straightforward strategy might simply be the buying or selling of a single option; however, option strategies often refer to a combination of simultaneous buying and or selling of options. Options strategies allow traders to profit from movements in the underlying assets based on market sentiment (i.e., bullish, bearish or neutral). In the case of neutral strategies, they can be further classified into those that are bullish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling (finance)
Rolling a contract is an investment concept meaning trading out of a standard contract and then buying the contract with next longest maturity, so as to maintain a position with constant maturity. Motivation One may roll a contract because one has a special preference for a specific maturity—for example, the five-year CDS rate of a given name—or because a given on-the-run security is more liquid than off-the-run securities. Examples While holding US Treasuries, one may wish to hold only the most recently issued security of a given maturity, the so-called on-the-run security. Thus, if one has purchased the on-the-run 30-year treasury and a new 30-year auction occurs, one may sell the old treasury, which is now off-the-run, and purchase the new on-the-run treasury. There is generally very high trading activity on these dates, as contracts whose maturity falls on them are rolled. Index roll congestion When an index has a published policy for rolling its contracts, such as on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly (options)
In finance, a butterfly (or simply fly) is a limited risk, non-directional options strategy that is designed to have a high probability of earning a limited profit when the future volatility of the underlying asset is expected to be lower (when long the butterfly) or higher (when short the butterfly) than that asset's current implied volatility. Long butterfly A long butterfly position will make profit if the future volatility is lower than the implied volatility. A long butterfly options strategy consists of the following options: * Long 1 call with a strike price of (X − a) * Short 2 calls with a strike price of X * Long 1 call with a strike price of (X + a) where X = the spot price (i.e. current market price of underlying) and a > 0. Using put–call parity a long butterfly can also be created as follows: * Long 1 put with a strike price of (X + a) * Short 2 puts with a strike price of X * Long 1 put with a strike price of (X − a) where X = the spot price and a > 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Spread (options)
In options trading, a box spread is a combination of positions that has a certain (i.e., riskless) payoff, considered to be simply "delta neutral interest rate position". For example, a bull spread constructed from calls (e.g., long a 50 call, short a 60 call) combined with a bear spread constructed from puts (e.g., long a 60 put, short a 50 put) has a constant payoff of the difference in exercise prices (e.g. 10) assuming that the underlying stock does not go ex-dividend before the expiration of the options. If the underlying asset has a dividend of X, then the settled value of the box will be 10 + x. Under the no-arbitrage assumption, the net premium paid out to acquire this position should be equal to the present value of the payoff. Box spreads' name derives from the fact that the prices for the underlying options form a rectangular box in two columns of a quotation. An alternate name is "alligator spread," derived from the large number of trades required to open and close th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Options
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** Citizenship of the European Union ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
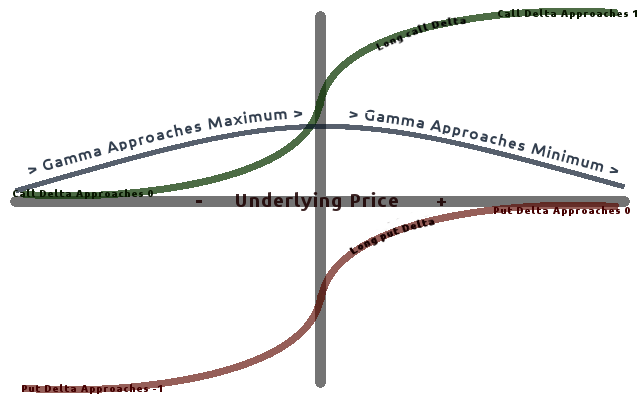
Delta (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futures Contract
In finance, a futures contract (sometimes called a futures) is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the ''forward price''. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the ''delivery date''. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative. Contracts are traded at futures exchanges, which act as a marketplace between buyers and sellers. The buyer of a contract is said to be the long position holder and the selling party is said to be the short position holder. As both parties risk their counter-party reneging if the price goes against them, the contract may involve both parties lodging as security a margin of the value of the contract with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underlying
In finance, a derivative is a contract that ''derives'' its value from the performance of an underlying entity. This underlying entity can be an asset, index, or interest rate, and is often simply called the "underlying". Derivatives can be used for a number of purposes, including insuring against price movements ( hedging), increasing exposure to price movements for speculation, or getting access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Some of the more common derivatives include forwards, futures, options, swaps, and variations of these such as synthetic collateralized debt obligations and credit default swaps. Most derivatives are traded over-the-counter (off-exchange) or on an exchange such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, while most insurance contracts have developed into a separate industry. In the United States, after the financial crisis of 2007–2009, there has been increased pressure to move derivatives to trade on exchanges. Derivatives are one of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |