|
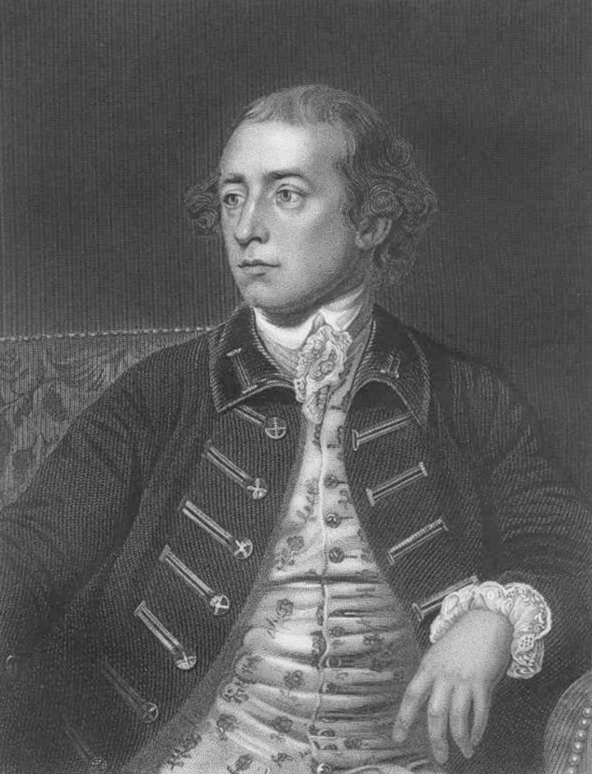
James Augustus Hicky
James Augustus Hicky was an Irishman who launched the first printed newspaper in India, ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette''. Early life Hicky was born in Ireland around the year 1740. While young, he moved to London to apprentice with William Faden, a Scottish printer. However, Hicky never took his freedom from the printers' guild, and instead secured a clerkship with an English lawyer, William Davy. At some point Hicky quit his career in law, and, after a brief attempt practicing as a surgeon in London, he boarded an East Indiaman as a surgeon's mate bound for Calcutta in 1772. Upon landing in Calcutta, Hicky practiced as both a surgeon and a merchant, shipping and trading goods along India's coast. But, by 1776, his shipping business collapsed as his vessel returned to port with its cargo badly damaged. Unable to reassure his creditors, Hicky entered debtors' prison in October 1776. While in jail, Hicky acquired a printing press and types and by 1777 began a printing business from j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hicky's Bengal Gazette
''Hicky's Bengal Gazette or the Original Calcutta General Advertiser'' was an English-language weekly newspaper published in Kolkata (then Calcutta), the capital of British India. It was the first newspaper printed in Asia, and was published for two years, between 1780 and 1782, before the East India Company seized the newspaper's types and printing press. Founded by James Augustus Hicky, a highly eccentric Irishman who had previously spent two years in jail for debt, the newspaper was strong critical of the administration of Governor General Warren Hastings. The newspaper was important for its provocative journalism and its fight for free expression in India. Newspaper history ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette'' was first published on 29 January 1780, it's founder, James Augustus Hicky, having earlier printed a prospectus announcing that he would begin printing a newspaper. The idea of printing a newspaper in India had been floated twelve years earlier by the Dutch Adventurer William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Council Of Bengal
The Supreme Council of Bengal, also known as Council of Four, was the highest level of executive government in British India from 1774 to 1833: the period in which the East India Company, a private company, exercised political control of British colonies in India. It was formally subordinate to both the East India Company's Court of Directors and to the British Crown. The Council was established by the British government, under Regulating Act 1773. It consisted of four members. The Governor General was given a casting vote but no veto. It was appointed by the Court of Directors (board) of the East India Company. At times it also included the British military Commander-in-Chief of India (although this post was usually held concurrently by the Governor General). Hence the council was also known as Governor-General in Council. The Government of India Act 1833 formally separated the East India Company from political control, and the governor-general of Bengal became the governor ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Indian People
The 18th century lasted from 1 January 1701 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCI) to 31 December 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the Atlantic Revolutions. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures. The Industrial Revolution began mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. The European colonization of the Americas and other parts of the world intensified and associated mass migrations of people grew in size as part of the Age of Sail. During the century, slave trading expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, while declining in Russia and China. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Imprisoned For Debt
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Irish People
The 18th century lasted from 1 January 1701 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCI) to 31 December 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the Atlantic Revolutions. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures. The Industrial Revolution began mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. The European colonization of the Americas and other parts of the world intensified and associated mass migrations of people grew in size as part of the Age of Sail. During the century, slave trading expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, while declining in Russia and China. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Newspaper Editors
Irish commonly refers to: * Someone or something of, from, or related to: ** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe ***Éire, Irish language name for the island and the sovereign state *** Erse (other), Scots language name for the Irish language or Irish people ** Republic of Ireland, a sovereign state ** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland * Irish language, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family spoken in Ireland * Irish English, set of dialects of the English language native to Ireland * Irish people, people of Irish ethnicity Irish may also refer to: Places * Irish Creek (Kansas), a stream in Kansas * Irish Creek (South Dakota), a stream in South Dakota * Irish Lake, Watonwan County, Minnesota * Irish Sea, the body of water which separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain People * Irish (surname), a list of people * William Irish, pse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journalists From British India
A journalist is a person who gathers information in the form of text, audio or pictures, processes it into a newsworthy form and disseminates it to the public. This is called journalism. Roles Journalists can work in broadcast, print, advertising, or public relations personnel. Depending on the form of journalism, "journalist" may also describe various categories of people by the roles they play in the process. These include reporters, correspondents, citizen journalists, editors, editorial writers, columnists, and photojournalists. A reporter is a type of journalist who researches, writes and reports on information in order to present using sources. This may entail conducting interviews, information-gathering and/or writing articles. Reporters may split their time between working in a newsroom, from home or outside to witness events or interview people. Reporters may be assigned a specific beat (area of coverage). Matthew C. Nisbet, who has written on science communication, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
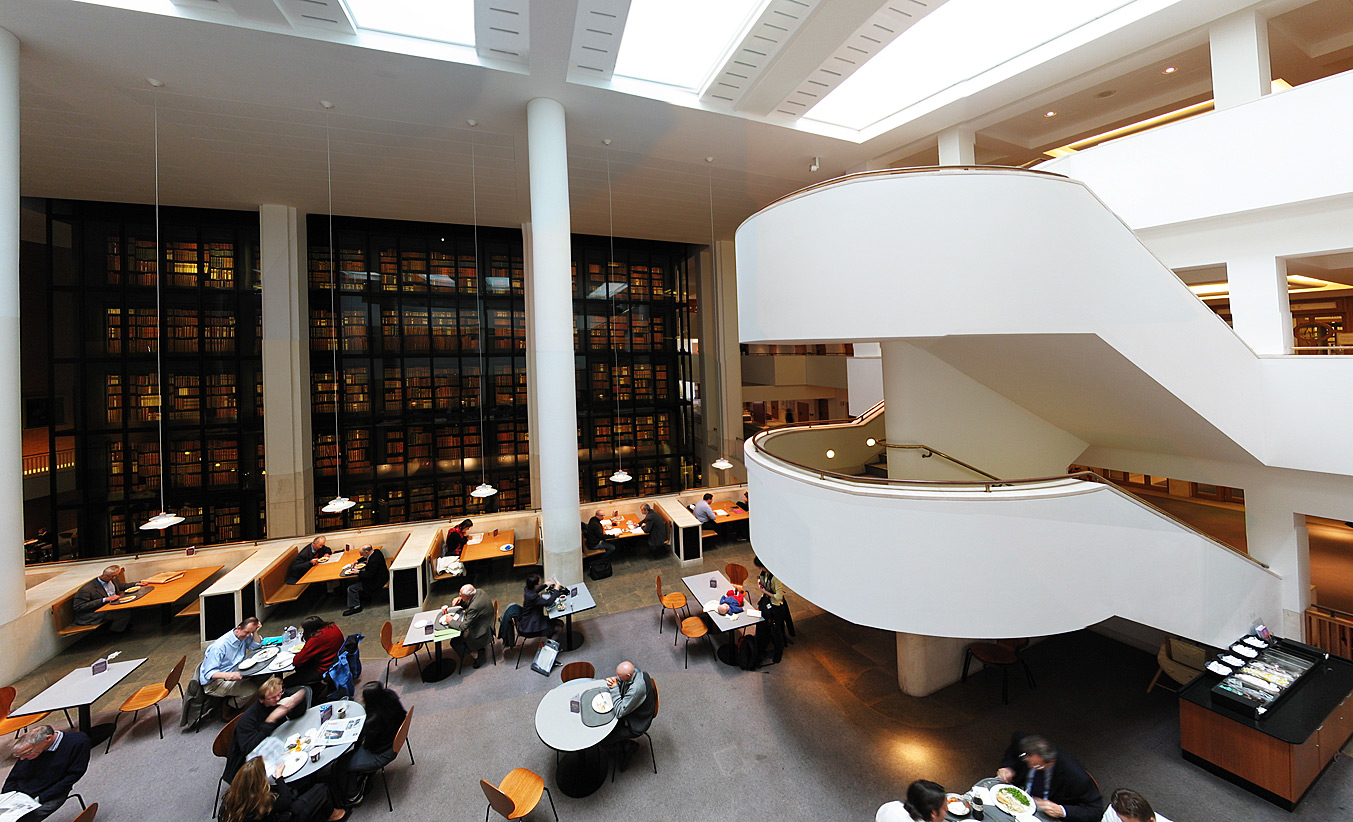
British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom. Based in London, it is one of the largest libraries in the world, with an estimated collection of between 170 and 200 million items from multiple countries. As a legal deposit library, it receives copies of all books produced in the United Kingdom and Ireland, as well as a significant proportion of overseas titles distributed in the United Kingdom. The library operates as a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The British Library is a major research library, with items in many languages and in many formats, both print and digital: books, manuscripts, journals, newspapers, magazines, sound and music recordings, videos, play-scripts, patents, databases, maps, stamps, prints, drawings. The Library's collections include around 14 million books, along with substantial holdings of manuscripts and items dating as far back as 2000 BC. The library maintains a programme for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor-General Of India
The governor-general of India (1833 to 1950, from 1858 to 1947 the viceroy and governor-general of India, commonly shortened to viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom in their capacity as the emperor or empress of India and after Indian independence in 1947, the representative of the monarch of India. The office was created in 1773, with the title of governor-general of the Presidency of Fort William. The officer had direct control only over his presidency but supervised other East India Company officials in India. Complete authority over all of British territory in the Indian subcontinent was granted in 1833, and the official came to be known as the governor-general of India. In 1858, because of the Indian Rebellion the previous year, the territories and assets of the East India Company came under the direct control of the British Crown; as a consequence, company rule in India was succeeded by the British Raj. The governor-general ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impeachment Of Warren Hastings
The impeachment of Warren Hastings, the first governor-general of the Bengal Presidency in India, was attempted between 1787 and 1795 in the Parliament of Great Britain. Hastings was accused of misconduct during his time in Calcutta, particularly relating to mismanagement and personal corruption. The impeachment prosecution was led by Edmund Burke and became a wider debate about the role of the East India Company and the expanding empire in India. According to historian Mithi Mukherjee, the impeachment trial became the site of a debate between two radically opposed visions of empire—one represented by Hastings, based on ideas of absolute power and conquest in pursuit of the exclusive national interests of the colonizer, versus one represented by Burke, of sovereignty based on a recognition of the rights of the colonized. The trial did not sit continuously and the case dragged on for seven years. When the eventual verdict was given, Hastings was overwhelmingly acquitted. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Zachariah Kiernander
John Zachariah Kiernander (1 December 1710–10 May 1799), also known as Johann Zacharias Kiernander, was a Swedish Lutheran missionary in British India. He was the first Protestant Missionary to establish a base in Bengal. He built the Old Mission Church in Calcutta and founded one of the first printing presses in Calcutta. In 1781, he accused James Augustus Hicky, the editor and publisher of ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette ''Hicky's Bengal Gazette or the Original Calcutta General Advertiser'' was an English-language weekly newspaper published in Kolkata (then Calcutta), the capital of British India. It was the first newspaper printed in Asia, and was published fo ...'' of libel and won the trial. He was the author of ''The Trial and Conviction of James Augustus Hicky''. Notes 1710 births 1799 deaths Swedish Protestant missionaries Lutheran missionaries in India Swedish expatriates in India People from Östergötland County {{Sweden-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |