|
Japanese Space Program
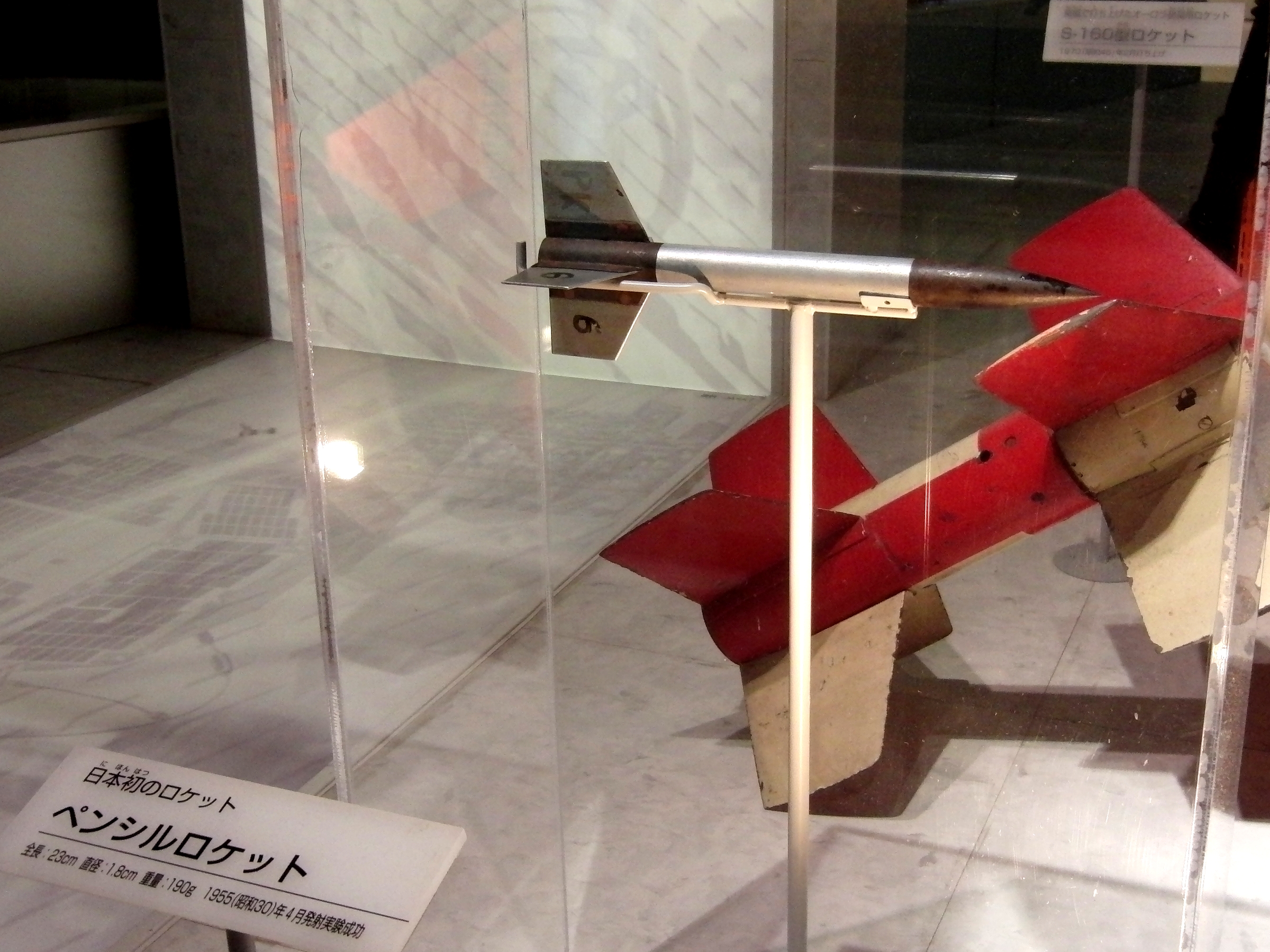
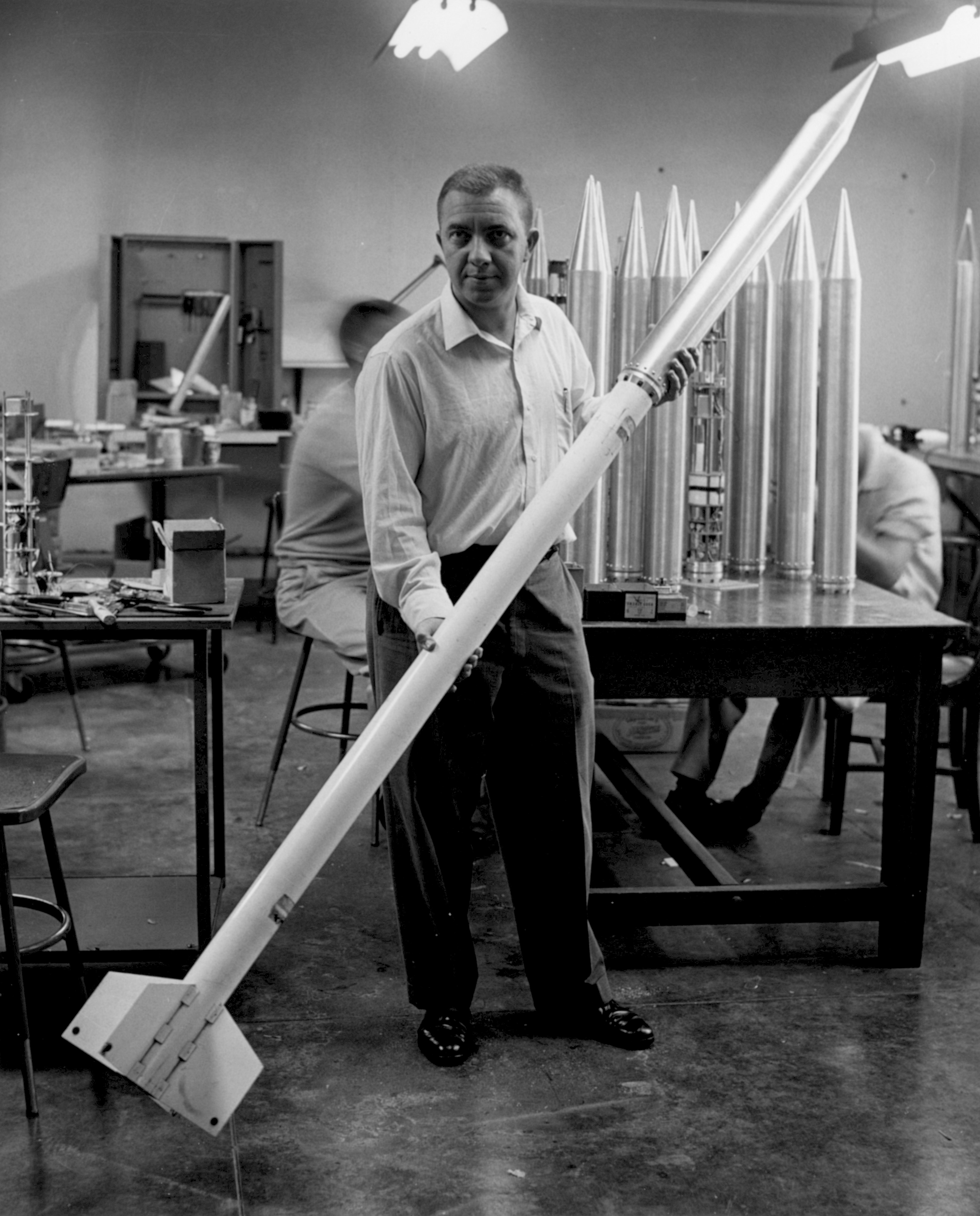
The Japanese space program ( ja, 日本の宇宙開発) originated in the mid-1950s as a research group led by Hideo Itokawa at the University of Tokyo. The size of the rockets produced gradually increased from under at the start of the project, to over by the mid-1960s. The aim of the original research project was to launch a man-made satellite. By the 1960s, two organizations, the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), were developing their own rockets. After experiencing numerous failures in the 1990s and 2000s, ISAS and NASDA merged — along with the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL) — to form the unified Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in 2003. History After World War II, many aeronautical engineers lost their jobs as aircraft development was banned under the US Occupation of Japan. This changed following the San Francisco Peace Treaty in 1951, which once again allowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-IIA
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbiting spacecraft; '' Akatsuki'', which studied the planet Venus; and the Emirates Mars Mission, which was launched to Mars in July 2020. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center. The H-IIA first flew in 2001. , H-IIA rockets were launched 45 times, including 39 consecutive missions without a failure, dating back to 29 November 2003. Production and management of the H-IIA shifted from JAXA to MHI on 1 April 2007. Flight 13, which launched the lunar orbiter SELENE, was the first H-IIA launched after this privatization. The H-IIA is a derivative of the earlier H-II rocket, substantially redesigned to improve reliability and minimize costs. There have been four variants, with two in active service (as of 2020) for various purposes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo University
, abbreviated as or UTokyo, is a public research university located in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1877, the university was the first Imperial University and is currently a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project by the Japanese government. UTokyo has 10 faculties, 15 graduate schools and enrolls about 30,000 students, about 4,200 of whom are international students. In particular, the number of privately funded international students, who account for more than 80%, has increased 1.75 times in the 10 years since 2010, and the university is focusing on supporting international students. Its five campuses are in Hongō, Komaba, Kashiwa, Shirokane and Nakano. It is considered to be the most selective and prestigious university in Japan. As of 2021, University of Tokyo's alumni, faculty members and researchers include seventeen prime ministers, 18 Nobel Prize laureates, four Pritzker Prize laureates, five astronauts, and a Fields Medalist. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagoshima Space Center
The is a space launch facility in the Japanese town of Kimotsuki, Kagoshima Prefecture. Before the establishment of the JAXA space agency in 2003, it was simply called the (KSC). All of Japan's scientific satellites were launched from Uchinoura prior to the M-V launch vehicles being decommissioned in 2006. It continues to be used for suborbital launches, and has also been used for the Epsilon orbital launch vehicle. Additionally, the center has antennas for communication with interplanetary space probes. History Established in February 1962, the Kagoshima Space Center (KSC) was constructed on the Pacific coast of Kagoshima Prefecture in Uchinoura (now part of Kimotsuki) for the purpose of launching large rockets with probe payloads. Prior to establishment of KSC, test launches of the Pencil Rocket, Baby Rocket and Kappa Rocket had been performed at the pioneering Akita rocket test facility ( Michikawa) from the mid-1950s to the 1960s. However, progress in rocket developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
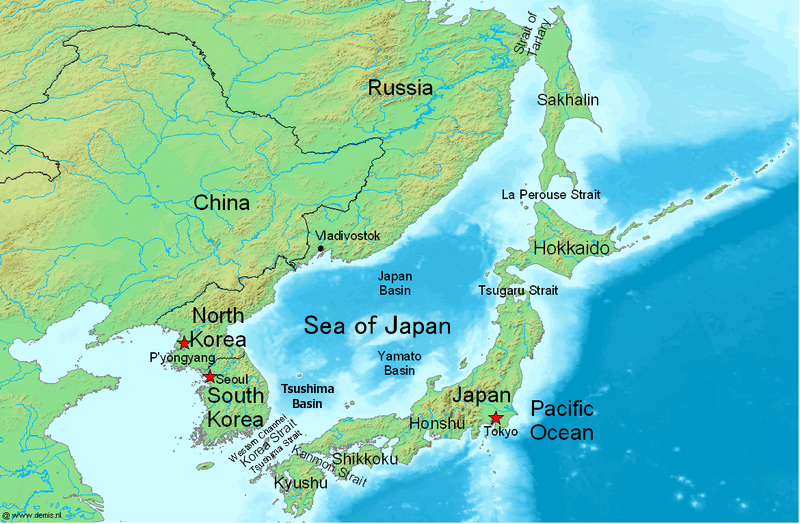
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downrange
Downrange, or down range, is the horizontal distance traveled by a spacecraft, or the spacecraft's horizontal distance from the launch site. More often, it is used as an adverb or adjective specifying the direction of that travel being measured in a horizontal direction. In military slang, ''downrange'' is a term for being deployed overseas, usually in a war zone. It is also the name of a comic strip published in the newspaper Stars and Stripes. It can also refer to the direction of fire: away from the source and in the direction of the target. In the 1960s and 1970s, a down range tracking system existed at Gulkula, in the Northern Territory of Australia, to track rockets launched from the Woomera Test Range in South Australia South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial And Error
Trial and error is a fundamental method of problem-solving characterized by repeated, varied attempts which are continued until success, or until the practicer stops trying. According to W.H. Thorpe, the term was devised by C. Lloyd Morgan (1852–1936) after trying out similar phrases "trial and failure" and "trial and practice". Under Morgan's Canon, animal behaviour should be explained in the simplest possible way. Where behavior seems to imply higher mental processes, it might be explained by trial-and-error learning. An example is a skillful way in which his terrier Tony opened the garden gate, easily misunderstood as an insightful act by someone seeing the final behavior. Lloyd Morgan, however, had watched and recorded the series of approximations by which the dog had gradually learned the response, and could demonstrate that no insight was required to explain it. Edward Lee Thorndike was the initiator of the theory of trial and error learning based on the findings he sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa (rocket)
Kappa is a family of solid-fuel Japanese sounding rockets, which were built starting from 1956. Rockets Kappa 1 * Ceiling: 40 km * Takeoff thrust: 10.00 kN * Diameter: 0.13 m * Length: 2.70 m Kappa 2 * Ceiling: 40 km * Mass: 300 kg * Diameter: 0.22 m * Length: 5 m Kappa 6 (in two stages) * Pay load: 20 kg * Ceiling: 60 km * Takeoff weight: 270 kg * Diameter: 0.25 m * Length: 5.61 m Kappa 7 * Ceiling: 50 km * Diameter: 0.42 m * Length: 8.70 m Kappa 8 (in two stages) * Pay load: 50 kg * Ceiling: 160 km * Takeoff weight: 1500 kg * Diameter: 0.42 m * Length: 10.90 m Kappa 4 * Ceiling: 80 km * Takeoff thrust: 105.00 kN * Diameter: 0.33 m * Length: 5.90 m Kappa 9L * Pay load: 15 kg * Ceiling: 350 km * Takeoff weight: 1550 kg * Diameter: 0.42 m * Length: 12.50 m Kappa 9M * Pay load: 50 kg * Ceiling: 350 km * Mass: 1500 kg * Diameter: 0.42 m * Length: 11.10 m Kappa 8L * Pay load: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockoon
A rockoon (from ''rocket'' and ''balloon'') is a solid fuel sounding rocket that, rather than being immediately lit while on the ground, is first carried into the upper atmosphere by a gas-filled balloon, then separated from the balloon and ignited. This allows the rocket to achieve a higher altitude, as the rocket does not have to move under power through the lower and thicker layers of the atmosphere. The original concept was developed by Cmdr. Lee Lewis, Cmdr. G. Halvorson, S. F. Singer, and James A. Van Allen during the Aerobee rocket firing cruise of the U.S.S. ''Norton Sound'' on March 1, 1949. A serious disadvantage is that unpiloted balloons cannot be steered, and consequently the location from which the rocket is launched can be uncertain. Therefore, a large area for the fall of the rocket is required for safety reasons. Early atmospheric research ''Time'' magazine reported in 1959: "Van Allen's 'Rockoons' could not be fired in Iowa for fear that the spent rocket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akita Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Provinces and prefectures" in ; "Tōhoku" in . Its population is approximately 966,000 (as of 1 October 2019) and its geographic area is 11,637 km2 (4,493 sq mi). Akita Prefecture is bordered by Aomori Prefecture to the north, Iwate Prefecture to the east, Miyagi Prefecture to the southeast, and Yamagata Prefecture to the south. Akita is the capital and largest city of Akita Prefecture. Other major cities include Yokote, Daisen, and Yurihonjō. Akita Prefecture is located on the coast of the Sea of Japan and extends east to the Ōu Mountains, the longest mountain range in Japan, at the border with Iwate Prefecture. Akita Prefecture formed the northern half of the historic Dewa Province with Yamagata Prefecture. History The region of Akita was created from the ancient provinces of Dewa and Mutsu. Separated from the principal Japanese centres of commerce, politics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West had been seriously interrupted. Sixty-seven countries participated in IGY projects, although one notable exception was the mainland People's Republic of China, which was protesting against the participation of the Republic of China (Taiwan). East and West agreed to nominate the Belgian Marcel Nicolet as secretary general of the associated international organization. The IGY encompassed eleven Earth sciences: aurora and airglow, cosmic rays, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology, and solar activity. The timing of the IGY was particularly suited for studying some of these phenomena, since it covered th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |